Lesson: Using Swing Components
Section: How to Use Various Components
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
How to Use Root Panes如何使用根窗格
In general, you don't directly create a 通常,您不直接创建JRootPane object. JRootPane对象。Instead, you get a 但是,当您实例化JRootPane (whether you want it or not!) when you instantiate JInternalFrame or one of the top-level Swing containers, such as JApplet, JDialog, and JFrame.JInternalFrame或顶级Swing容器之一时(例如JApplet、JDialog和JFrame)你会得到一个JRootPane(不管你是否想要!)。
Using Top-Level Containers使用顶级容器 tells you the basics of using root panes — getting the content pane, setting its layout manager, and adding Swing components to it. 告诉您使用根窗格的基本知识;获取内容窗格,设置其布局管理器,并向其中添加Swing组件。This section tells you more about root panes, including the components that make up a root pane and how you can use them.本节将介绍有关根窗格的更多信息,包括组成根窗格的组件以及如何使用它们。
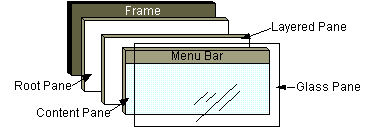
As the preceding figure shows, a root pane has four parts:如上图所示,根窗格有四个部分:
The glass pane玻璃窗格Hidden, by default.默认情况下隐藏。If you make the glass pane visible, then it's like a sheet of glass over all the other parts of the root pane.如果您使玻璃窗格可见,那么它就像根窗格所有其他部分上的一块玻璃。It's completely transparent unless you implement the glass pane's它是完全透明的,除非您实现了玻璃窗格的paintComponentmethod so that it does something, and it can intercept input events for the root pane.paintComponent方法,以便它执行某些操作,并且它可以拦截根窗格的输入事件。In the next section, you'll see an example of using a glass pane.在下一节中,您将看到使用玻璃窗格的示例。The layered pane分层窗格Serves to position its contents, which consist of the content pane and the optional menu bar.用于定位其内容,包括内容窗格和可选菜单栏。Can also hold other components in a specified Z order.也可以按指定的Z顺序保存其他零部件。For information, see The Layered Pane.有关信息,请参阅分层窗格。The content pane内容窗格The container of the root pane's visible components, excluding the menu bar.根窗格可见组件的容器,不包括菜单栏。For information on using the content pane, see Using Top-Level Containers.有关使用内容窗格的信息,请参阅使用顶级容器。The optional menu bar可选菜单栏The home for the root pane's container's menus.根窗格容器菜单的主页。If the container has a menu bar, you generally use the container's如果容器具有菜单栏,则通常使用容器的setJMenuBarmethod to put the menu bar in the appropriate place.setJMenuBar方法将菜单栏放置在适当的位置。For more information on using menus and menu bars, see How to Use Menus.有关使用菜单和菜单栏的详细信息,请参阅如何使用菜单。
The Glass Pane玻璃窗格
The glass pane is useful when you want to be able to catch events or paint over an area that already contains one or more components. 当您希望能够捕捉事件或在已包含一个或多个组件的区域上绘制时,玻璃窗格非常有用。For example, you can deactivate mouse events for a multi-component region by having the glass pane intercept the events. 例如,可以通过让玻璃窗格拦截事件来停用多组件区域的鼠标事件。Or you can display an image over multiple components using the glass pane.也可以使用玻璃窗格在多个组件上显示图像。
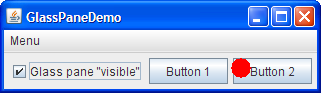
Here's a picture of an application that demonstrates glass pane features. 这是一个演示玻璃窗格功能的应用程序的图片。It contains a check box that lets you set whether the glass pane is "visible" — whether it can get events and paint itself onscreen. 它包含一个复选框,用于设置玻璃窗格是否“可见”—它是否可以获取事件并在屏幕上显示自己。When the glass pane is visible, it blocks all input events from reaching the components in the content pane. 当玻璃窗格可见时,它将阻止所有输入事件到达内容窗格中的组件。It also paints a red dot in the place where it last detected a mouse-pressed event.它还在上次检测到鼠标按下事件的位置绘制一个红点。
Try this:
- Click the Launch button to run GlassPaneDemo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.

Click Button 1.单击按钮1。
The button's appearance changes to show that it's been clicked.按钮的外观将更改,以显示已单击。Click the check box so that the glass pane becomes "visible," and then click Button 1 again.单击复选框,使玻璃窗格变为“可见”,然后再次单击按钮1。
The button does not act clicked because the glass pane intercepts all the mouse events.按钮不会被点击,因为玻璃窗格会截获所有鼠标事件。The glass pane paints a red circle where you release the mouse.释放鼠标时,玻璃窗格会绘制一个红色圆圈。Click the check box again so that the glass pane is hidden.再次单击复选框以隐藏玻璃窗格。
When the glass pane detects an event over the check box, it forwards it to the check box.当玻璃窗格检测到复选框上的事件时,它将其转发到复选框。Otherwise, the check box would not respond to clicks.否则,复选框将不会响应单击。
The following code from GlassPaneDemo.java shows and hides the glass pane. GlassPaneDemo.java中的以下代码显示和隐藏了玻璃窗格。This program happens to create its own glass pane. 这个程序碰巧创建了自己的玻璃窗格。However, if a glass pane doesn't do any painting, the program might simply attach listeners to the default glass pane, as returned by 但是,如果玻璃窗格不进行任何绘制,程序可能会简单地将侦听器附加到默认玻璃窗格,如getGlassPane.getGlassPane返回的。
myGlassPane = new MyGlassPane(...);
changeButton.addItemListener(myGlassPane);
frame.setGlassPane(myGlassPane);
...
class MyGlassPane extends JComponent
implements ItemListener {
...
//React to change button clicks.
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e) {
setVisible(e.getStateChange() == ItemEvent.SELECTED);
}
...
}The next code snippet implements the mouse-event handling for the glass pane. 下一个代码片段实现了玻璃窗格的鼠标事件处理。If a mouse event occurs over the check box, then the glass pane redispatches the event so that the check box receives it.如果鼠标事件发生在复选框上,则玻璃窗格将重新修补该事件,以便复选框接收该事件。
...//In the implementation of the glass pane's mouse listener:
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent e) {
redispatchMouseEvent(e, false);
}
.../* The mouseDragged, mouseClicked, mouseEntered,
* mouseExited, and mousePressed methods have the same
* implementation as mouseMoved. */...
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
redispatchMouseEvent(e, true);
}
private void redispatchMouseEvent(MouseEvent e,
boolean repaint) {
Point glassPanePoint = e.getPoint();
Container container = contentPane;
Point containerPoint = SwingUtilities.convertPoint(
glassPane,
glassPanePoint,
contentPane);
if (containerPoint.y < 0) { //we're not in the content pane
//Could have special code to handle mouse events over
//the menu bar or non-system window decorations, such as
//the ones provided by the Java look and feel.
} else {
//The mouse event is probably over the content pane.
//Find out exactly which component it's over.
Component component =
SwingUtilities.getDeepestComponentAt(
container,
containerPoint.x,
containerPoint.y);
if ((component != null)
&& (component.equals(liveButton))) {
//Forward events over the check box.
Point componentPoint = SwingUtilities.convertPoint(
glassPane,
glassPanePoint,
component);
component.dispatchEvent(new MouseEvent(component,
e.getID(),
e.getWhen(),
e.getModifiers(),
componentPoint.x,
componentPoint.y,
e.getClickCount(),
e.isPopupTrigger()));
}
}
//Update the glass pane if requested.
if (repaint) {
glassPane.setPoint(glassPanePoint);
glassPane.repaint();
}
}Here is the code in 下面是MyGlassPane that implements the painting.MyGlassPane中实现绘画的代码。
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
if (point != null) {
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.fillOval(point.x - 10, point.y - 10, 20, 20);
}
}The Layered Pane分层窗格
A layered pane is a container with depth such that overlapping components can appear one on top of the other. 分层窗格是一个具有深度的容器,这样重叠的组件可以一个在另一个上出现。General information about layered panes is in How to Use Layered Panes. 有关分层窗格的一般信息,请参阅如何使用分层窗格。This section discusses the particulars of how root panes use layered panes.本节讨论根窗格如何使用分层窗格的详细信息。
Each root pane places its menu bar and content pane in an instance of 每个根窗格将其菜单栏和内容窗格放置在JLayeredPane. JLayeredPane的实例中。The Z ordering that the layered pane provides enables behavior such as displaying popup menus above other components.分层窗格提供的Z顺序启用了诸如在其他组件上方显示弹出菜单的行为。
You can choose to put components in the root pane's layered pane. 您可以选择将组件放在根窗格的分层窗格中。If you do, then you should be aware that certain depths are defined to be used for specific functions, and you should use the depths as intended. 如果您这样做了,那么您应该知道某些深度被定义为用于特定功能,并且您应该按照预期使用深度。Otherwise, your components might not play well with the others. 否则,您的组件可能无法与其他组件很好地配合。Here's a diagram that shows the functional layers and their relationship:下图显示了功能层及其关系:
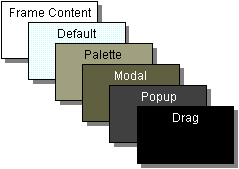
The table below describes the intended use for each layer and lists the 下表描述了各层的预期用途,并列出了与各层相对应的JLayeredPane constant that corresponds to each layer:JLayeredPane常数:
FRAME_CONTENT_LAYER |
new Integer(-30000) |
|
DEFAULT_LAYER |
new Integer(0) |
|
PALETTE_LAYER |
new Integer(100) |
|
MODAL_LAYER |
new Integer(200) |
|
POPUP_LAYER |
new Integer(300) |
|
DRAG_LAYER |
new Integer(400) |
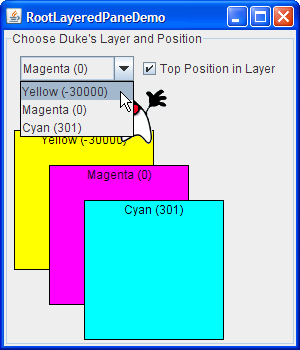
Here is a picture of RootLayeredPaneDemo, which is a version of LayeredPaneDemo that uses the root pane's layered pane, rather than creating a new layered pane.下面是RootLayeredPaneDemo的图片,它是LayeredPaneDemo版本,使用根窗格的分层窗格,而不是创建新的分层窗格。
Try this:
- Click the Launch button to run RootLayeredPaneDemo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.

Move the cursor around in the window, so that Duke moves on top of other components.在窗口中四处移动光标,以便Duke在其他组件上移动。
Note that when the cursor is on top of non-label components — whether it's in the content pane or in the Java-look-and-feel provided title bar — Duke's movement is temporarily stopped.注意,当光标位于非标签组件的顶部时;无论是在内容窗格中还是在Java外观提供的标题栏中;杜克的行动暂时停止。This is because mouse-motion events go to the component that's deepest in the containment hierarchy and is interested in mouse events.这是因为鼠标运动事件会转到包含层次结构中最深的组件,并且对鼠标事件感兴趣。The mouse-motion listener that moves Duke is registered on the layered pane, and most of the components in that pane (with the exception of the labels) happen to have mouse-motion listeners.移动Duke的鼠标运动监听器注册在分层窗格中,该窗格中的大多数组件(标签除外)恰好有鼠标运动监听器。When the mouse moves over an interested component in the layered pane, the layered pane doesn't get the event and the interested component does.当鼠标移动到分层窗格中感兴趣的组件上时,分层窗格不会获取事件,而感兴趣组件会获取事件。Making sure the Top Position in Layer check box is selected, change Duke's layer to Yellow (-30000).确保选中层中的顶部位置复选框,将杜克的层更改为黄色(-30000)。
As before, he appears on top of other components, except for the Magenta (0) and Cyan (301) rectangles.如前所述,他出现在除品红色(0)和青色(301)矩形之外的其他组件的顶部。Keeping Duke in the Yellow layer, click the check box to send Duke to the back of layer -30000.将Duke保持在黄色层中,单击复选框将Duke发送到层-30000的后面。
Duke disappears because the content pane and all the components in it are now above him.杜克消失了,因为内容窗格和其中的所有组件现在都在他的上方。Change Duke's layer to Cyan (301), move Duke down a bit so he's standing on the top edge of the Yellow rectangle, and then press Space to bring up the combo box's drop-down list.将杜克的图层更改为青色(301),将杜克向下移动一点,使他站在黄色矩形的上边缘,然后按空格键打开组合框的下拉列表。
If the look and feel implements the drop-down list as a lightweight popup, Duke appears on top of the drop-down list.如果look-and-feel将下拉列表实现为轻量级弹出窗口,则Duke将出现在下拉列表的顶部。
The Root Pane API根窗格API
The tables that follow list the API for using root panes, glass panes, and content panes. 下表列出了使用根窗格、玻璃窗格和内容窗格的API。For more information on using content panes, go to Using Top-Level Containers. 有关使用内容窗格的更多信息,请转到使用顶级容器。Here are the tables in this section:本节中的表格如下:
The API for using other parts of the root pane is described elsewhere:其他地方描述了使用根窗格其他部分的API:
JRootPane getRootPane()(in JApplet, JDialog, JFrame, JInternalFrame, and JWindow) |
|
static JRootPane getRootPane(Component)(in SwingUtilities) |
|
JRootPane getRootPane()(in JComponent) |
SwingUtilities getRootPane method for the JComponent.JComponent的SwingUtilities getRootPane方法。 |
void setDefaultButton(JButton)JButton getDefaultButton() |
void setGlassPane(Component)Component getGlassPane() |
|
void setLayeredPane(JLayeredPane)Container getLayeredPane() |
|
void setContentPane(Container)Container getContentPane() |
|
void setJMenuBar(JMenuBar)JMenuBar getJMenuBar()(not defined in JWindow) |
Examples that Use Root Panes使用根窗格的示例
Every Swing program has a root pane, but few reference it directly. 每个Swing程序都有一个根窗格,但很少直接引用它。The examples in the following list illustrate how to use features of 以下列表中的示例说明了如何使用JRootPane or the glass pane. JRootPane或玻璃窗格的功能。Also see these lists:另请参阅以下列表:
Examples that Use Layered Panes使用分层窗格的示例Examples that Use Menus使用菜单的示例Examples that Use Frames使用框架的示例(for examples of using content panes)(有关使用内容窗格的示例)
GlassPaneDemo |
||
RootLayeredPaneDemo |
||
ListDialog |
JDialog.JDialog的默认按钮。 | |
FrameDemo2 |
JFrame.JFrame的默认按钮。 |