Lesson: Using Swing Components
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
How to Use Icons如何使用图标
Many Swing components, such as labels, buttons, and tabbed panes, can be decorated with an icon — a fixed-sized picture. 许多Swing组件,如标签、按钮和选项卡式窗格,可以用图标,即固定大小的图片装饰。An icon is an object that adheres to the 图标是附着于Icon interface. Icon界面的对象。Swing provides a particularly useful implementation of the Swing提供了一个特别有用的图标接口实现:Icon interface:
ImageIcon, which paints an icon from a GIF, JPEG, or PNG image.ImageIcon,它从GIF、JPEG或PNG图像绘制图标。
Here's a snapshot of an application with three labels, two decorated with an icon:这是一个应用程序的快照,有三个标签,其中两个用图标装饰:

The program uses one image icon to contain and paint the yellow splats. 该程序使用一个图像图标来包含和绘制黄色斑点。One statement creates the image icon and two more statements include the image icon on each of the two labels:一条语句创建图像图标,另外两条语句在两个标签中的每个标签上都包含图像图标:
ImageIcon icon = createImageIcon("images/middle.gif",
"a pretty but meaningless splat");
label1 = new JLabel("Image and Text", icon, JLabel.CENTER);
...
label3 = new JLabel(icon);The createImageIcon method (used in the preceding snippet) is one we use in many of our code samples. createImageIcon方法(在前面的代码片段中使用)是我们在许多代码示例中使用的方法。It finds the specified file and returns an 它查找指定的文件并返回该文件的ImageIcon for that file, or null if that file couldn't be found. ImageIcon,如果找不到该文件,则返回null。Here is a typical implementation:以下是一个典型的实现:
/** Returns an ImageIcon, or null if the path was invalid. */
protected ImageIcon createImageIcon(String path,
String description) {
java.net.URL imgURL = getClass().getResource(path);
if (imgURL != null) {
return new ImageIcon(imgURL, description);
} else {
System.err.println("Couldn't find file: " + path);
return null;
}
}In the preceding snippet, the first argument to the 在前面的代码片段中,ImageIcon constructor is relative to the location of the current class, and will be resolved to an absolute URL. ImageIcon构造函数的第一个参数与当前类的位置相关,并将解析为绝对URL。The 描述参数是一个字符串,允许辅助技术帮助视障用户理解图标传达的信息。description argument is a string that allows assistive technologies to help a visually impaired user understand what information the icon conveys.
Generally, applications provide their own set of images used as part of the application, as is the case with the images used by many of our demos. 通常,应用程序提供自己的图像集,作为应用程序的一部分,许多演示使用的图像也是如此。You should use the 您应该使用类Class getResource method to obtain the path to the image. getResource方法获取图像的路径。This allows the application to verify that the image is available and to provide sensible error handling if it is not. 这允许应用程序验证图像是否可用,并在不可用时提供合理的错误处理。When the image is not part of the application, 当图像不是应用程序的一部分时,不应使用getResource should not be used and the ImageIcon constructor is used directly. getResource,直接使用ImageIcon构造函数。For example:例如:
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon("images/middle.gif",
"a pretty but meaningless splat");When you specify a filename or URL to an 当您为ImageIcon constructor, processing is blocked until after the image data is completely loaded or the data location has proven to be invalid. ImageIcon构造函数指定文件名或URL时,将阻止处理,直到图像数据完全加载或数据位置被证明无效。If the data location is invalid (but non-null), an 如果数据位置无效(但非空),仍会成功创建ImageIcon is still successfully created; it just has no size and, therefore, paints nothing. ImageIcon;它只是没有尺寸,因此什么也画不出来。As shown in the 如createImageIcon method, it is advisable to first verify that the URL points to an existing file before passing it to the ImageIcon constructor. createImageIcon方法所示,建议先验证URL是否指向现有文件,然后再将其传递给ImageIcon构造函数。This allows graceful error handling when the file isn't present. 这允许在文件不存在时进行优雅的错误处理。If you want more information while the image is loading, you can register an observer on an image icon by calling its 如果在加载图像时需要更多信息,可以通过调用图像图标的setImageObserver method.setImageObserver方法在图像图标上注册观察者。
Under the covers, each image icon uses an 在封面下,每个图像图标都使用一个Image object to hold the image data.Image对象来保存图像数据。
The rest of this section covers the following topics:本节其余部分包括以下主题:
A More Complex Image Icon Example更复杂的图像图标示例Loading Images Using getResource使用getResource加载图像Loading Images Into Applets将图像加载到小程序中Improving Perceived Performance When Loading Image Icons提高加载图像图标时的感知性能Creating a Custom Icon Implementation创建自定义图标实现The Image Icon API图像图标APIExamples that Use Icons使用图标的示例
A More Complex Image Icon Example更复杂的图像图标示例
Here's an application that uses six image icons. 这是一个使用六个图像图标的应用程序。Five of them display thumbnail images and the sixth displays the full-size photograph.其中五个显示缩略图图像,第六个显示全尺寸照片。
Try this:
Click the Launch button to run IconDemo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later).单击Launch按钮,使用Java™Web启动运行IconDemo(下载JDK 7或更高版本)。Or, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.或者,要自己编译和运行示例,请参考示例索引。
Click any of the thumbnail images to view the full size photographs.单击任何缩略图以查看全尺寸照片。Hold the mouse over a photograph.将鼠标悬停在照片上。A tool tip appears that displays the photograph caption.将出现一个工具提示,显示照片标题。
IconDemoApp demonstrates icons used in the following ways:演示以下列方式使用的图标:
As a GUI element attached to a button (the thumbnail images on the buttons).作为附加到按钮的GUI元素(按钮上的缩略图)。To display an image (the five photographs).显示图像(五张照片)。
The photographs are loaded in a separate thread by 照片由loadimages.execute. loadimages.execute在单独的线程中加载。The 本节稍后将显示loadimages code is shown a little later in this section.loadimages代码。
The ThumbnailAction class, an inner class in IconDemoApp.java, is a descendant of AbstractAction that manages our full size image icon, a thumbnail version, and its description. ThumbnailAction类是IconDemoApp.java中的一个内部类,它是AbstractAction的后代,用于管理全尺寸图像图标、缩略图版本及其描述。When the 当调用actionPerformed method is called the full size image is loaded into the main display area. actionPerformed方法时,会将全尺寸图像加载到主显示区域。Each button has its own instance of 每个按钮都有自己的ThumbnailAction which specifies a different image to show.ThumbnailAction实例,该实例指定要显示的不同图像。
/**
* Action class that shows the image specified in it's constructor.
*/
private class ThumbnailAction extends AbstractAction{
/**
*The icon if the full image we want to display.
*/
private Icon displayPhoto;
/**
* @param Icon - The full size photo to show in the button.
* @param Icon - The thumbnail to show in the button.
* @param String - The description of the icon.
*/
public ThumbnailAction(Icon photo, Icon thumb, String desc){
displayPhoto = photo;
// The short description becomes the tooltip of a button.
putValue(SHORT_DESCRIPTION, desc);
// The LARGE_ICON_KEY is actually the key for setting the
// icon when an Action is applied to a button.
putValue(LARGE_ICON_KEY, thumb);
}
/**
* Shows the full image in the main area and sets the application title.
*/
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
photographLabel.setIcon(displayPhoto);
setTitle("Icon Demo: " + getValue(SHORT_DESCRIPTION).toString());
}
}Loading Images Using getResource使用getResource加载图像
Most often, an image icon's data comes from an image file. 通常,图像图标的数据来自图像文件。There are a number of valid ways that your application's class and image files may be configured on your file server. 有许多有效的方法可以在文件服务器上配置应用程序的类和图像文件。You might have your class files in a JAR file, or your image files in a JAR file; they might be in the same JAR file, or they might be in different JAR files. 您可能将类文件放在JAR文件中,或者将图像文件放在JAR文件中;它们可能位于同一JAR文件中,也可能位于不同的JAR文件。The following figures illustrate a few of the ways these files can be configured:下图说明了配置这些文件的几种方法:
 |
 |
images directory.images目录中的所有图像创建的。 | |
 |
 |
If you are writing a real-world application, it is likely (and recommended) that you put your files into a package. 如果您正在编写一个真实的应用程序,那么很可能(并且建议)将文件放入一个包中。For more information on packages, see Creating and Using Packages in the Learning the Java Language trail. 有关软件包的更多信息,请参阅学习Java语言教程中的创建和使用包。Here are some possible configurations using a package named "omega":以下是使用名为“omega”的软件包的一些可能配置:
 |
 |
omega. omega的目录中的类文件。omega/images directory.omega/images目录中的图像。 |
omega directory. omega目录中的类文件。omega directory, but created with omega/images hierarchy.omega目录内,而是使用omega/images层次结构创建的。 |
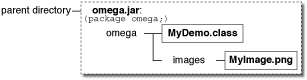 | |
omega directory and image files under omega/images directory.omega目录下,图像文件位于omega/images目录下。 |
All seven configurations shown are valid, and the same code reads the image:所示的七种配置都有效,相同的代码读取图像:
java.net.URL imageURL = myDemo.class.getResource("images/myImage.gif");
...
if (imageURL != null) {
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(imageURL);
}The getResource method causes the class loader to look through the directories and JAR files in the program's class path, returning a URL as soon as it finds the desired file. getResource方法使类加载器查看程序类路径中的目录和JAR文件,一旦找到所需的文件,就会返回URL。In the example the MyDemo program attempts to load the 在该示例中,MyDemo程序尝试从images/myImage.png file from the omega class. omega类加载images/myImage.png文件。The class loader looks through the directories and JAR files in the program's class path for 类加载器查看/omega/images/myImage.png. /omega/images/myImage.png程序类路径中的目录和JAR文件。If the class loader finds the file, it returns the URL of the JAR file or directory that contained the file. 如果类装入器找到该文件,它将返回包含该文件的JAR文件或目录的URL。If another JAR file or directory in the class path contains the 如果类路径中的另一个JAR文件或目录包含images/myImage.png file, the class loader returns the first instance that contains the file.images/myImage.png文件,那么类加载器将返回包含该文件的第一个实例。
Here are three ways to specify the class path:以下是指定类路径的三种方法:
Using the使用-cpor-classpathcommand-line argument.-cp或-classpath命令行参数。For example, in the case where the images are in a JAR file named例如,如果图像位于名为images.jarand the class file is in the current directory:images.jar的JAR文件中,而类文件位于当前目录中:java -cp .;images.jar MyDemo [Microsoft Windows] java -cp ".;images.jar" MyDemo [UNIX-emulating shell on Microsoft Windows — you must quote the path] java -cp .:images.jar MyDemo [UNIX]If your image and class files are in separate JAR files, your command line will look something like:如果图像和类文件位于单独的JAR文件中,则命令行将类似于:java -cp .;MyDemo.jar;images.jar MyDemo [Microsoft Windows]
In the situation where all the files are in one JAR file, you can use either of the following commands:在所有文件都在一个JAR文件中的情况下,可以使用以下任一命令:java -jar MyAppPlusImages.jar java -cp .;MyAppPlusImages.jar MyApp [Microsoft Windows]
For more information, see the JAR Files trail.有关更多信息,请参阅JAR文件跟踪。In the program's JNLP file (used by Java Web Start).在程序的JNLP文件中(由Java Web Start使用)。For example, here is the JNLP file used by例如,以下是DragPictureDemo:DragPictureDemo使用的JNLP文件:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- JNLP File for DragPictureDemo --> <jnlp spec="1.0+" codebase="https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorialJWS/src/uiswing/misc/examples" href="DragPictureDemo.jnlp"> <information> <title>DragPictureDemo</title> <vendor>The Java(tm) Tutorial: Sun Microsystems, Inc.</vendor> <homepage href="https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/uiswing/misc/examples/index.html#DragPictureDemo"/> <description>DragPictureDemo</description> <description kind="short">A demo showing how to install data transfer on a custom component.</description> <offline-allowed/> </information> <resources> <j2se version="1.6+"/> <jar href="allClasses.jar"/> <jar href="images.jar"/> </resources> <application-desc main-class="DragPictureDemo"/> </jnlp>In this example, the class files and the images files are in separate JAR files.在本例中,类文件和图像文件位于单独的JAR文件中。The JAR files are specified using the XMLJAR文件是使用XMLjartag.jar标记指定的。Setting the正在设置CLASSPATHenvironment variable.CLASSPATH环境变量。This last approach is not recommended.不建议使用最后一种方法。If如果未设置CLASSPATHis not set, the current directory (".") followed by the location of the system classes shipped with the JRE are used by default.CLASSPATH,则默认使用当前目录(“.”),后跟JRE附带的系统类的位置。
Most of the Swing Tutorial examples put the images in an 大多数Swing教程示例都将图像放在包含示例类文件的目录下的images directory under the directory that contains the examples' class files. images目录中。When we create JAR files for the examples, we keep the same relative locations, although often we put the class files in a different JAR file than the image JAR file. 当我们为示例创建JAR文件时,我们保持相同的相对位置,尽管我们经常将类文件放在与图像JAR文件不同的JAR文件中。No matter where the class and image files are in the file system — in one JAR file, or in multiple JAR files, in a named package, or in the default package — the same code finds the image files using 无论类和图像文件在文件系统中的何处—在一个JAR文件中,或在多个JAR文档中,在一个命名包中,或默认包中—相同的代码使用getResource.getResource查找图像文件。
For more information, see Accessing Resources in a Location-Independent Manner and the Application Development Considerations.有关更多信息,请参阅以独立于位置的方式访问资源和应用程序开发注意事项。
Loading Images Into Applets将图像加载到小程序
Applets generally load image data from the computer that served up the applet. 小程序通常从为小程序提供服务的计算机加载图像数据。The APPLET tag is where you specify information about the images used in the applet. APPLET标记用于指定有关小程序中使用的图像的信息。For more information on the 有关APPLET tag see Using the APPLET TagAPPLET标记的更多信息,请参阅使用APPLET标签
Improving Perceived Performance When Loading Image Icons提高加载图像图标时的感知性能
Because the photograph images can be slow to access, 由于照片图像的访问速度可能很慢,IconDemoApp.java uses a SwingWorker to improve the performance of the program as perceived by the user.IconDemoApp.java使用SwingWorker来提高用户感知到的程序性能。
Background image loading背景图像加载 — the program uses a javax.swing.SwingWorker object to load each photograph image and compute it's thumbnail in a background thread. 该程序使用javax.swing.SwingWorker对象加载每个照片图像,并在后台线程中计算其缩略图。Using a 使用SwingWorker prevents the program from appearing to freeze up while loading and scaling the images.SwingWorker可防止程序在加载和缩放图像时出现冻结。
Here's the code to process each image:以下是处理每个图像的代码:
/**
* SwingWorker class that loads the images a background thread and calls publish
* when a new one is ready to be displayed.
*
* We use Void as the first SwingWorker param as we do not need to return
* anything from doInBackground().
*/
private SwingWorker<Void, ThumbnailAction> loadimages = new SwingWorker<Void, ThumbnailAction>() {
/**
* Creates full size and thumbnail versions of the target image files.
*/
@Override
protected Void doInBackground() throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < imageCaptions.length; i++) {
ImageIcon icon;
icon = createImageIcon(imagedir + imageFileNames[i], imageCaptions[i]);
ThumbnailAction thumbAction;
if(icon != null){
ImageIcon thumbnailIcon = new
ImageIcon(getScaledImage(icon.getImage(), 32, 32));
thumbAction = new ThumbnailAction(icon, thumbnailIcon, imageCaptions[i]);
} else {
// the image failed to load for some reason
// so load a placeholder instead
thumbAction = new ThumbnailAction(placeholderIcon, placeholderIcon, imageCaptions[i]);
}
publish(thumbAction);
}
// unfortunately we must return something, and only null is valid to
// return when the return type is void.
return null;
}
/**
* Process all loaded images.
*/
@Override
protected void process(List<ThumbnailAction> chunks) {
for (ThumbnailAction thumbAction : chunks) {
JButton thumbButton = new JButton(thumbAction);
// add the new button BEFORE the last glue
// this centers the buttons in the toolbar
buttonBar.add(thumbButton, buttonBar.getComponentCount() - 1);
}
}
};SwingWorker invokes the SwingWorker在后台线程中调用doInBackground method in a background thread. doInBackground方法。The method places a full size image, thumbnail size image and caption into a 该方法将全尺寸图像、缩略图尺寸图像和标题放置到ThumbnailAction object. ThumbnailAction对象中。The SwingWorker then delivers the ThumbnailAction to the process method. SwingWorker然后将ThumbnailAction传递给process方法。The process method executes on the event dispatch thread and updates the GUI by adding a button to the toolbar. process方法在事件分派线程上执行,并通过向工具栏添加按钮来更新GUI。JButton has a constructor that takes an action object. 具有接受操作对象的构造函数。The action object determines a number of the button's properties. 操作对象确定按钮的许多属性。In our case the button icon, the caption and the action to be performed when the button is pressed is all determined by the 在例子中,按钮图标、标题和按钮按下时要执行的操作都由ThumbnailAction.ThumbnailAction决定。
Overhead开销 — this program eventually loads all the source images into memory. 这个程序最终将所有源图像加载到内存中。This may not be desirable in all situations. 并非在所有情况下都需要这样做。Loading a number of very large files could cause the program to allocate a very large amount or memory. 加载大量非常大的文件可能会导致程序分配非常大的数量或内存。Care should be taken to manage the number and size of images that are loaded.应注意管理加载的图像的数量和大小。
As with all performance-related issues, this technique is applicable in some situations and not others. 与所有与性能相关的问题一样,此技术适用于某些情况,而不适用于其他情况。Also the technique described here is designed to improve the program's perceived performance, but does not necessarily impact its real performance.此外,这里描述的技术旨在提高程序的感知性能,但不一定影响其实际性能。
Creating a Custom Icon Implementation创建自定义图标实现
The createImageIcon method returns null when it cannot find an image, but what should the program do then? createImageIcon方法在找不到图像时返回null,但程序应该怎么做?One possibility would be to ignore that image and move on. 一种可能是忽略这张图片,继续前进。Another option would be to provide some sort of default icon to display when the real one cannot be loaded. 另一个选项是提供某种默认图标,以便在无法加载真实图标时显示。Making another call to 再次调用createImageIcon might result in another null so using that is not a good idea. createImageIcon可能会导致另一个null,因此使用它不是一个好主意。Instead lets create a custom 相反,让我们创建一个自定义Icon implementation.Icon实现。
You can find the implementation of the custom icon class in 您可以在MissingIcon.java. MissingIcon.java中找到自定义图标类的实现。Here are the interesting parts of its code:以下是其代码中有趣的部分:
/**
* The "missing icon" is a white box with a black border and a red x.
* It's used to display something when there are issues loading an
* icon from an external location.
*
* @author Collin Fagan
*/
public class MissingIcon implements Icon{
private int width = 32;
private int height = 32;
private BasicStroke stroke = new BasicStroke(4);
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics g, int x, int y) {
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g.create();
g2d.setColor(Color.WHITE);
g2d.fillRect(x +1 ,y + 1,width -2 ,height -2);
g2d.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g2d.drawRect(x +1 ,y + 1,width -2 ,height -2);
g2d.setColor(Color.RED);
g2d.setStroke(stroke);
g2d.drawLine(x +10, y + 10, x + width -10, y + height -10);
g2d.drawLine(x +10, y + height -10, x + width -10, y + 10);
g2d.dispose();
}
public int getIconWidth() {
return width;
}
public int getIconHeight() {
return height;
}
}The paintIcon method is passed a Graphics object. paintIcon方法被传递给Graphics对象。The Graphics object gives the paintIcon method access to the entire Java2D API. Graphics对象使paintIcon方法可以访问整个Java2D API。For more information about painting and Java2D, see Performing Custom Painting.有关绘制和Java2D的更多信息,请参阅执行自定义绘制。
The following code demonstrates how the 以下代码演示了如何在MissingIcon class is used in the SwingWorker doInBackground method.SwingWorker doInBackground方法中使用MissingIcon类。
private MissingIcon placeholderIcon = new MissingIcon();
...
if(icon != null) {
...
} else {
// the image failed to load for some reason
// so load a placeholder instead
thumbAction = new ThumbnailAction(placeholderIcon, placeholderIcon, imageCaptions[i]);
}Using a custom icon has a few implications:使用自定义图标有几个含义:
Because the icon's appearance is determined dynamically, the icon painting code can use any information — component and application state, for example — to determine what to paint.因为图标的外观是动态确定的,所以图标绘制代码可以使用任何信息—组件和应用程序状态,例如—确定要绘制的内容。Depending on the platform and the type of image, you may get a performance boost with custom icons, since painting simple shapes can sometimes be faster than copying images.根据平台和图像类型,使用自定义图标可能会提高性能,因为绘制简单形状有时比复制图像更快。Because因为MissingIcondoes not do any file I/O there is no need for separate threads to load the image.MissingIcon不执行任何文件I/O,所以不需要单独的线程来加载图像。
The Image Icon API图像Icon API
The following tables list the commonly used 下表列出了常用的ImageIcon constructors and methods. ImageCon构造函数和方法。Note that 请注意,ImageIcon is not a descendent of JComponent or even of Component.ImageCon不是JComponent甚至Component的后代。
The API for using image icons falls into these categories:使用图像图标的API分为以下几类:
Setting, Getting, and Painting the Image Icon's Image设置、获取和绘制图像图标的图像Setting or Getting Information about the Image Icon设置或获取有关图像图标的信息Watching the Image Icon's Image Load观看图像图标的图像加载
ImageIcon()ImageIcon(byte[])ImageIcon(byte[], String)ImageIcon(Image)ImageIcon(Image, String)ImageIcon(String)ImageIcon(String, String)ImageIcon(URL)ImageIcon(URL, String) |
ImageIcon instance, initializing it to contain the specified image. ImageIcon实例,将其初始化为包含指定的图像。java.awt.Image class: namely GIF, JPEG, or PNG. java.awt.Image类支持的格式:即GIF、JPEG或PNG。setDescription and provides useful textual information for assistive technologies.setDescription设置,并为辅助技术提供有用的文本信息。 |
void setImage(Image)Image getImage() |
|
void paintIcon(Component, Graphics, int, int) |
Component object is used as an image observer. Component对象用作图像观测器。Component class, and pass in any component. Component类提供的默认行为,并传入任何组件。int arguments specify the top-left corner where the icon is painted.int参数指定绘制图标的左上角。 |
URL getResource(String)in (java.lang.ClassLoader) |
getResource加载图像。 |
InputStream getResourceAsStream(String)in (java.lang.ClassLoader) |
void setDescription(String)String getDescription() |
|
int getIconWidth()int getIconHeight() |
void setImageObserver(ImageObserver)ImageObserver getImageObserver() |
|
int getImageLoadStatus() |
MediaTracker.MediaTracker定义。 |
Examples that Use Icons使用图标的示例
The following table lists just a few of the many examples that use 下表仅列出了许多使用ImageIcon.ImageIcon的示例中的几个。
LabelDemo |
||
IconDemo |
||
CustomIconDemo |
ArrowIcon.java.ArrowIcon.java实现的自定义图标类。 | |
TumbleItem |
ImageIcon's paintIcon method.ImageIcon的paintIcon方法。 | |
ButtonDemo |
||
CheckBoxDemo |
||
TabbedPaneDemo |
||
DialogDemo |
||
TreeIconDemo |
||
ActionDemo |
Action.Action在工具栏按钮或菜单项中指定图标。 | |
FileChooserDemo2 |
PNG image. PNG图像。 |
Note:
IconDemo are copyright ©2006 spriggs.net and licenced under a Creative Commons Licence. IconDemo中使用的照片属于版权所有©2006spriggs.net,并获得知识共享许可证。