Lesson: Language Basics
Section: Variables
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
Arrays数组
An array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single type.数组是一个容器对象,它包含固定数量的单一类型的值。The length of an array is established when the array is created.数组的长度是在创建数组时确定的。After creation, its length is fixed.创建后,其长度是固定的。You have seen an example of arrays already, in the 您已经在“Hello World!”的main method of the "Hello World!" application.main方法中看到了一个数组示例应用This section discusses arrays in greater detail.本节将更详细地讨论数组。
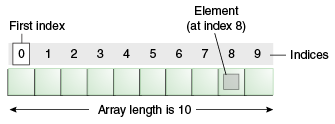
An array of 10 elements.由10个元素组成的数组。
Each item in an array is called an element, and each element is accessed by its numerical index.数组中的每个项都称为元素,每个元素都通过其数字索引进行访问。As shown in the preceding illustration, numbering begins with 0.如上图所示,编号从0开始。The 9th element, for example, would therefore be accessed at index 8.例如,第9个元素将在索引8处访问。
The following program, 下面的程序ArrayDemo, creates an array of integers, puts some values in the array, and prints each value to standard output.ArrayDemo创建一个整数数组,在数组中放入一些值,并将每个值打印到标准输出。
class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declares an array of integers
int[] anArray;
// allocates memory for 10 integers
anArray = new int[10];
// initialize first element
anArray[0] = 100;
// initialize second element
anArray[1] = 200;
// and so forth
anArray[2] = 300;
anArray[3] = 400;
anArray[4] = 500;
anArray[5] = 600;
anArray[6] = 700;
anArray[7] = 800;
anArray[8] = 900;
anArray[9] = 1000;
System.out.println("Element at index 0: "
+ anArray[0]);
System.out.println("Element at index 1: "
+ anArray[1]);
System.out.println("Element at index 2: "
+ anArray[2]);
System.out.println("Element at index 3: "
+ anArray[3]);
System.out.println("Element at index 4: "
+ anArray[4]);
System.out.println("Element at index 5: "
+ anArray[5]);
System.out.println("Element at index 6: "
+ anArray[6]);
System.out.println("Element at index 7: "
+ anArray[7]);
System.out.println("Element at index 8: "
+ anArray[8]);
System.out.println("Element at index 9: "
+ anArray[9]);
}
}The output from this program is:该程序的输出为:
Element at index 0: 100 Element at index 1: 200 Element at index 2: 300 Element at index 3: 400 Element at index 4: 500 Element at index 5: 600 Element at index 6: 700 Element at index 7: 800 Element at index 8: 900 Element at index 9: 1000
In a real-world programming situation, you would probably use one of the supported looping constructs to iterate through each element of the array, rather than write each line individually as in the preceding example.在现实编程环境中,您可能会使用一种受支持的循环构造来迭代数组的每个元素,而不是像前面的示例中那样单独编写每一行。However, the example clearly illustrates the array syntax.但是,该示例清楚地说明了数组语法。You will learn about the various looping constructs (您将在控制流部分中了解各种循环构造(for, while, and do-while) in the Control Flow section.for、while和do-while)。
Declaring a Variable to Refer to an Array声明引用数组的变量
The preceding program declares an array (named 前面的程序使用以下代码行声明一个数组(名为anArray) with the following line of code:anArray):
// declares an array of integers int[] anArray;
Like declarations for variables of other types, an array declaration has two components: the array's type and the array's name.与其他类型变量的声明一样,数组声明有两个组件:数组的类型和数组的名称。An array's type is written as 数组的类型写为type[], where type is the data type of the contained elements; the brackets are special symbols indicating that this variable holds an array.type[],其中type是所包含元素的数据类型;括号是表示此变量包含数组的特殊符号。The size of the array is not part of its type (which is why the brackets are empty).数组的大小不是其类型的一部分(这就是括号为空的原因)。An array's name can be anything you want, provided that it follows the rules and conventions as previously discussed in the naming section.数组的名称可以是您想要的任何名称,只要它遵循前面在命名部分中讨论的规则和约定。As with variables of other types, the declaration does not actually create an array; it simply tells the compiler that this variable will hold an array of the specified type.与其他类型的变量一样,声明并不实际创建数组;它只是告诉编译器该变量将保存指定类型的数组。
Similarly, you can declare arrays of other types:类似地,您可以声明其他类型的数组:
byte[] anArrayOfBytes; short[] anArrayOfShorts; long[] anArrayOfLongs; float[] anArrayOfFloats; double[] anArrayOfDoubles; boolean[] anArrayOfBooleans; char[] anArrayOfChars; String[] anArrayOfStrings;
You can also place the brackets after the array's name:也可以将括号放在数组名称之后:
// this form is discouraged float anArrayOfFloats[];
However, convention discourages this form; the brackets identify the array type and should appear with the type designation.然而,传统不鼓励这种形式;括号用于标识数组类型,并应与类型名称一起出现。
Creating, Initializing, and Accessing an Array创建、初始化和访问数组
One way to create an array is with the 创建数组的一种方法是使用new operator.new运算符。The next statement in the ArrayDemo program allocates an array with enough memory for 10 integer elements and assigns the array to the anArray variable.ArrayDemo程序中的下一条语句为10个整数元素分配一个具有足够内存的数组,并将该数组分配给anArray变量。
// create an array of integers anArray = new int[10];
If this statement is missing, then the compiler prints an error like the following, and compilation fails:如果缺少此语句,编译器将打印如下错误,编译失败:
ArrayDemo.java:4: Variable anArray may not have been initialized.
The next few lines assign values to each element of the array:接下来的几行为数组的每个元素指定值:
anArray[0] = 100; // initialize first element anArray[1] = 200; // initialize second element anArray[2] = 300; // and so forth
Each array element is accessed by its numerical index:每个数组元素通过其数字索引进行访问:
System.out.println("Element 1 at index 0: " + anArray[0]);
System.out.println("Element 2 at index 1: " + anArray[1]);
System.out.println("Element 3 at index 2: " + anArray[2]);Alternatively, you can use the shortcut syntax to create and initialize an array:或者,可以使用快捷方式语法创建和初始化数组:
int[] anArray = {
100, 200, 300,
400, 500, 600,
700, 800, 900, 1000
};Here the length of the array is determined by the number of values provided between braces and separated by commas.这里,数组的长度由大括号之间提供的值的数量决定,并用逗号分隔。
You can also declare an array of arrays (also known as a multidimensional array) by using two or more sets of brackets, such as 您还可以通过使用两组或多组括号(例如String[][] names.String[][] names)来声明数组数组(也称为多维数组)。Each element, therefore, must be accessed by a corresponding number of index values.因此,每个元素必须由相应数量的索引值访问。
In the Java programming language, a multidimensional array is an array whose components are themselves arrays.在Java编程语言中,多维数组是一种数组,其组件本身就是数组。This is unlike arrays in C or Fortran.这与C或Fortran中的数组不同。A consequence of this is that the rows are allowed to vary in length, as shown in the following 这样做的结果是允许行的长度发生变化,如以下MultiDimArrayDemo program:MultiDimArrayDemo程序所示:
class MultiDimArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] names = {
{"Mr. ", "Mrs. ", "Ms. "},
{"Smith", "Jones"}
};
// Mr. Smith
System.out.println(names[0][0] + names[1][0]);
// Ms. Jones
System.out.println(names[0][2] + names[1][1]);
}
}The output from this program is:该程序的输出为:
Mr. Smith Ms. Jones
Finally, you can use the built-in 最后,您可以使用内置的length property to determine the size of any array.length属性来确定任何数组的大小。The following code prints the array's size to standard output:以下代码将数组大小打印为标准输出:
System.out.println(anArray.length);
Copying Arrays复制数组
The System class has an arraycopy method that you can use to efficiently copy data from one array into another:System类有一个arraycopy方法,可用于将数据从一个数组高效复制到另一个数组:
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos, int length)The two 这两个Object arguments specify the array to copy from and the array to copy to.Object参数指定要从中复制的数组和要复制到的数组。The three 三个int arguments specify the starting position in the source array, the starting position in the destination array, and the number of array elements to copy.int参数指定源数组中的起始位置、目标数组中的起始位置以及要复制的数组元素数。
The following program, 下面的程序ArrayCopyDemo, declares an array of String elements.ArrayCopyDemo声明了一个字符串元素数组。It uses the 它使用System.arraycopy method to copy a subsequence of array components into a second array:System.arraycopy方法将数组组件的子序列复制到第二个数组中:
class ArrayCopyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] copyFrom = {
"Affogato", "Americano", "Cappuccino", "Corretto", "Cortado",
"Doppio", "Espresso", "Frappucino", "Freddo", "Lungo", "Macchiato",
"Marocchino", "Ristretto" };
String[] copyTo = new String[7];
System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2, copyTo, 0, 7);
for (String coffee : copyTo) {
System.out.print(coffee + " ");
}
}
}The output from this program is:该程序的输出为:
Cappuccino Corretto Cortado Doppio Espresso Frappucino Freddo
Array Manipulations数组操作
Arrays are a powerful and useful concept used in programming.数组是编程中使用的一个强大而有用的概念。Java SE provides methods to perform some of the most common manipulations related to arrays.JavaSE提供了一些方法来执行与数组相关的一些最常见的操作。For instance, the 例如,ArrayCopyDemo example uses the arraycopy method of the System class instead of manually iterating through the elements of the source array and placing each one into the destination array.ArrayCopyDemo示例使用System类的arraycopy方法,而不是手动迭代源数组的元素并将每个元素放入目标数组。This is performed behind the scenes, enabling the developer to use just one line of code to call the method.这是在后台执行的,使开发人员能够只使用一行代码来调用该方法。
For your convenience, Java SE provides several methods for performing array manipulations (common tasks, such as copying, sorting and searching arrays) in the java.util.Arrays class.为了方便起见,Java SE提供了几种方法来执行java.util.Arrays类中的数组操作(常见任务,如复制、排序和搜索数组)。For instance, the previous example can be modified to use the 例如,前面的示例可以修改为使用copyOfRange method of the java.util.Arrays class, as you can see in the ArrayCopyOfDemo example.java.util.Arrays类的copyOfRange方法,正如您在ArrayCopyOfDemo示例中看到的那样。The difference is that using the 不同之处在于,使用copyOfRange method does not require you to create the destination array before calling the method, because the destination array is returned by the method:copyOfRange方法不需要在调用该方法之前创建目标数组,因为目标数组由该方法返回:
class ArrayCopyOfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] copyFrom = {
"Affogato", "Americano", "Cappuccino", "Corretto", "Cortado",
"Doppio", "Espresso", "Frappucino", "Freddo", "Lungo", "Macchiato",
"Marocchino", "Ristretto" };
String[] copyTo = java.util.Arrays.copyOfRange(copyFrom, 2, 9);
for (String coffee : copyTo) {
System.out.print(coffee + " ");
}
}
}As you can see, the output from this program is the same, although it requires fewer lines of code.正如您所看到的,这个程序的输出是相同的,尽管它需要更少的代码行。Note that the second parameter of the 请注意,copyOfRange method is the initial index of the range to be copied, inclusively, while the third parameter is the final index of the range to be copied, exclusively.copyOfRange方法的第二个参数是要复制的范围的初始索引(包括),而第三个参数是要复制的范围的最终索引(排除)。In this example, the range to be copied does not include the array element at index 9 (which contains the string 在本例中,要复制的范围不包括索引9处的数组元素(其中包含字符串Lungo).Lungo)。
Some other useful operations provided by methods in the java.util.Arrays class are:java.util.Arrays类中的方法提供的一些其他有用操作包括:
Searching an array for a specific value to get the index at which it is placed (the在数组中搜索特定值以获取放置该值的索引(binarySearchmethod).binarySearch方法)。Comparing two arrays to determine if they are equal or not (the比较两个数组以确定它们是否相等(equalsmethod).equals方法)。Filling an array to place a specific value at each index (the填充数组以在每个索引处放置特定值(fillmethod).fill方法)。Sorting an array into ascending order.将数组按升序排序。This can be done either sequentially, using the这可以使用sortmethod, or concurrently, using theparallelSortmethod introduced in Java SE 8.sort方法按顺序完成,也可以同时使用Java SE 8中引入的parallelSort方法完成。Parallel sorting of large arrays on multiprocessor systems is faster than sequential array sorting.在多处理器系统上,大型阵列的并行排序比顺序阵列排序快。Creating a stream that uses an array as its source (the创建使用数组作为源的流(streammethod).stream方法)。For example, the following statement prints the contents of the例如,以下语句以与上一示例相同的方式打印copyToarray in the same way as in the previous example:copyTo数组的内容:java.util.Arrays.stream(copyTo).map(coffee -> coffee + " ").forEach(System.out::print);
See Aggregate Operations for more information about streams.有关流的更多信息,请参阅聚合操作。Converting an array to a string.将数组转换为字符串。ThetoStringmethod converts each element of the array to a string, separates them with commas, then surrounds them with brackets.toString方法将数组的每个元素转换为字符串,用逗号分隔,然后用括号括起来。For example, the following statement converts the例如,以下语句将copyToarray to a string and prints it:copyTo数组转换为字符串并打印它:System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(copyTo));
This statement prints the following:此语句打印以下内容:[Cappuccino, Corretto, Cortado, Doppio, Espresso, Frappucino, Freddo]