Lesson: Using Swing Components
Section: How to Use Various Components
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
How to Use Layered Panes如何使用分层窗格
A layered pane is a Swing container that provides a third dimension for positioning components: depth, also known as Z order. 分层窗格是一个Swing容器,它为定位组件提供了第三个维度:深度,也称为Z顺序。When adding a component to a layered pane, you specify its depth as an integer. 将组件添加到分层窗格时,可以将其深度指定为整数。The higher the number, closer the component is to the "top" position within the container. 数字越高,组件越接近容器内的“顶部”位置。If components overlap, the "closer" components are drawn on top of components at a lower depth. 如果组件重叠,则在较低深度的组件顶部绘制“较近”组件。The relationship between components at the same depth is determined by their positions within the depth.相同深度的组件之间的关系由其在深度内的位置确定。
Note:
The AWT Container has an API that allows you to manipulate component Z order. AWT容器有一个API,允许您操作组件Z顺序。For more information, see the AWT Focus Specification.有关更多信息,请参阅AWT焦点规范。
Every Swing container that has a root pane — such as 具有根窗格的每个Swing容器;例如JFrame, JApplet, JDialog, or JInternalFrame — automatically has a layered pane. JFrame、JApplet、JDialog或JInternalFrame;自动具有分层窗格。Most programs do not explicitly use the root pane's layered pane, so this section will not discuss it. 大多数程序不显式使用根窗格的分层窗格,因此本节将不讨论它。You can find information about it in The Root Pane, which provides an overview, and The Layered Pane, which has further details. 您可以在根窗格(提供概述)和分层窗格(提供更多详细信息)中找到有关它的信息。This section tells you how to create your own layered pane and use it anywhere you can use a regular Swing container.本节告诉您如何创建自己的分层窗格,并在任何可以使用常规Swing容器的地方使用它。
Swing provides two layered pane classes. Swing提供了两层窗格类。The first, 第一个类JLayeredPane, is the class that root panes use and is the class used by the example in this section. JLayeredPane是根窗格使用的类,也是本节示例使用的类。The second, 第二个,JDesktopPane, is a JLayeredPane subclass that is specialized for the task of holding internal frames. JDesktopPane,是一个JLayeredPane子类,专门用于保存内部帧。For examples of using 有关使用JDesktopPane, see How to Use Internal Frames.JDesktopPane的示例,请参阅如何使用内部框架。
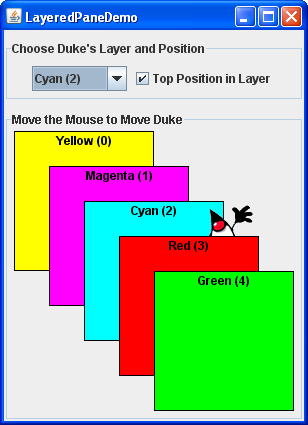
Here is a picture of an application that creates a layered pane and places overlapping, colored labels at different depths:下面是一个应用程序的图片,它创建了一个分层窗格,并在不同深度放置重叠的彩色标签:
Try this::
Click the Launch button to run the LayeredPane Demo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later).单击启动按钮,使用Java™Web启动运行分层窗格演示(下载JDK 7或更高版本)。Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.或者,要自己编译和运行示例,请参考示例索引。
Move the mouse around in the lower part of the window.在窗口的下部移动鼠标。The image of Duke drags behind the green and red labels, but in front of the other three labels.杜克的图像拖在绿色和红色标签后面,但在其他三个标签前面。Use the combo box at the top of the window to change Duke's depth.使用窗口顶部的组合框更改杜克深度。Use the check box to set whether Duke is in the top position — position 0 — within the current depth.使用复选框设置杜克是否处于顶部位置—位置0—在当前深度内。
Here is the code from 以下是LayeredPaneDemo.java that creates the layered pane:LayeredPaneDemo.java中创建分层窗格的代码:
layeredPane = new JLayeredPane();
layeredPane.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300, 310));
layeredPane.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(
"Move the Mouse to Move Duke"));
layeredPane.addMouseMotionListener(new MouseMotionAdapter() {
...
});The code uses 代码使用JLayeredPane's only constructor — the no-argument constructor — to create the layered pane. JLayeredPane的唯一构造函数—无参数构造函数—创建分层窗格。The rest of the code uses methods inherited from superclasses to give the layered pane a preferred size and a border, and add a mouse-motion listener to it. 其余代码使用从超类继承的方法为分层窗格提供首选大小和边框,并向其添加鼠标运动侦听器。The mouse-motion listener just moves the Duke image around in response to mouse movement. 鼠标运动监听器只是响应鼠标移动而移动杜克图像。Although we do not show the code here, the example adds the layered pane to the frame's content pane.虽然这里没有显示代码,但示例将分层窗格添加到框架的内容窗格中。
As we will show you a bit later, you add components to a layered pane using an 正如我们稍后将向您展示的,您可以使用add method. add方法将组件添加到分层窗格中。When adding a component to a layered pane, you specify the component depth, and optionally, its position within its depth. 将组件添加到分层窗格时,可以指定组件深度,也可以指定组件在其深度内的位置。The layered pane in the demo program contains six labels — the five colored labels and a sixth one that displays the Duke image. 演示程序中的分层窗格包含六个标签;五个彩色标签和显示杜克图像的第六个标签。As the program demonstrates, both the depth of a component and its position within that depth can change dynamically.如程序所示,组件的深度及其在该深度内的位置都可以动态变化。
The rest of this section covers these topics:本节其余部分包括以下主题:
Adding Components and Setting Component Depth添加组件和设置组件深度Setting a Component Position Within Its Depth在其深度内设置组件位置Laying Out Components in a Layered Pane在分层窗格中布局组件The Layered Pane API分层窗格APIExamples that Use Layered Panes使用分层窗格的示例
Adding Components and Setting Component Depth添加组件和设置组件深度
Here is the code from the sample program that adds the colored labels to the layered pane:下面是将彩色标签添加到分层窗格的示例程序中的代码:
for (int i = 0; i < ...number of labels...; i++) {
JLabel label = createColoredLabel(...);
layeredPane.add(label, new Integer(i));
...
}You can find the implementation of the 您可以在程序的源代码中找到createColoredLabel method in the source code for the program. createColoredLabel方法的实现。It just creates an opaque 它只是创建了一个不透明的JLabel initialized with a background color, a border, some text, and a size.JLabel,初始化为背景色、边框、一些文本和大小。
The example program uses a two-argument version of the 示例程序使用两参数版本的add method. add方法。The first argument is the component to add, the second is an 第一个参数是要添加的组件,第二个参数是Integer object, specifying the depth. Integer对象,指定深度。This program uses the 该程序使用for loop iteration variable to specify depths. for循环迭代变量指定深度。The actual values do not matter much. What matters is the relative value of the depths and that you are consistent within your program in how you use each depth.实际值并不重要。重要的是深度的相对值,以及您在程序中如何使用每个深度的一致性。
Note:
If you use the root pane's layered pane, be sure to use its depth conventions. 如果使用根窗格的分层窗格,请确保使用其深度约定。Refer to The Layered Pane for details. 有关详细信息,请参阅分层窗格。That section shows you how to modify 本节介绍如何修改LayeredPaneDemo to use the root pane's layered pane. LayeredPaneDemo以使用根窗格的分层窗格。With the modifications, you can see how the dragging Duke image relates to the combo box in the control panel.修改后,您可以看到拖动Duke图像与控制面板中的组合框的关系。
As you can see from the example program, if components overlap, components at a higher depth are on top of components at a lower depth. 从示例程序中可以看到,如果组件重叠,则深度较高的组件位于深度较低的组件之上。To change a component depth dynamically, use the 要动态更改组件深度,请使用setLayer method. setLayer方法。In the example, the user can change Duke's layer by making a selection from the combo box. 在本例中,用户可以通过从组合框中进行选择来更改Duke的图层。Here is the 下面是在组合框中注册的动作监听器的actionPerformed method of the action listener registered on the combo box:actionPerformed方法:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int position = onTop.isSelected() ? 0 : 1;
layeredPane.setLayer(dukeLabel,
layerList.getSelectedIndex(),
position);
}The 这里使用的setLayer method used here takes three arguments: the component whose depth is to be set, the new depth, and the position within the depth. setLayer方法有三个参数:要设置深度的组件、新深度和深度内的位置。JLayeredPane has a two-argument version of setLayer that takes only the component and the new depth. JLayeredPane有一个两参数版本的setLayer,它只接受组件和新深度。That method puts the component at the bottom position in its depth.该方法将组件置于其深度的底部位置。
When adding a component to a layered pane you specify the layer with an 将组件添加到分层窗格时,可以使用Integer. Integer指定层。When using 使用setLayer to change a component's layer, you use an int. setLayer更改组件的层时,使用int。You might think that if you use an 您可能认为,如果在int instead of an Integer with the add method, the compiler would complain or your program would throw an illegal argument exception. add方法中使用int而不是Integer,编译器会抱怨,或者程序会抛出非法参数异常。But the compiler says nothing, which results in a common layered pane problem. 但是编译器什么也不说,这导致了一个常见的分层窗格问题。You can use the API tables at the end of this section to check the types of the arguments and return values for methods that deal with layers.您可以使用本节末尾的API表来检查处理层的方法的参数类型和返回值。
Setting a Component's Position Within Its Depth在其深度内设置零部件的位置
The following code creates the label that displays Duke's image, and then adds the label to the layered pane.下面的代码创建显示Duke图像的标签,然后将标签添加到分层窗格。
final ImageIcon icon = createImageIcon("images/dukeWaveRed.gif");
...
dukeLabel = new JLabel(icon);
...
dukeLabel.setBounds(15, 225,
icon.getIconWidth(),
icon.getIconHeight());
...
layeredPane.add(dukeLabel, new Integer(2), 0);This code uses the three-argument version of the 此代码使用add method. add方法的三参数版本。The third argument specifies the Duke label position within its depth, which determines the component's relationship with other components at the same depth.第三个参数指定Duke标签在其深度内的位置,该位置确定组件与相同深度的其他组件的关系。
Positions are specified with an 位置用一个介于-1和(n - 1)之间的int between -1 and (n - 1), where n is the number of components at the depth. int指定,其中n是深度处的组件数。Unlike layer numbers, the smaller the position number, the higher the component within its depth. 与层编号不同,位置编号越小,其深度内的组件越高。Using -1 is the same as using n - 1; it indicates the bottom-most position. 使用-1与使用n-1相同;它指示最底部的位置。Using 0 specifies that the component should be in the top-most position within its depth. 使用0指定组件应位于其深度内的最顶部位置。As the following figure shows, with the exception of -1, a lower position number indicates a higher position within a depth.如下图所示,除-1外,较低的位置编号表示深度内的较高位置。

A component's position within its layer can change dynamically. 组件在其层中的位置可以动态变化。In the example, you can use the check box to determine whether Duke label is in the top position at its depth. 在本例中,您可以使用复选框确定杜克标签是否位于其深度的顶部位置。Here's the 下面是在复选框中注册的动作监听器的actionPerformed method for the action listener registered on the check box:actionPerformed方法:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (onTop.isSelected())
layeredPane.moveToFront(dukeLabel);
else
layeredPane.moveToBack(dukeLabel);
}When the user selects the check box, the 当用户选中复选框时,moveToFront method moves Duke to the front (position 0). moveToFront方法将杜克移动到前面(位置0)。And when the user deselects check box, Duke gets moved to the back with the 当用户取消选中复选框时,Duke将使用moveToBack method. moveToBack方法移到后面。You can also use the 您还可以使用setPosition method or the three-argument version of setLayer to change a component's position.setPosition方法或setLayer的三参数版本来更改组件的位置。
Laying Out Components in a Layered Pane在分层窗格中布局组件
By default a layered pane has no layout manager. 默认情况下,分层窗格没有布局管理器。This means that you typically have to write the code that positions and sizes the components you put in a layered pane.这意味着您通常必须编写代码来定位和调整放置在分层窗格中的组件的大小。
The example uses the 该示例使用setBounds method to set the size and position of each of the labels:setBounds方法设置每个标签的大小和位置:
dukeLabel.setBounds(15, 225,
icon.getIconWidth(),
icon.getIconHeight());
...
label.setBounds(origin.x, origin.y, 140, 140);When the user moves the mouse around, the program calls 当用户移动鼠标时,程序调用setPosition to change Duke's position:setPosition来更改杜克的位置:
dukeLabel.setLocation(e.getX()-XFUDGE, e.getY()-YFUDGE);
Although a layered pane has no layout manager by default, you can still assign a layout manager to the layered pane. 尽管默认情况下分层窗格没有布局管理器,但您仍然可以为分层窗格指定布局管理器。All of the layout managers provided by the Java platform arrange the components as if they were all on one layer. Java平台提供的所有布局管理器都将组件安排在一个层上。Here is a version of the previous demo that sets the layered pane's layout manager to an instance of 这是之前演示的一个版本,它将分层窗格的布局管理器设置为GridLayout, using that layout manager to lay out six colored labels.GridLayout的一个实例,使用该布局管理器来布局六个彩色标签。
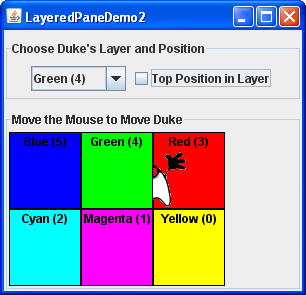
You can find the code for this program in 您可以在LayeredPaneDemo2.java. LayeredPaneDemo2.java中找到该程序的代码。You can run LayeredPaneDemo2 ( download JDK 7 or later). 您可以运行LayeredPaneDemo2(下载JDK 7或更高版本)。If you want to compile the example, consult the example index for a list of all necessary files.如果要编译示例,请参考示例索引以获取所有必要文件的列表。
Many programs use intermediate containers (such as panels) and their layout managers to lay out components on the same layer, but use absolute positioning to lay out components on different layers. 许多程序使用中间容器(如面板)及其布局管理器在同一层上布局组件,但使用绝对定位在不同层上布局。For more information about absolute positioning, see Doing Without a Layout Manager (Absolute Positioning).有关绝对定位的详细信息,请参阅不使用布局管理器(绝对定位)。
The Layered Pane API分层窗格API
The following tables list the commonly used 下表列出了常用的JLayeredPane constructors and methods. JLayeredPane构造函数和方法。Other methods you are most likely to invoke on a 您最可能在JLayeredPane object are those it inherits from its superclasses, such as setBorder, setPreferredSize, and so on. JLayeredPane对象上调用的其他方法是从其超类继承的方法,如setOrder、setPreferredSize等。See The JComponent API for tables of commonly used inherited methods.有关常用继承方法的表,请参阅JComponent API。
The API for using layered pane falls into these categories:使用分层窗格的API分为以下几类:
Creating or Getting a Layered Pane创建或获取分层窗格Layering Components分层组件Setting Component's Intra-Layer Positions设置组件的层内位置
JLayeredPane() |
|
JLayeredPane getLayeredPane()JApplet, JDialog, JFrame, and JInternalFrame)JApplet、JDialog、JFrame和JInternalFrame中) |
void add(Component)void add(Component, Object)void add(Component, Object, int) |
Integer that indicates the layer. Integer。 |
void setLayer(Component, int)void setLayer(Component, int, int) |
|
int getLayer(Component)int getLayer(JComponent) |
|
int getComponentCountInLayer(int) |
|
Component[] getComponentsInLayer(int) |
|
int highestLayer()int lowestLayer() |
void setPosition(Component, int)int getPosition(Component) |
|
void moveToFront(Component)void moveToBack(Component) |
Examples that Use Layered Panes使用分层窗格的示例
This table shows the examples that use 下表显示了使用JLayeredPane and where those examples are described.JLayeredPane的示例以及这些示例的描述位置。
LayeredPaneDemo |
JLayeredPane.JLayeredPane的层和层内位置。 | |
LayeredPaneDemo2 |
||
RootLayeredPaneDemo |
LayeredPaneDemo modified to use the root pane's layered pane.LayeredPaneDemo的一个版本被修改为使用根窗格的分层窗格。 | |
InternalFrameDemo |
JDesktopFrame to manage internal frames.JDesktopFrame管理内部帧。 |