Lesson: Using Swing Components
Section: How to Use Various Components
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
How to Use Scroll Panes如何使用滚动窗格
A JScrollPane provides a scrollable view of a component. JScrollPane提供组件的可滚动视图。When screen real estate is limited, use a scroll pane to display a component that is large or one whose size can change dynamically. 当屏幕空间有限时,使用滚动窗格显示较大的组件或其大小可以动态更改的组件。Other containers used to save screen space include split panes and tabbed panes.用于节省屏幕空间的其他容器包括拆分窗格和选项卡式窗格。
The code to create a scroll pane can be minimal. 创建滚动窗格的代码可以是最少的。For example, here's a picture of a demo program that puts a text area in a scroll pane because the text area's size grows dynamically as text is appended to it: 例如,这是一个演示程序的图片,它将文本区域放在滚动窗格中,因为文本区域的大小随着文本的添加而动态增长:

Here's the code that creates the text area, makes it the scroll pane's client, and adds the scroll pane to a container:以下代码创建文本区域,使其成为滚动窗格的客户端,并将滚动窗格添加到容器中:
//In a container that uses a BorderLayout: textArea = new JTextArea(5, 30); ... JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea); ... setPreferredSize(new Dimension(450, 110)); ... add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
The boldface line of code creates the 粗体代码行创建JScrollPane, specifying the text area as the scroll pane's client. JScrollPane,将文本区域指定为滚动窗格的客户端。The program doesn't invoke any methods on the 程序不会调用JScrollPane object, since the scroll pane handles everything automatically: creating the scroll bars when necessary, redrawing the client when the user moves the scroll knobs, and so on.JScrollPane对象上的任何方法,因为滚动窗格会自动处理所有事情:在必要时创建滚动条,在用户移动滚动旋钮时重新绘制客户端,等等。
You might have noticed that the preceding code sets the preferred size of the scroll pane's container. 您可能已经注意到,前面的代码设置了滚动窗格容器的首选大小。In the Java look and feel, this preferred size happens to be a bit less tall than required for the text area to display the 5 rows that we requested when creating it, so the scroll bar initially displays a vertical scroll bar. 在Java look and feel中,这个首选的大小恰好比文本区域在创建时显示我们请求的5行所需的高度稍低,因此滚动条最初显示垂直滚动条。If we didn't restrict the size of the scroll pane's container, the scroll pane would be big enough for the text area to display the full 5 rows and 30 columns specified with the 如果我们不限制滚动窗格容器的大小,滚动窗格将足够大,文本区域可以显示JTextArea constructor. JTextArea构造函数指定的全部5行和30列。Refer to Sizing a Scroll Pane for information about techniques for making a scroll pane the size you want.有关使滚动窗格达到所需大小的技术信息,请参阅调整滚动窗格的大小。
The rest of this section discusses the following topics:本节其余部分讨论以下主题:
How a Scroll Pane Works滚动窗格的工作方式Setting the Scroll Bar Policy设置滚动条策略Providing Custom Decorations提供定制装饰Implementing a Scrolling-Savvy Client实现具有滚动能力的客户端Sizing a Scroll Pane调整滚动窗格的大小Dynamically Changing the Client's Size动态更改客户端的大小The Scroll Pane API滚动窗格APIExamples that Use Scroll Panes使用滚动窗格的示例
How a Scroll Pane Works滚动窗格的工作方式
Here is a snapshot of an application that uses a customized scroll pane to view a photograph:以下是使用自定义滚动窗格查看照片的应用程序的快照:

The scroll pane in this application looks very different from the one in the previous demo program. 此应用程序中的滚动窗格看起来与先前演示程序中的非常不同。Rather than displaying text, this scroll pane contains a image. 此滚动窗格不显示文本,而是包含图像。The scroll pane also has two scroll bars, a row header, a column header, and four corners, three of which have been customized. 滚动窗格还具有两个滚动条,一个行标题、一个列标题和四个角,其中三个已自定义。
Try this::
Click the Launch button to run ScrollDemo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later).单击启动按钮,使用Java™Web启动运行ScrollDemo(下载JDK 7或更高版本)。Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.或者,要自己编译和运行示例,请参考示例索引。
Move the knobs on the scroll bars.移动滚动条上的旋钮。Watch the image scroll and the horizontal and vertical rulers scroll along.观看图像滚动以及水平和垂直标尺的滚动。If you have a mouse with a wheel (which is generally between the mouse buttons) use the mouse wheel to scroll the image vertically.如果您的鼠标带有滚轮(通常位于鼠标按钮之间),请使用鼠标滚轮垂直滚动图像。Click the cm toggle in the upper left corner of the scroll pane.单击滚动窗格左上角的cm切换。The units on the row and column headers change to inches (or back to centimeters).行标题和列标题上的单位更改为英寸(或厘米)。Click the arrow buttons on the scroll bars.单击滚动条上的箭头按钮。Also, try clicking on the track above or below the knob on the vertical scroll bar, or to the left or right of the horizontal one.此外,尝试单击垂直滚动条上旋钮上方或下方的轨迹,或水平滚动条左侧或右侧的轨迹。Move the cursor over the image and press the cursor.将光标移到图像上并按下光标。Continuing to press the cursor, drag to a point outside the image and pause.继续按光标,拖动到图像外的点并暂停。The visible area of the image moves toward the cursor.图像的可见区域向光标移动。This scroll-by-dragging functionality is enabled by the scroll pane, and with the此拖动滚动功能由滚动窗格和JComponentAPI, but it is implemented by the custom component that displays the image.JComponentAPI启用,但由显示图像的自定义组件实现。Resize the window.调整窗口大小。Notice that the scroll bars disappear when the scroll pane is large enough to display the entire image and reappear again when the scroll pane is too small to show the entire image.请注意,当滚动窗格足够大以显示整个图像时,滚动条会消失,而当滚动窗格太小而无法显示整个图像后,滚动条再次出现。
The ScrollDemo program establishes the scroll pane's client when creating the scroll pane:ScrollDemo程序在创建滚动窗格时建立滚动窗格的客户端:
//Where the member variables are declared: private ScrollablePicture picture; ... //Where the GUI is created: picture = new ScrollablePicture( ...); JScrollPane pictureScrollPane = new JScrollPane(picture);
The scroll pane's client is also known as the view or viewport view. 滚动窗格的客户端也称为视图或视口视图。You can change the client dynamically by calling the 您可以通过调用setViewportView method. setViewportView方法动态更改客户端。Note that 请注意,JScrollPane has no corresponding getViewportView method. JScrollPane没有相应的getViewportView方法。If you need to refer to the client object again, you can either cache it in a variable or invoke 如果需要再次引用客户端对象,可以将其缓存在变量中,也可以在滚动窗格上调用getViewport().getViewportView() on the scroll pane.getViewport().getViewportView()。
When the user manipulates the scroll bars in a scroll pane, the area of the client that is visible changes accordingly. 当用户操作滚动窗格中的滚动条时,客户端的可见区域会相应地改变。This picture shows the relationship between the scroll pane and its client and indicates the classes that the scroll pane commissions to help:此图显示了滚动窗格与其客户端之间的关系,并指出滚动窗格委托帮助的类:
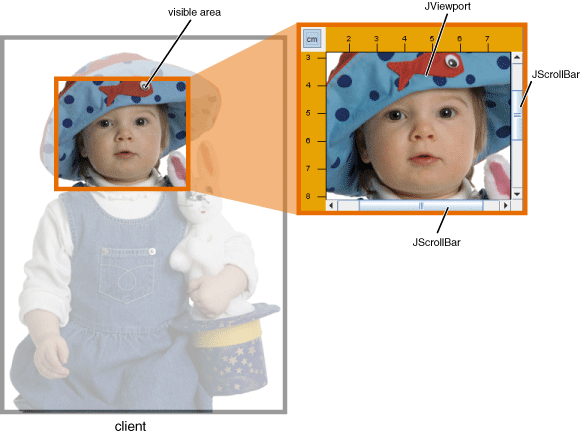
A scroll pane uses a 滚动窗格使用JViewport instance to manage the visible area of the client. JViewport实例来管理客户端的可见区域。The viewport is responsible for positioning and sizing the client, based on the positions of the scroll bars, and displaying it.视口负责根据滚动条的位置定位和调整客户端的大小,并显示它。
A scroll pane may use two separate instances of 滚动窗格可以使用两个单独的JScrollBar for the scroll bars. JScrollBar实例作为滚动条。The scroll bars provide the interface for the user to manipulate the visible area. 滚动条为用户提供了操作可见区域的界面。The following figure shows the three areas of a scroll bar: the knob (sometimes called the thumb), the (arrow) buttons, and the track.下图显示了滚动条的三个区域:旋钮(有时称为拇指)、箭头按钮和轨迹。

When the user moves the knob on the vertical scroll bar up and down, the visible area of the client moves up and down. 当用户上下移动垂直滚动条上的旋钮时,客户端的可见区域上下移动。Similarly, when the user moves the knob on the horizontal scroll bar to the right and left, the visible area of the client moves back and forth accordingly. 类似地,当用户左右移动水平滚动条上的旋钮时,客户端的可见区域相应地前后移动。The position of the knob relative to its track is proportionally equal to the position of the visible area relative to the client. 旋钮相对于其轨迹的位置与可视区域相对于客户的位置成比例相等。In the Java look and feel and some others, the size of the knob gives a visual clue as to how much of the client is visible.在Java外观和其他一些设计中,旋钮的大小提供了一个可视化的线索,显示了客户端的可视程度。
By clicking an arrow button, the user can scroll by a unit increment. 通过单击箭头按钮,用户可以滚动单位增量。By clicking within the track, the user can scroll by a block increment. 通过在轨迹内单击,用户可以滚动块增量。If the user has a mouse with a wheel, then the user can scroll vertically using the mouse wheel. The amount that the mouse wheel scrolls is platform dependent. 如果用户有带滚轮的鼠标,则用户可以使用鼠标滚轮垂直滚动。鼠标滚轮的滚动量取决于平台。For example, by default on Windows XP, the mouse wheel scrolls three unit increments; the Mouse control panel allows you to specify a different number of unit increments or to use a block increment instead. 例如,默认情况下,在Windows XP上,鼠标滚轮滚动三个单位增量;鼠标控制面板允许您指定不同数量的单位增量或使用块增量。More information about unit and block increments is in Implementing a Scrolling-Savvy Client.有关单位和块增量的更多信息,请参阅实现滚动智能客户端。
Typical programs don't directly instantiate or call methods on a viewport or scroll bar. 典型的程序不会直接实例化或调用视口或滚动条上的方法。Instead, programs achieve their scrolling behavior using the 相反,程序使用JScrollPane API and the API discussed in Implementing a Scrolling-Savvy Client. JScrollPane API和实现滚动智能客户端中讨论的API实现滚动行为。Some scrolling-savvy components such as 一些熟悉滚动的组件,如JList, JTable, and JTree also provide additional API to help you affect their scrolling behavior.JList、JTable和JTree,还提供了额外的API来帮助您影响它们的滚动行为。
Setting the Scroll Bar Policy设置滚动条策略
On startup, the scroll pane in the 启动时,ScrollDemo application has two scroll bars. ScrollDemo应用程序中的滚动窗格有两个滚动条。If you make the window large, both scroll bars disappear because they are no longer needed. 如果窗口变大,两个滚动条都会消失,因为它们不再需要。If you then shrink the height of the window without changing its width, the vertical scroll bar reappears. 如果在不改变窗口宽度的情况下缩小窗口的高度,垂直滚动条将重新出现。Further experimentation will show that in this application both scroll bars disappear and reappear as needed. 进一步的实验将表明,在这个应用程序中,两个滚动条都会根据需要消失和重新出现。This behavior is controlled by the scroll pane's scroll bar policy, Actually, it's two policies: each scroll bar has its own.此行为由滚动窗格的滚动条策略控制,实际上,它有两个策略:每个滚动条都有自己的策略。
ScrollDemo doesn't explicitly set the scroll pane's scroll bar policies — it uses the default. ScrollDemo没有显式设置滚动窗格的滚动条策略;它使用默认值。You can set the policies when you create the scroll pane or change them dynamically.您可以在创建滚动窗格时设置策略,也可以动态更改策略。
Of the constructors provided by 在JScrollPane, these two let you set the scroll bar policies when you create the scroll pane:JScrollPane提供的构造函数中,这两个允许您在创建滚动窗格时设置滚动条策略:
JScrollPane(Component, int, int) JScrollPane(int, int)
The first 第一个int specifies the policy for the vertical scroll bar; the second specifies the policy for the horizontal scroll bar. int指定垂直滚动条的策略;第二个指定水平滚动条的策略。You can also set the policies dynamically with the 还可以使用setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy and setVerticalScrollBarPolicy methods. setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy和setVerticalScrollBarPolicy方法动态设置策略。With both the constructors and the methods, use one of the following constants defined in the 对于构造函数和方法,使用ScrollPaneConstants interface (which is implemented by JScrollPane):ScrollPaneConstants接口(由JScrollPane实现)中定义的以下常量之一:
VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDEDHORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED |
|
VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYSHORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS |
|
VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVERHORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER |
Providing Custom Decorations提供定制装饰
The area drawn by a scroll pane consists of up to nine parts: the center, four sides, and four corners. 滚动窗格绘制的区域最多由九个部分组成:中心、四个边和四个角。The center is the only component that is always present in all scroll panes. 中心是所有滚动窗格中始终存在的唯一组件。Besides scroll bars, the sides can contain column and row headers. 除了滚动条,侧面还可以包含列标题和行标题。A corner component is visible only if both sides that intersect at that corner contain visible components.只有在拐角处相交的两侧都包含可见构件时,拐角构件才可见。

As shown in the figure, the scroll pane in 如图所示,ScrollDemo has custom row and column headers. ScrollDemo中的滚动窗格具有自定义的行和列标题。Additionally, because all four sides are populated, all four corners are present. 此外,因为所有四个边都已填充,所以所有四个角都存在。The program customizes three of the corners — two just fill their area with the same color as the 该程序定制三个角—两个只是用与Rules, and the other contains a toggle button. Rule相同的颜色填充其区域,另一个包含切换按钮。The fourth corner, the lower right corner, is the default provided by the scroll pane. 第四个角(右下角)是滚动窗格提供的默认值。Notice that because the row and column headers are always present in this example, the toggle button is also always present.请注意,由于在本例中始终存在行标题和列标题,因此切换按钮也始终存在。
If a corner contains a control that the user needs access to all the time, make sure the sides that intersect at the corner are always present. 如果角包含用户需要随时访问的控件,请确保始终存在与角相交的边。For example, if this application placed the toggle in the lower right corner where the scroll bars intersect, then the toggle would disappear if the user resized the window and even one of the scroll bars disappeared.例如,如果此应用程序将切换放置在滚动条相交的右下角,则如果用户调整窗口大小,甚至其中一个滚动条消失,则切换将消失。
The scroll pane's row and column headers are provided by a custom 滚动窗格的行和列标题由自定义JComponent subclass, Rule, that draws a ruler in centimeters or inches. JComponent子类Rule提供,该子类以厘米或英寸为单位绘制标尺。Here's the code that creates and sets the scroll pane's row and column headers:下面是创建和设置滚动窗格的行标题和列标题的代码:
//Where the member variables are defined:
private Rule columnView;
private Rule rowView;
...
//Where the GUI is initialized:
ImageIcon bee = createImageIcon("images/flyingBee.jpg");
...
//Create the row and column headers.
columnView = new Rule(Rule.HORIZONTAL, true);
rowView = new Rule(Rule.VERTICAL, true);
...
pictureScrollPane.setColumnHeaderView(columnView);
pictureScrollPane.setRowHeaderView(rowView);You can use any component for a scroll pane's row and column headers. 您可以将任何组件用于滚动窗格的行标题和列标题。The scroll pane puts the row and column headers in 滚动窗格将行标题和列标题放在各自的JViewPorts of their own. jViewport中。Thus, when scrolling horizontally, the column header follows along, and when scrolling vertically, the row header follows along. 因此,水平滚动时,列标题跟随,垂直滚动时,行标题跟随。Make sure the row and column have the same width and height as the view, because JScrollPane does not enforce these values to have the same size. 确保行和列具有与视图相同的宽度和高度,因为JScrollPane不强制这些值具有相同的大小。If one differs from the other, you are likely to not get the desired behavior.如果一个与另一个不同,则可能无法获得所需的行为。
As a 作为JComponent subclass, our custom Rule class puts its rendering code in its paintComponent method. JComponent子类,自定义Rule类将其呈现代码放在其paintComponent方法中。The Rule rendering code takes care to draw only within the current clipping bounds, to ensure speedy scrolling. Rule呈现代码只在当前剪切边界内绘制,以确保快速滚动。Your custom row and column headers should do the same.自定义行标题和列标题也应该这样做。
You can also use any component for the corners of a scroll pane. 您还可以将任何组件用于滚动窗格的角。ScrollDemo illustrates this by putting a toggle button in the upper left corner, and custom Corner objects in the upper right and lower left corners. Corner对象来说明这一点。Here's the code that creates the 下面是创建角Corner objects and calls setCorner to place them:Corner对象并调用setCorner放置它们的代码:
//Create the corners.
JPanel buttonCorner = new JPanel(); //use FlowLayout
isMetric = new JToggleButton("cm", true);
isMetric.setFont(new Font("SansSerif", Font.PLAIN, 11));
isMetric.setMargin(new Insets(2,2,2,2));
isMetric.addItemListener(this);
buttonCorner.add(isMetric);
...
//Set the corners.
pictureScrollPane.setCorner(JScrollPane.UPPER_LEFT_CORNER,
buttonCorner);
pictureScrollPane.setCorner(JScrollPane.LOWER_LEFT_CORNER,
new Corner());
pictureScrollPane.setCorner(JScrollPane.UPPER_RIGHT_CORNER,
new Corner());Remember that the size of each corner is determined by the size of the sides intersecting there. 请记住,每个角点的大小由相交的边的大小决定。For some components you must take care that the specific instance of the component fits in its corner. 对于某些组件,必须注意组件的特定实例适合其角落。For example, the program sets the font and margins on the toggle button so that it fits within the space established by the headers. 例如,程序在切换按钮上设置字体和边距,使其适合标题所建立的空间。It's not an issue with the Corner class because that class colors its entire bounds, whatever they happen to be, with a solid color.Corner类没有问题,因为该类使用纯色为其整个边界着色,不管它们是什么。
As you can see from the code, constants indicate the corner positions. 从代码中可以看到,常量表示角点位置。This figure shows the constant for each position:该图显示了每个位置的常数:
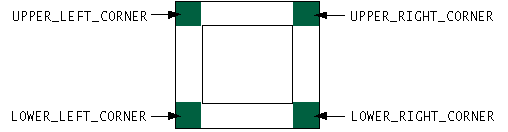
The constants are defined in the 常量在ScrollPaneConstants interface, which JScrollPane implements.ScrollPaneConstants接口中定义,JScrollPane实现了该接口。
Implementing a Scrolling-Savvy Client实现具有滚动能力的客户端
To customize the way that a client component interacts with its scroll pane, you can make the component implement the 要自定义客户端组件与其滚动窗格交互的方式,可以使组件实现Scrollable interface. Scrollable界面。By implementing 通过实现Scrollable, a client can specify both the size of the viewport used to view it and the amount to scroll for clicks on the different controls on a scroll bar. Scrollable,客户机可以指定用于查看它的视口的大小和滚动条上不同控件的点击量。You can also specify if the view should track the size of the viewport. 还可以指定视图是否应跟踪视口的大小。This is typically used when the viewport is bigger than the view, but the view should fill the available space.这通常在视口大于视图时使用,但视图应填充可用空间。
Note:
setUnitIncrement and setBlockIncrement methods of JScrollBar. JScrollBar的setUnitIncrement和setBlockIncrement方法指定单位和块增量。scrollPane.getVerticalScrollBar().setUnitIncrement(10);
Here again are the three control areas of a scroll bar: the knob, the buttons, and the track.这里同样是滚动条的三个控制区域:旋钮、按钮和轨迹。

You might have noticed when manipulating the scroll bars in 您可能已经注意到,在ScrollDemo中操作滚动条时,单击按钮会将图像滚动到刻度边界。ScrollDemo that clicking the buttons scrolls the image to a tick boundary. You might also have noticed that clicking in the track scrolls the picture by a "screenful". 您可能还注意到,单击轨迹会将图片滚动一个“屏幕”。More generally, the button scrolls the visible area by a unit increment and the track scrolls the visible area by a block increment. 更一般地,按钮以单位增量滚动可见区域,轨迹以块增量滚动可见区。The behavior you see in the example is not the scroll pane's default behavior, but is specified by the client in its implementation of the 您在示例中看到的行为不是滚动窗格的默认行为,而是由客户端在Scrollable interface.Scrollable界面的实现中指定的。
The client for the ScrollDemo program is ScrollablePicture. ScrollDemo程序的客户端是ScrollablePicture。ScrollablePicture is a subclass of JLabel that provides implementations of all five Scrollable methods:ScrollablePicture是JLabel的一个子类,它提供了所有五种Scrollable方法的实现:
getScrollableBlockIncrementgetScrollableUnitIncrementgetPreferredScrollableViewportSizegetScrollableTracksViewportHeightgetScrollableTracksViewportWidth
ScrollablePicture implements the Scrollable interface primarily to affect the unit and block increments. ScrollablePicture实现Scrollable界面主要是为了影响单位和块增量。However, it must provide implementations for all five methods. 然而,它必须为所有五种方法提供实现。Thus, it provides reasonable defaults for the other three methods that you might want to copy for your scrolling-savvy classes.因此,它为其他三种方法提供了合理的默认值,您可能希望为您的滚动类复制这些方法。
The scroll pane calls the client's 每当用户单击滚动条上的一个按钮时,滚动窗格就会调用客户端的getScrollableUnitIncrement method whenever the user clicks one of the buttons on the scroll bar. getScrollableUnitIncrement方法。This is true as long as the client implements Scrollable. 只要客户机实现可滚动,这是正确的。This method returns the number of pixels to scroll. 此方法返回要滚动的像素数。An obvious implementation of this method returns the number of pixels between tick marks on the header rulers. 此方法的一个明显实现返回标题标尺上刻度线之间的像素数。ScrollablePicture, however, does something different: It returns the value required to position the image on a tick mark boundary. ScrollablePicture做了一些不同的事情:它返回将图像定位在刻度线边界上所需的值。Here's the implementation:实现如下:
public int getScrollableUnitIncrement(Rectangle visibleRect,
int orientation,
int direction) {
//Get the current position.
int currentPosition = 0;
if (orientation == SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL) {
currentPosition = visibleRect.x;
} else {
currentPosition = visibleRect.y;
}
//Return the number of pixels between currentPosition
//and the nearest tick mark in the indicated direction.
if (direction < 0) {
int newPosition = currentPosition -
(currentPosition / maxUnitIncrement)
* maxUnitIncrement;
return (newPosition == 0) ? maxUnitIncrement : newPosition;
} else {
return ((currentPosition / maxUnitIncrement) + 1)
* maxUnitIncrement
- currentPosition;
}
}If the image is already on a tick mark boundary, this method returns the number of pixels between ticks. 如果图像已经位于刻度线边界上,则此方法返回刻度之间的像素数。Otherwise, it returns the number of pixels from the current location to the nearest tick.否则,它将返回从当前位置到最近刻度的像素数。
Likewise, the scroll pane calls the client's 同样,每次用户单击轨迹时,滚动窗格调用客户端的getScrollableBlockIncrement method each time the user clicks on the track, but only if the client implements Scrollable. Here's ScrollablePicture's implementation of this method:getScrollableBlockIncrement方法,但仅当客户端实现可滚动时。下面是ScrollablePicture对该方法的实现:
public int getScrollableBlockIncrement(Rectangle visibleRect,
int orientation,
int direction) {
if (orientation == SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL)
return visibleRect.width - maxUnitIncrement;
else
return visibleRect.height - maxUnitIncrement;
}This method returns the height of the visible rectangle minus a tick mark. 此方法返回可见矩形的高度减去刻度线。This behavior is typical, but true if scrolling vertically, otherwise, it's the width.这种行为很典型,但如果垂直滚动,则为真,否则为宽度。A block increment should be slightly smaller than the viewport to leave a little of the previous visible area for context. 块增量应略小于视口,以便为上下文保留一点以前的可见区域。For example, a text area might leave one or two lines of text for context and a table might leave a row or column (depending on the scroll direction).例如,文本区域可能会为上下文保留一行或两行文本,而表格可能会保留行或列(取决于滚动方向)。
ScrollablePicture.java has one more bit of code that's not required by the 还有一段代码是Scrollable interface, but is common in scrollable components: a mouse motion listener that lets the user scroll the picture by dragging from it. Scrollable界面不需要的,但在可滚动组件中很常见:鼠标运动监听器,允许用户通过拖动来滚动图片。The boldface code in the following snippet implements scrolling by dragging:以下代码段中的粗体代码通过拖动实现滚动:
public class ScrollablePicture extends JLabel
implements Scrollable,
MouseMotionListener {
...
public ScrollablePicture(...) {
...
setAutoscrolls(true); //enable synthetic drag events
addMouseMotionListener(this); //handle mouse drags
}
...
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
//The user is dragging us, so scroll!
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(e.getX(), e.getY(), 1, 1);
scrollRectToVisible(r);
}
...
}This snippet scrolls the picture whenever the user drags from the picture to a location outside the picture and pauses. 每当用户从图片拖动到图片之外的位置并暂停时,此代码段将滚动图片。The setAutoscrolls method is defined by JComponent for the purpose of assisting — but not implementing — scrolling by dragging. setAutoscrolls方法由JComponent定义,目的是帮助;但不实现;通过拖动滚动。Setting the autoscrolls property to 将true makes the component fire synthetic mouse-dragged events even when the mouse isn't moving (because it stopped, mid-drag, outside the component). autoscrolls属性设置为true会使组件触发合成鼠标拖动事件,即使鼠标没有移动(因为它在组件外的拖动过程中停止)。It's up to the component's mouse motion listener to listen for these events and react accordingly.由组件的鼠标运动侦听器来侦听这些事件并做出相应的反应。
Sizing a Scroll Pane调整滚动窗格的大小
Unless you explicitly set a scroll pane's preferred size, the scroll pane computes it based on the preferred size of its nine components (the viewport, and, if present, the two scroll bars, the row and column headers, and the four corners). 除非明确设置滚动窗格的首选大小,否则滚动窗格将根据其九个组件(视口、两个滚动条(如果存在)、行标题和列标题以及四个角)的首选大小进行计算。The largest factor, and the one most programmers care about, is the size of the viewport used to display the client.最大的因素,也是大多数程序员关心的因素,是用于显示客户端的视口的大小。
If the client is not scrolling-savvy, then the scroll pane sizes itself so that the client displays at its preferred size. 如果客户端不善于滚动,则滚动窗格会调整自身大小,以便客户端以其首选大小显示。For typical unsavvy clients, this makes the scroll pane redundant. 对于典型的未保存客户端,这会使滚动窗格变得多余。That is, the scroll pane has no scroll bars because the client's preferred size is big enough to display the entire client. 也就是说,滚动窗格没有滚动条,因为客户端的首选大小足以显示整个客户端。In this case, if the client doesn't change size dynamically, you should probably limit the size of the scroll pane by setting its preferred size or the preferred size of its container.在这种情况下,如果客户端不动态更改大小,您可能应该通过设置滚动窗格的首选大小或其容器的首选大小来限制滚动窗格的大小。
If the client is scrolling-savvy, then the scroll pane uses the value returned by the client's 如果客户端能够滚动,则滚动窗格使用客户端的getPreferredScrollableViewportSize method to compute the size of its viewport. getPreferredScrollableViewportSize方法返回的值来计算其视口的大小。Implementations of this method generally report a preferred size for scrolling that's smaller than the component's standard preferred size. 此方法的实现通常报告滚动的首选大小,该大小小于组件的标准首选大小。For example, by default, the value returned by 例如,默认情况下,JList's implementation of getPreferredScrollableViewportSize is just big enough to display eight rows.JList实现getPreferredScrollableViewportSize返回的值刚好足够显示八行。
Scrolling-savvy classes, like lists, tables, text components, and trees, often provide one or more methods that let programmers affect the size returned from 滚动类,如列表、表格、文本组件和树,通常提供一个或多个方法,让程序员影响从getPreferredScrollableViewportSize. getPreferredScrollableViewportSize返回的大小。For example, you can set the number of visible rows in a list or a tree by calling the 例如,可以通过调用setVisibleRowCount method. setVisibleRowCount方法来设置列表或树中的可见行数。The list or tree takes care of figuring out the size needed to display that number of rows.列表或树负责计算显示该行数所需的大小。
Refer to Methods in Other Classes Related to Scrolling for information about scrolling-related methods provided by classes other than 有关JScrollPane以外的类提供的滚动相关方法的信息,请参阅与滚动相关的其他类中的方法。JScrollPane. And remember — if you don't like the value that 并记住—如果您不喜欢getPreferredScrollableViewportSize returns, you can always set the preferred size of the scroll pane or its container.getPreferredScrollableViewportSize返回的值,您可以始终设置滚动窗格或其容器的首选大小。
Dynamically Changing the Client's Size动态更改客户端的大小
Changing the size of a scroll pane's client is a two-step process. 更改滚动窗格客户端的大小需要两个步骤。First, set the client's preferred size. 首先,设置客户端的首选大小。Then, call 然后,在客户端上调用revalidate on the client to let the scroll pane know that it should update itself and its scroll bars. revalidate,让滚动窗格知道它应该更新自身及其滚动条。Let's look at an example.让我们看一个例子。
Here's a picture of an application that changes the client's size whenever the user places a circle whose bounds fall outside of the client's current bounds. 这是一个应用程序的图片,每当用户放置一个边界超出客户端当前边界的圆时,该应用程序就会更改客户端的大小。The program also changes the client's size when the user clears the drawing area:当用户清除绘图区域时,程序还会更改客户端的大小:
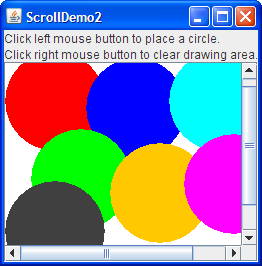
You can find the full source code for this example in 您可以在ScrollDemo2.java, which is based on an example provided by tutorial reader John Vella. ScrollDemo2.java中找到该示例的完整源代码,它基于教程读者John Vella提供的示例。You can run ScrollDemo2 ( download JDK 7 or later).您可以运行ScrollDemo2(下载JDK 7或更高版本)。
Here's the code that changes the drawing area's size when necessary:以下是必要时更改绘图区域大小的代码:
if (changed) {
//Update client's preferred size because
//the area taken up by the graphics has
//gotten larger or smaller (if cleared).
drawingArea.setPreferredSize(/* the new size */);
//Let the scroll pane know to update itself
//and its scroll bars.
drawingArea.revalidate();
}Note that when the client changes size, the scroll bars adjust. 请注意,当客户端更改大小时,滚动条会调整。The scroll pane doesn't resize, nor does the viewport.滚动窗格不调整大小,视口也不调整大小。
Refer to 有关客户端对象更改大小的另一个示例,请参阅SplitPaneDemo for another example in which the client object changes size.SplitPaneDemo。
The Scroll Pane API滚动窗格API
The following tables list the commonly used scroll-related constructors and methods. 下表列出了常用的与滚动相关的构造函数和方法。Other methods you are most likely to invoke on a 您最可能在JScrollPane object are those such as setPreferredSize that its superclasses provide. JScrollPane对象上调用的其他方法是其超类提供的setPreferredSize。See The JComponent API for tables of commonly used inherited methods.有关常用继承方法的表,请参阅JComponent API。
The API for using scroll panes falls into these categories:使用滚动窗格的API分为以下几类:
Setting Up the Scroll Pane设置滚动窗格Decorating the Scroll Pane装饰滚动窗格Implementing a Scrolling-Savvy Client实现具有滚动能力的客户端Methods in Other Classes Related to Scrolling与滚动相关的其他类中的方法
JScrollPane()JScrollPane(Component)JScrollPane(int, int)JScrollPane(Component, int, int) |
Component parameter, when present, sets the scroll pane's client. Component参数(如果存在)设置滚动窗格的客户端。int parameters, when present, set the vertical and horizontal scroll bar policies (respectively).int参数(如果存在)分别设置垂直和水平滚动条策略。 |
void setViewportView(Component) |
|
void setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(int)int getVerticalScrollBarPolicy() |
ScrollPaneConstants defines three values for specifying this policy: VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED (the default), VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS, and VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER.ScrollPaneConstants定义了三个用于指定此策略的值:VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED(默认值)、VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS和VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER。 |
void setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(int)int getHorizontalScrollBarPolicy() |
ScrollPaneConstants defines three values for specifying this policy: HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED (the default), HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS, and HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER.ScrollPaneConstants定义了三个用于指定此策略的值:HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED(默认值)、HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_ALWAYS和HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_NEVER。 |
void setViewportBorder(Border)Border getViewportBorder() |
|
boolean isWheelScrollingEnabled() |
void setColumnHeaderView(Component)void setRowHeaderView(Component) |
|
void setCorner(String, Component)Component getCorner(String) |
int parameter specifies which corner and must be one of the following constants defined in ScrollPaneConstants: UPPER_LEFT_CORNER, UPPER_RIGHT_CORNER, LOWER_LEFT_CORNER, LOWER_RIGHT_CORNER, LOWER_LEADING_CORNER, LOWER_TRAILING_CORNER, UPPER_LEADING_CORNER, and UPPER_TRAILING_CORNER.int参数指定哪个角点,并且必须是ScrollPaneConstants中定义的以下常量之一:UPPER_LEFT_CORNER、UPPER_RIGHT_CORNER、LOWER_LEFT_CORNER、LOWER_RIGHT_CORNER、LOWER_LEADING_CORNER、LOWER_TRAILING_CORNER、UPPER_LEADING_CORNER和UPPER_TRAILING_CORNER。 |
int getScrollableUnitIncrement(Rectangle, int, int)int getScrollableBlockIncrement(Rectangle, int, int)Scrollable interface)Scrollable界面需要) |
Rectangle parameter is the bounds of the currently visible rectangle. Rectangle参数是当前可见矩形的边界。int parameter is either SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL or SwingConstants.VERTICAL depending on what scroll bar the user clicked on. int参数是SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL或SwingConstants.VERTICAL,具体取决于用户单击的滚动条。int parameter indicates which direction to scroll. int参数指示滚动的方向。 |
Dimension getPreferredScrollableViewportSize()Scrollable interface)Scrollable界面需要) |
getPreferredSize.getPreferredSize。 |
boolean getScrollableTracksViewportWidth()boolean getScrollableTracksViewportHeight()(required by the Scrollable interface) |
true from either of these methods effectively disallows horizontal or vertical scrolling (respectively).true,有效地禁止水平或垂直滚动(分别)。 |
void setAutoscrolls(boolean)(in JComponent) |
false, but many scrollable components such as JTable and custom components set the value to true.false,但许多可滚动组件(如JTable和自定义组件)将该值设置为true。 |
void scrollRectToVisible(Rectangle)(in JComponent) |
|
void setVisibleRowCount(int)int getVisibleRowCount()(in JList) |
getPreferredScrollableViewportSize method uses the visible row count to compute its return value.getPreferredScrollableViewportSize方法使用可见行计数来计算其返回值。 |
void ensureIndexIsVisible(int)(in JList) |
scrollRectToVisible and works only if the list is in a container, such as a scroll pane, that supports scrolling.scrollRectToVisible,仅当列表位于支持滚动的容器(如滚动窗格)中时才有效。 |
void setVisibleRowCount(int)int getVisibleRowCount()(in JTree) |
getPreferredScrollableViewportSize method uses the visible row count to compute its return value.getPreferredScrollableViewportSize方法使用可见行计数来计算其返回值。 |
void scrollPathToVisible(TreePath)void scrollRowToVisible(int)(in JTree) |
scrollRectToVisible and work only if the tree is in a container, such as a scroll pane, that supports scrolling.scrollRectToVisible,仅当树位于支持滚动的容器(如滚动窗格)中时才起作用。 |
void setScrollsOnExpand(boolean)boolean getScrollsOnExpand()(in JTree) |
True。此功能仅在树位于支持滚动的容器(如滚动窗格)中时有效。 |
void setPreferredScrollableViewportSize(Dimension)(in JTable) |
getPreferredScrollableViewportSize.getPreferredScrollableViewportSize返回的值。 |
Examples that Use Scroll Panes使用滚动窗格的示例
This table shows the examples that use 下表显示了使用JScrollPane and where those examples are described.JScrollPane的示例以及这些示例的描述位置。
ToolBarDemo |
||
ScrollDemo |
||
ScrollDemo2 |
||
SplitPaneDemo |
||
TableDemo |
||
TextSamplerDemo |
||
TreeDemo |
If you are programming in JavaFX, see Scroll Pane.如果您使用JavaFX编程,请参阅滚动窗格。