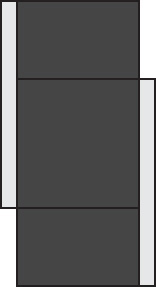
FIGURE 6-1 The UNION operator.UNION运算符。
Set operators are operators that combine rows from two query result sets (or multisets). 集运算符是组合两个查询结果集(或多集)中的行的运算符。Some of the operators remove duplicates from the result, and hence return a set, whereas others don't, and hence return a multiset. 有些运算符从结果中删除重复项,因此返回一个集合,而另一些运算符则不删除,因此返回一个多集合。T-SQL supports the following operators: T-SQL支持以下运算符:UNION, UNION ALL, INTERSECT, and EXCEPT. UNION、UNION ALL、INTERSECT和EXCEPT。In this chapter, I first introduce the general form and requirements of these operators, and then I describe each operator in detail.在本章中,我首先介绍这些运算符的一般形式和要求,然后详细描述每个运算符。
The general form of a query with a set operator is as follows:使用集合运算符的查询的一般形式如下:
Input Query1
<set_operator>
Input Query2
[ORDER BY ...];
A set operator compares complete rows between the results of the two input queries involved. set运算符比较两个输入查询结果之间的完整行。Whether a row will be returned in the result of the operator depends on the outcome of the comparison and the operator used. 运算符的结果中是否返回一行取决于比较结果和使用的运算符。Because a set operator expects multisets as inputs, the two queries involved cannot have 因为集合运算符需要多个集合作为输入,所以所涉及的两个查询不能包含ORDER BY clauses. ORDER BY子句。Remember that a query with an 记住,带有ORDER BY clause does not return a multiset—it returns a cursor. ORDER BY子句的查询不会返回多集,而是返回一个游标。However, although the queries involved cannot have 但是,尽管所涉及的查询不能包含ORDER BY clauses, you can optionally add an ORDER BY clause to the result of the operator. ORDER BY子句,但可以选择向运算符的结果中添加ORDER BY子句。If you're wondering how you apply a set operator to queries with 如果您想知道如何将set运算符应用于带有TOP and OFFSET-FETCH filters, I'll get to this later in the chapter in the section “Circumventing unsupported logical phases.”TOP和OFFSET-FETCH筛选器的查询,我将在“绕过不支持的逻辑阶段”一节的后面一章中讨论这一点。
In terms of logical-query processing, each of the individual queries can have all logical-query processing phases except for a presentation 就逻辑查询处理而言,每个单独的查询都可以有所有的逻辑查询处理阶段,除了外观ORDER BY, as I just explained. ORDER BY,正如我刚才解释的那样。The operator is applied to the results of the two queries, and the outer 运算符应用于两个查询的结果,外部ORDER BY clause (if one exists) is applied to the result of the operator.ORDER BY子句(如果存在)应用于运算符的结果。
The two input queries must produce results with the same number of columns, and corresponding columns must have compatible data types. 两个输入查询必须生成具有相同列数的结果,并且相应的列必须具有兼容的数据类型。By 所谓compatible data types, I mean that the data type that is lower in terms of data-type precedence must be implicitly convertible to the higher data type. 兼容数据类型,我的意思是,数据类型优先级较低的数据类型必须隐式转换为较高的数据类型。Of course, you also can explicitly convert the data type of a column in one query to the data type of the corresponding column in the other query using the 当然,还可以使用CAST or CONVERT function.CAST或CONVERT函数将一个查询中的列的数据类型显式转换为另一个查询中相应列的数据类型。
The names of the columns in the result are determined by the first query; therefore, if you need to assign aliases to result columns, you should assign those in the first query.结果中列的名称由第一个查询确定;因此,如果需要为结果列指定别名,则应在第一个查询中指定别名。
Interestingly, when a set operator compares rows between the two inputs, it doesn't use an equality operator; rather, it uses a so-called 有趣的是,当set运算符比较两个输入之间的行时,它不使用相等运算符;相反,它使用了一个所谓的distinct predicate. 独立谓词。This predicate produces a 当比较两个空值时,该谓词生成TRUE when comparing two NULLs. TRUE。I'll demonstrate the importance of this point later in the chapter.我将在本章后面部分演示这一点的重要性。
Standard SQL supports two “flavors” of each operator—标准SQL支持每个运算符的两种“风格”——DISTINCT (the default) and ALL. DISTINCT(默认)和ALL。The DISTINCT flavor eliminates duplicates and returns a set. DISTINCT风格消除重复项并返回一个集合。ALL doesn't attempt to remove duplicates and therefore returns a multiset. ALL不会尝试删除重复项,因此会返回多集。All three operators in T-SQL support an implicit distinct version, but only the T-SQL中的所有三个运算符都支持隐式UNION operator supports the ALL version. DISTINCT版本,但只有UNION运算符支持ALL版本。In terms of syntax, T-SQL doesn't allow you to specify the 在语法方面,T-SQL不允许显式指定DISTINCT clause explicitly. DISTINCT子句。Instead, it's implied when you don't specify 相反,当您没有指定ALL. ALL时,它是隐含的。I'll provide alternatives to the missing 我将在本章后面的“INTERSECT ALL and EXCEPT ALL operators in the “The INTERSECT ALL operator” and “The EXCEPT ALL operator” sections later in this chapter.INTERSECT ALL运算符”和“EXCEPT ALL运算符”部分中提供缺少的INTERSECT ALL运算符和EXCEPT ALL运算符的替代方法。
UNION operatorUNION运算符The UNION operator unifies the results of two input queries. UNION运算符统一两个输入查询的结果。If a row appears in any of the input sets, it will appear in the result of the 如果一行出现在任何输入集中,它将出现在UNION operator. UNION运算符的结果中。T-SQL supports both the T-SQL支持UNION ALL and UNION (implicit DISTINCT) flavors of the UNION operator.UNION运算符的UNION ALL和UNION(隐式DISTINCT)风格。
Figure 6-1 illustrates the Figure 6-1显示了UNION operator. UNION运算符。The shaded area represents the result of the operator. 阴影区域表示运算符的结果。The nonshaded areas reflect the fact that the operator doesn't have to include all attributes of the original relations.非阴影区域反映了一个事实,即运算符不必包含原始关系的所有属性。

FIGURE 6-1 The UNION operator.UNION运算符。
UNION ALL operatorUNION ALL运算符The UNION ALL operator unifies the two input query results without attempting to remove duplicates from the result. UNION ALL运算符统一两个输入查询结果,而不尝试从结果中删除重复项。Assuming that 假设Query1 returns m rows and Query2 returns n rows, Query1 UNION ALL Query2 returns m + n rows.Query1返回m行,Query2返回n行,Query1 UNION ALL Query2返回m+n行。
For example, the following code uses the 例如,以下代码使用UNION ALL operator to unify employee locations and customer locations:UNION ALL运算符统一员工位置和客户位置:
USE TSQLV4;
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees
UNION ALL
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers;
The result has 100 rows—9 from the 结果有100行——Employees table and 91 from the Customers table—and is shown here in abbreviated form:Employees表中有9行,Customers表中有91行,以下以缩写形式显示:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
USA WA Seattle
USA WA Tacoma
USA WA Kirkland
USA WA Redmond
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
...
Finland NULL Oulu
Brazil SP Resende
USA WA Seattle
Finland NULL Helsinki
Poland NULL Warszawa
(100 row(s) affected)
Because 因为UNION ALL doesn't eliminate duplicates, the result is a multiset and not a set. UNION ALL不能消除重复项,所以结果是一个多集,而不是一个集。The same row can appear multiple times in the result, as is the case with 同一行可以在结果中多次出现,这与此查询结果中的(UK, NULL, London) in the result of this query.(UK, NULL, London)一样。
UNION (DISTINCT) operatorUNION(DISTINCT)运算符The UNION (implicit DISTINCT) operator unifies the results of the two queries and eliminates duplicates. UNION(隐式DISTINCT)运算符统一两个查询的结果并消除重复项。Note that if a row appears in both input sets, it will appear only once in the result; in other words, the result is a set and not a multiset.请注意,如果一行出现在两个输入集中,它将在结果中只出现一次;换句话说,结果是一个集合而不是多集合。
For example, the following code returns distinct locations that are either employee locations or customer locations:例如,以下代码返回不同的位置,即员工位置或客户位置:
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees
UNION
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers;
This code returns 71 distinct rows (unlike the 100 rows in the result with the duplicates), as shown here in abbreviated form:此代码返回71个不同的行(不同于结果中包含重复项的100行),如以下缩略形式所示:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
Argentina NULL Buenos Aires
Austria NULL Graz
Austria NULL Salzburg
Belgium NULL Bruxelles
Belgium NULL Charleroi
...
USA WY Lander
Venezuela DF Caracas
Venezuela Lara Barquisimeto
Venezuela Nueva Esparta I. de Margarita
Venezuela Táchira San Cristóbal
(71 row(s) affected)
So when should you use 那么什么时候应该使用UNION ALL and when should you use UNION? UNION ALL,什么时候应该使用UNION?If duplicates are possible in the unified result and you do not need to return them, use 如果统一结果中可能存在重复项,并且您不需要返回它们,请使用UNION. Otherwise, use UNION ALL. UNION。否则,使用UNION ALL。If duplicates cannot exist when unifying the inputs, 如果统一输入时不存在重复项,UNION and UNION ALL will return the same result. UNION和UNION ALL将返回相同的结果。However, in such a case I recommend you use 但是,在这种情况下,我建议您使用UNION ALL so that you don't pay the unnecessary performance penalty related to checking for duplicates.UNION ALL,这样您就不会因为检查副本而支付不必要的性能损失。
INTERSECT OperatorINTERSECT运算符The INTERSECT operator returns only the rows that are common to the results of the two input queries. INTERSECT运算符只返回两个输入查询结果的公用行。Figure 6-2 illustrates this operator.Figure 6-2显示了该运算符。

FIGURE 6-2 The INTERSECT operator.INTERSECT运算符。
INTERSECT (DISTINCT) operatorINTERSECT(DISTINCT)运算符The INTERSECT operator (implied DISTINCT) returns only distinct rows that appear in both input query results. INTERSECT运算符(隐含的DISTINCT)只返回出现在两个输入查询结果中的不同行。As long as a row appears at least once in both query results, it's returned only once in the operator's result.只要一行在两个查询结果中至少出现一次,它在运算符的结果中只返回一次。
For example, the following code returns distinct locations that are both employee locations and customer locations:例如,以下代码返回不同的位置,即员工位置和客户位置:
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees
INTERSECT
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers;
This query returns the following output:此查询返回以下输出:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
UK NULL London
USA WA Kirkland
USA WA Seattle
I mentioned earlier that when these operators compare rows, they use an implied distinct predicate, which returns a 我之前提到过,当这些运算符比较行时,它们使用一个隐含的独立谓词,当比较两个TRUE when comparing two NULLs. NULL值时,该谓词返回TRUE。For example, observe that the location 例如,观察交集结果中出现的位置(UK, NULL, London) appears in the result of the intersection. (UK, NULL, London)。If instead of using the 如果不使用INTERSECT operator you use an alternative tool like an inner join or a correlated subquery, you need to add special treatment for NULLs—for example, assuming the alias E for Employees and C for Customers, using the predicate E.region = C.region OR (E.region IS NULL AND C.region IS NULL). INTERSECT运算符,而是使用内部联接或相关子查询之类的替代工具,则需要为NULL添加特殊处理,例如,假设Employees的别名为E,Customers的别名为C,使用谓词E.region = C.region OR (E.region IS NULL AND C.region IS NULL)。Using the 使用INTERSECT operator, the solution is much simpler—you don't need to explicitly compare corresponding attributes, and you don't need to add special treatment for NULLs.INTERSECT运算符,解决方案简单得多——不需要显式比较相应的属性,也不需要为NULL值添加特殊处理。
INTERSECT ALL operatorINTERSECT ALL运算符I provide this section as optional reading for those who feel comfortable with the material covered so far in this chapter. 对于那些对本章到目前为止所涵盖的内容感到满意的人,我提供本节作为可选阅读。Standard SQL supports an 标准SQL支持ALL flavor of the INTERSECT operator, but this flavor has not been implemented in T-SQL. INTERSECT运算符的全风格,但这种风格尚未在T-SQL中实现。However, you can write your own logical equivalent with T-SQL.但是,您可以使用T-SQL编写自己的逻辑等价物。
Remember the meaning of the 记住ALL keyword in the UNION ALL operator: it returns all duplicate rows. UNION ALL运算符中ALL关键字的含义:它返回所有重复的行。Similarly, the keyword 类似地,ALL in the INTERSECT ALL operator means that duplicate intersections will not be removed. INTERSECT ALL运算符中的关键字ALL意味着不会删除重复的交点。INTERSECT ALL returns the number of duplicate rows matching the lower of the counts in both input multisets. INTERSECT ALL返回与两个输入多重集中的计数中较低者匹配的重复行数。It's as if this operator looks for matches for each occurrence of each row. 这就好像这个运算符为每行的每一次出现寻找匹配项一样。If there are 如果第一个输入多重集中有x occurrences of a row R in the first input multiset and y occurrences of R in the second, R appears minimum(x, y) times in the result. x个行R,第二个输入多重集中有y个行R,则R在结果中出现minimum(x, y)次。For example, the location 例如,地点(UK, NULL, London) appears four times in Employees and six times in Customers; hence, INTERSECT ALL returns four occurrences in the output.(UK, NULL, London)在Employees中出现四次,在Customers中出现六次;因此,INTERSECT ALL在输出中返回四个匹配项。
Even though T-SQL does not support a built-in 尽管T-SQL不支持内置的INTERSECT ALL operator, you can write your own alternative solution that produces the same result. INTERSECT ALL运算符,但您可以编写自己的替代解决方案来产生相同的结果。You can use the 可以使用ROW_NUMBER function to number the occurrences of each row in each input query. ROW_NUMBER函数对每个输入查询中出现的每一行进行编号。To achieve this, specify all participating attributes in the 要实现这一点,请在函数的PARTITION BY clause of the function, and use (SELECT <constant>) in the ORDER BY clause of the function to indicate that order doesn't matter. PARTITION BY子句中指定所有参与属性,并在函数的ORDER BY子句中使用(SELECT <constant>)来表示顺序无关紧要。Window functions, including the 窗口函数,包括ROW_NUMBER function, are covered in Chapter 7, “Beyond the fundamentals of querying.”ROW_NUMBER函数,将在第7章“超越查询的基本原理”中介绍。
 Tip
Tip
A window order clause is mandatory in window ranking functions like 在诸如ROW_NUMBER. ROW_NUMBER之类的窗口排序函数中,窗口顺序子句是必需的。As a trick, when you don't care about ordering, use 作为一个技巧,当您不关心排序时,使用ORDER BY (SELECT <constant>) as the window order clause. ORDER BY (SELECT <constant>)作为窗口排序子句。Microsoft SQL Server realizes in such a case that order doesn't matter.在这种情况下,Microsoft SQL Server意识到顺序并不重要。
Then apply the 然后使用INTERSECT operator between the two queries with the ROW_NUMBER function. ROW_NUMBER函数在两个查询之间应用INTERSECT运算符。Because the occurrences of the rows are numbered, the intersection is based on the row numbers in addition to the original attributes. 因为行的引用是编号的,所以除了原始属性外,交点还基于行编号。For example, in the 例如,在Employees table the four occurrences of the location (UK, NULL, London) are numbered 1 through 4. Employees表中,位置的四个匹配项(UK, NULL, London)编号为1到4。In the 在Customers table the six occurrences of the same row are numbered 1 through 6. Customers表中,同一行的六个匹配项编号为1到6。Occurrences 1 through 4 intersect between the two.引用1到4在这两个引用之间相交。
Here's the complete solution code:以下是完整的解决方案代码:
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY country, region, city
ORDER BY (SELECT 0)) AS rownum,
country, region, city
FROM HR.Employees
INTERSECT
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY country, region, city
ORDER BY (SELECT 0)),
country, region, city
FROM Sales.Customers;
This code produces the following output.此代码生成以下输出。
rownum country region city
-------------------- --------------- --------------- ---------------
1 UK NULL London
1 USA WA Kirkland
1 USA WA Seattle
2 UK NULL London
3 UK NULL London
4 UK NULL London
The standard 标准的INTERSECT ALL operator is not supposed to return any row numbers. INTERSECT ALL运算符不应返回任何行号。To exclude those from the output, define a table expression based on this query, and in the outer query select only the attributes you want to return. 要从输出中排除这些属性,请基于此查询定义一个表表达式,并在外部查询中仅选择要返回的属性。Here's the complete solution code:以下是完整的解决方案代码:
WITH INTERSECT_ALL
AS
(
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY country, region, city
ORDER BY (SELECT 0)) AS rownum,
country, region, city
FROM HR.Employees
INTERSECT
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY country, region, city
ORDER BY (SELECT 0)),
country, region, city
FROM Sales.Customers
)
SELECT country, region, city
FROM INTERSECT_ALL;
This code generates the following output:此代码生成以下输出:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
UK NULL London
USA WA Kirkland
USA WA Seattle
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
EXCEPT operatorEXCEPT运算符The EXCEPT operator implements set differences. EXCEPT运算符实现差集。It operates on the results of two input queries and returns rows that appear in the first input but not the second. 它对两个输入查询的结果进行操作,并返回第一个输入中出现但第二个输入中没有出现的行。Figure 6-3 illustrates this operator.Figure 6-3显示了该运算符。

FIGURE 6-3 The EXCEPT operator.EXCEPT运算符
EXCEPT (DISTINCT) operatorEXCEPT(DISTINCT)运算符The EXCEPT operator (implied DISTINCT) returns only distinct rows that appear in the first set but not the second. EXCEPT运算符(隐含的DISTINCT)只返回出现在第一个集合中但不出现在第二个集合中的不同行。In other words, a row is returned once in the output as long as it appears at least once in the first input multiset and zero times in the second. 换句话说,一行在输出中返回一次,只要它在第一个输入多集中至少出现一次,在第二个输入多集中至少出现零次。Note that unlike 注意,与UNION and INTERSECT, EXCEPT is noncummutative; that is, the order in which you specify the two input queries matters.UNION和INTERSECT不同,EXCEPT是非求和的;也就是说,指定两个输入查询的顺序很重要。
For example, the following code returns distinct locations that are employee locations but not customer locations:例如,以下代码返回不同的位置,这些位置是员工位置,但不是客户位置:
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees
EXCEPT
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers;
This query returns the following two locations:此查询返回以下两个位置:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
USA WA Redmond
USA WA Tacoma
The following query returns distinct locations that are customer locations but not employee locations:以下查询返回不同的位置,这些位置是客户位置,但不是员工位置:
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers
EXCEPT
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees;
This query returns 66 locations, shown here in abbreviated form:此查询返回66个位置,以缩写形式显示:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
Argentina NULL Buenos Aires
Austria NULL Graz
Austria NULL Salzburg
Belgium NULL Bruxelles
Belgium NULL Charleroi
...
USA WY Lander
Venezuela DF Caracas
Venezuela Lara Barquisimeto
Venezuela Nueva Esparta I. de Margarita
Venezuela Táchira San Cristóbal
(66 row(s) affected)
Naturally, there are alternatives to the 当然,除了EXCEPT operator. EXCEPT运算符,还有其他选择。One is an outer join that filters only outer rows, and another is to use the 一种是只筛选外部行的外部联接,另一种是使用NOT EXISTS predicate. NOT EXISTS谓词。However, recall that with set operators the comparison between corresponding columns is implied, and also when comparing two 然而,请记住,使用集合运算符时,对应列之间的比较是隐含的,而且在比较两个NULLs you get a TRUE. null时,也会得到一个TRUE。With joins and subqueries, you need to be explicit about comparisons and you also need to explicitly add special treatment for 对于连接和子查询,您需要明确地进行比较,还需要明确地为NULLs.NULL值添加特殊处理。
EXCEPT ALL operatorEXCEPT ALL运算符The EXCEPT ALL operator is similar to the EXCEPT operator, but it also takes into account the number of occurrences of each row. EXCEPT ALL运算符与EXCEPT运算符类似,但它还考虑了每行的出现次数。If a row R appears 如果一行R在第一个多重集中出现x times in the first multiset and y times in the second, and x > y, R will appear x – y times in Query1 EXCEPT ALL Query2. x次,在第二个多重集中出现y次,并且x>y,则R将在查询Query1 EXCEPT ALL Query2中出现x-y次。In other words, 换句话说,EXCEPT ALL returns only occurrences of a row from the first multiset that do not have a corresponding occurrence in the second.EXCEPT ALL只返回第一个多重集合中的行的出现次数,而第二个多重集合中没有相应的出现次数。
T-SQL does not provide a built-in T-SQL不提供内置的EXCEPT ALL operator, but you can provide an alternative of your own similar to how you handled INTERSECT ALL. EXCEPT ALL运算符,但您可以提供自己的替代方法,类似于处理INTERSECT ALL的方法。Namely, add a 也就是说,向每个输入查询添加ROW_NUMBER calculation to each of the input queries to number the occurrences of the rows, and use the EXCEPT operator between the two input queries. ROW_NUMBER计算,以对行的出现次数进行编号,并在两个输入查询之间使用EXCEPT运算符。Only occurrences that don't have matches will be returned.只返回不匹配的事件。
The following code returns occurrences of employee locations that have no corresponding occurrences of customer locations:以下代码返回没有相应客户位置的员工位置:
WITH EXCEPT_ALL
AS
(
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY country, region, city
ORDER BY (SELECT 0)) AS rownum,
country, region, city
FROM HR.Employees
EXCEPT
SELECT
ROW_NUMBER()
OVER(PARTITION BY country, region, city
ORDER BY (SELECT 0)),
country, region, city
FROM Sales.Customers
)
SELECT country, region, city
FROM EXCEPT_ALL;
This query returns the following output:此查询返回以下输出:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
USA WA Redmond
USA WA Tacoma
USA WA Seattle
SQL defines precedence among set operators. SQL定义了集合运算符之间的优先级。The INTERSECT operator precedes UNION and EXCEPT, and UNION and EXCEPT are evaluated in order of appearance. INTERSECT运算符位于UNION和EXCEPT之前,UNION和EXCEPT按外观顺序计算。Using the 使用ALL variant doesn't change the precedence. ALL变量不会改变优先级。In a query that contains multiple set operators, first 在包含多个集合运算符的查询中,首先计算INTERSECT operators are evaluated, and then operators with the same precedence are evaluated based on their order of appearance.INTERSECT运算符,然后根据它们的出现顺序计算具有相同优先级的运算符。
Consider the following code:
SELECT country, region, city FROM Production.Suppliers
EXCEPT
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees
INTERSECT
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers;
Because 因为INTERSECT precedes EXCEPT, the INTERSECT operator is evaluated first, even though it appears second in the code. INTERSECT在EXCEPT之前,所以INTERSECT运算符将首先求值,即使它在代码中出现在第二位。The meaning of this query is, “locations that are supplier locations, but not (locations that are both employee and customer locations).”此查询的意思是“供应商位置,但不是(员工和客户位置)。”
This query returns the following output:此查询返回以下输出:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
Australia NSW Sydney
Australia Victoria Melbourne
Brazil NULL Sao Paulo
Canada Québec Montréal
Canada Québec Ste-Hyacinthe
Denmark NULL Lyngby
Finland NULL Lappeenranta
France NULL Annecy
France NULL Montceau
France NULL Paris
Germany NULL Berlin
Germany NULL Cuxhaven
Germany NULL Frankfurt
Italy NULL Ravenna
Italy NULL Salerno
Japan NULL Osaka
Japan NULL Tokyo
Netherlands NULL Zaandam
Norway NULL Sandvika
Singapore NULL Singapore
Spain Asturias Oviedo
Sweden NULL Göteborg
Sweden NULL Stockholm
UK NULL Manchester
USA LA New Orleans
USA MA Boston
USA MI Ann Arbor
USA OR Bend
(28 row(s) affected)
To control the order of evaluation of set operators, use parentheses, because they have the highest precedence. 要控制集合运算符的求值顺序,请使用括号,因为它们具有最高的优先级。Also, using parentheses increases the readability, thus reducing the chance for errors. 此外,使用括号可以提高可读性,从而减少出错的机会。For example, if you want to return “(locations that are supplier locations but not employee locations) and that are also customer locations,” use the following code:例如,如果要返回“(属于供应商位置但非员工位置)和客户位置”,请使用以下代码:
(SELECT country, region, city FROM Production.Suppliers
EXCEPT
SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees)
INTERSECT
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers;
This query returns the following output:此查询返回以下输出:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
Canada Québec Montréal
France NULL Paris
Germany NULL Berlin
This section can be considered advanced for the book's target audience and is provided here as optional reading. 本节对于本书的目标读者来说是高级的,在这里作为可选阅读提供。The individual queries that are used as inputs to a set operator support all logical-query processing phases (such as table operators, 用作集合运算符输入的单个查询支持除OWHERE, GROUP BY, and HAVING) except for ORDER BY. RDER BY之外的所有逻辑查询处理阶段(例如表运算符、WHERE、GROUP BY和HAVING)。However, only the 但是,只有运算符的结果允许ORDER BY phase is allowed on the result of the operator.ORDER BY子句。
What if you need to apply other logical phases besides 如果需要对运算符的结果应用除ORDER BY to the result of the operator? ORDER BY之外的其他逻辑阶段,该怎么办?This is not supported directly as part of the query that applies the operator, but you can easily circumvent this restriction by using table expressions. 这在应用运算符的查询中不受直接支持,但可以通过使用表表达式轻松绕过此限制。Define a table expression based on a query with a set operator, and apply any logical-query processing phases you want in the outer query. 基于带有set运算符的查询定义表表达式,并在外部查询中应用所需的任何逻辑查询处理阶段。For example, the following query returns the number of distinct locations that are either employee or customer locations in each country:例如,以下查询返回每个国家/地区的员工或客户不同地点的数量:
SELECT country, COUNT(*) AS numlocations
FROM (SELECT country, region, city FROM HR.Employees
UNION
SELECT country, region, city FROM Sales.Customers) AS U
GROUP BY country;
This query returns the following output:此查询返回以下输出:
country numlocations
--------------- ------------
Argentina 1
Austria 2
Belgium 2
Brazil 4
Canada 3
Denmark 2
Finland 2
France 9
Germany 11
Ireland 1
Italy 3
Mexico 1
Norway 1
Poland 1
Portugal 1
Spain 3
Sweden 2
Switzerland 2
UK 2
USA 14
Venezuela 4
(21 row(s) affected)
This query demonstrates how to group the result of a 此查询演示如何对UNION operator; similarly, you can, of course, apply other logical-query phases in the outer query.UNION运算符的结果进行分组;同样,您当然可以在外部查询中应用其他逻辑查询阶段。
Remember that the 请记住,输入查询中不允许使用ORDER BY clause is not allowed in the input queries. ORDER BY子句。What if you need to restrict the number of rows in those queries with the 如果需要使用TOP or OFFSET-FETCH filter? TOP或OFFSET-FETCH筛选器限制这些查询中的行数,该怎么办?Again, you can resolve this problem with table expressions. 同样,可以用表表达式解决这个问题。Recall that an 回想一下,在具有ORDER BY clause is allowed in an inner query with TOP or OFFSET-FETCH. TOP或OFFSET-FETCH的内部查询中,允许使用ORDER BY子句。In such a case, the 在这种情况下,ORDER BY clause serves only the filtering-related purpose and has no presentation meaning. ORDER BY子句仅用于筛选相关目的,没有表示意义。For example, the following code uses 例如,以下代码使用TOP queries to return the two most recent orders for employees 3 and 5:TOP查询返回员工3和员工5的两个最新订单:
SELECT empid, orderid, orderdate
FROM (SELECT TOP (2) empid, orderid, orderdate
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE empid = 3
ORDER BY orderdate DESC, orderid DESC) AS D1
UNION ALL
SELECT empid, orderid, orderdate
FROM (SELECT TOP (2) empid, orderid, orderdate
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE empid = 5
ORDER BY orderdate DESC, orderid DESC) AS D2;
This query returns the following output:此查询返回以下输出:
empid orderid orderdate
----------- ----------- -----------
3 11063 2016-04-30
3 11057 2016-04-29
5 11043 2016-04-22
5 10954 2016-03-17
In this chapter, I covered the operators 在本章中,我介绍了运算符UNION, UNION ALL, EXCEPT, and INTERSECT. UNION、UNION ALL、EXCEPT和INTERSECT。I explained that standard SQL also supports operators called 我解释了标准SQL还支持名为INTERSECT ALL and EXCEPT ALL and explained how to achieve similar functionality in T-SQL. INTERSECT ALL和EXCEPT ALL的运算符,并解释了如何在T-SQL中实现类似的功能。Finally, I introduced precedence among set operators, and I explained how to circumvent unsupported logical-query processing phases by using table expressions.最后,我介绍了集合运算符之间的优先级,并解释了如何使用表表达式绕过不受支持的逻辑查询处理阶段。
This section provides exercises to help you familiarize yourself with the subjects discussed in Chapter 6. 本节提供练习,帮助您熟悉第6章中讨论的主题。All exercises require you to be connected to the sample database 所有练习都需要连接到示例数据库TSQLV4.TSQLV4。
Explain the difference between the 解释UNION ALL and UNION operators. UNION ALL和UNION运算符之间的区别。In what cases are the two equivalent? 在什么情况下,这两种情况是等价的?When they are equivalent, which one should you use?当它们相等时,你应该使用哪一个?
Write a query that generates a virtual auxiliary table of 10 numbers in the range 1 through 10 without using a looping construct. 编写一个查询,生成一个包含10个数字的虚拟辅助表,范围从1到10,而不使用循环构造。You do not need to guarantee any order of the rows in the output of your solution:您不需要保证解决方案输出中的行的任何顺序:

Tables involved: None涉及的表格:无

Desired output:期望输出:
n
-----------
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
(10 row(s) affected)
Write a query that returns customer and employee pairs that had order activity in January 2016 but not in February 2016:编写一个查询,返回在2016年1月有订单活动但在2016年2月没有订单活动的客户和员工对:

Table involved: 涉及的表格:Sales.Orders table

Desired output:期望输出:
custid empid
----------- -----------
1 1
3 3
5 8
5 9
6 9
7 6
9 1
12 2
16 7
17 1
20 7
24 8
25 1
26 3
32 4
38 9
39 3
40 2
41 2
42 2
44 8
47 3
47 4
47 8
49 7
55 2
55 3
56 6
59 8
63 8
64 9
65 3
65 8
66 5
67 5
70 3
71 2
75 1
76 2
76 5
80 1
81 1
81 3
81 4
82 6
84 1
84 3
84 4
88 7
89 4
(50 row(s) affected)
Write a query that returns customer and employee pairs that had order activity in both January 2016 and February 2016:编写一个查询,返回在2016年1月和2016年2月都有订单活动的客户和员工对:
 Table involved:
Table involved: Sales.Orders
 Desired output:
Desired output:
custid empid
----------- -----------
20 3
39 9
46 5
67 1
71 4
(5 row(s) affected)
Write a query that returns customer and employee pairs that had order activity in both January 2016 and February 2016 but not in 2015:编写一个查询,返回在2016年1月和2016年2月都有订单活动但在2015年没有的客户和员工对:

Table involved: 涉及的表格:Sales.Orders

Desired output:期望输出:
custid empid
----------- -----------
67 1
46 5
(2 row(s) affected)
You are given the following query:您将收到以下查询:
SELECT country, region, city
FROM HR.Employees
UNION ALL
SELECT country, region, city
FROM Production.Suppliers;
You are asked to add logic to the query so that it guarantees that the rows from 要求您向查询中添加逻辑,以确保在输出中,Employees are returned in the output before the rows from Suppliers. Employees的行比Suppliers的行先返回。Also, within each segment, the rows should be sorted by country, region, and city:此外,在每个段中,行应按国家、地区和城市排序:

Tables involved: 涉及的表格:HR.Employees and 和Production.Suppliers

Desired output:期望输出:
country region city
--------------- --------------- ---------------
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
UK NULL London
USA WA Kirkland
USA WA Redmond
USA WA Seattle
USA WA Seattle
USA WA Tacoma
Australia NSW Sydney
Australia Victoria Melbourne
Brazil NULL Sao Paulo
Canada Québec Montréal
Canada Québec Ste-Hyacinthe
Denmark NULL Lyngby
Finland NULL Lappeenranta
France NULL Annecy
France NULL Montceau
France NULL Paris
Germany NULL Berlin
Germany NULL Cuxhaven
Germany NULL Frankfurt
Italy NULL Ravenna
Italy NULL Salerno
Japan NULL Osaka
Japan NULL Tokyo
Netherlands NULL Zaandam
Norway NULL Sandvika
Singapore NULL Singapore
Spain Asturias Oviedo
Sweden NULL Göteborg
Sweden NULL Stockholm
UK NULL London
UK NULL Manchester
USA LA New Orleans
USA MA Boston
USA MI Ann Arbor
USA OR Bend
(38 row(s) affected)
This section provides solutions to the Chapter 6 exercises.本节提供了第6章练习的解决方案。
The UNION ALL operator unifies the two input query result sets and doesn't remove duplicates from the result. UNION ALL运算符统一两个输入查询结果集,并且不会从结果中删除重复项。The UNION operator (implied DISTINCT) also unifies the two input query result sets, but it does remove duplicates from the result.UNION运算符(隐含的DISTINCT)还统一了两个输入查询结果集,但它确实会从结果中删除重复项。
The two have different meanings when the result can potentially have duplicates. 当结果可能存在重复项时,这两个词有不同的含义。They have an equivalent meaning when the result can't have duplicates, such as when you're unifying disjoint sets (for example, sales 2015 with sales 2016).当结果不能有重复项时,例如当你统一不相交集(例如,sales 2015和sales 2016)时,它们具有相同的含义。
When they do have the same meaning, you need to use 当它们的含义相同时,默认情况下需要使用UNION ALL by default. UNION ALL。That's to avoid paying unnecessary performance penalties for the work involved in removing duplicates when they don't exist.这是为了避免在不存在副本的情况下,为删除副本所涉及的工作支付不必要的性能惩罚。
T-SQL supports a T-SQL支持基于不带SELECT statement based on constants with no FROM clause. FROM子句的常量的SELECT语句。Such a 这样的SELECT statement returns a table with a single row. SELECT语句返回一个只有一行的表。For example, the following statement returns a row with a single column called 例如,以下语句返回一行,其中一列名为n with the value 1:n,值为1:
SELECT 1 AS n;
Here's the output of this statement:以下是该语句的输出:
n
-----------
1
(1 row(s) affected)
By using the 通过使用UNION ALL operator, you can unify the result sets of multiple statements like the one just mentioned, each returning a row with a different number in the range 1 through 10, like the following:UNION ALL运算符,您可以统一多个语句的结果集,就像刚才提到的那样,每个语句返回的行的数字在1到10之间,如下所示:
SELECT 1 AS n
UNION ALL SELECT 2
UNION ALL SELECT 3
UNION ALL SELECT 4
UNION ALL SELECT 5
UNION ALL SELECT 6
UNION ALL SELECT 7
UNION ALL SELECT 8
UNION ALL SELECT 9
UNION ALL SELECT 10;
 Tip
Tip
SQL Server supports an enhanced SQL Server支持在VALUES clause you might be familiar with in the context of the INSERT statement. INSERT语句的上下文中可能熟悉的增强型VALUES子句。The VALUES clause is not restricted to representing a single row; it can represent multiple rows. VALUES子句不限于表示一行;它可以表示多行。Also, the 此外,VALUES clause is not restricted to INSERT statements but can be used to define a table expression with rows based on constants.VALUES子句不仅限于INSERT语句,还可用于定义基于常量的行的表表达式。
As an example, here's how you can use the 例如,以下是如何使用VALUES clause to provide a solution to this exercise instead of using the UNION ALL operator:VALUES子句为本练习提供解决方案,而不是使用UNION ALL运算符:
SELECT n
FROM (VALUES(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9),(10)) AS Nums(n);
I'll provide details about the 作为VALUES clause and such table value constructors in Chapter 8, “Data modification,” as part of the discussion of the INSERT statement.INSERT语句讨论的一部分,我将在第8章“数据修改”中提供有关VALUES子句和此类表值构造函数的详细信息。
You can solve this exercise by using the 可以使用集运算符EXCEPT set operator. EXCEPT解决此练习。The left input is a query that returns customer and employee pairs that had order activity in January 2016. 左边的输入是一个查询,返回2016年1月有订单活动的客户和员工对。The right input is a query that returns customer and employee pairs that had order activity in February 2016. Here's the solution query:正确的输入是一个查询,返回2016年2月有订单活动的客户和员工对。以下是解决方案查询:
USE TSQLV4;
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160101' AND orderdate < '20160201'
EXCEPT
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160201' AND orderdate < '20160301';
Whereas Exercise 2 requested customer and employee pairs that had activity in one period but not another, this exercise concerns customer and employee pairs that had activity in both periods. 练习2要求在一个时期内有活动但在另一个时期内没有活动的客户和员工对,而本练习涉及在两个时期内都有活动的客户和员工对。So this time, instead of using the 因此,这一次,您需要使用EXCEPT operator, you need to use the INTERSECT operator, like this:INTERSECT运算符,而不是使用EXCEPT运算符,如下所示:
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160101' AND orderdate < '20160201'
INTERSECT
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160201' AND orderdate < '20160301';
This exercise requires you to combine set operators. 本练习要求您组合集合运算符。To return customer and employee pairs that had order activity in both January 2016 and February 2016, you need to use the 要返回在2016年1月和2016年2月都有订单活动的客户和员工对,需要使用INTERSECT operator, as in Exercise 4. INTERSECT运算符,如练习4所示。To exclude customer and employee pairs that had order activity in 2015 from the result, you need to use the 要从结果中排除2015年有订单活动的客户和员工对,需要在结果和第三个查询之间使用EXCEPT operator between the result and a third query. EXCEPT运算符。The solution query looks like this:解决方案查询如下所示:
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160101' AND orderdate < '20160201'
INTERSECT
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160201' AND orderdate < '20160301'
EXCEPT
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20150101' AND orderdate < '20160101';
Keep in mind that the 请记住,INTERSECT operator precedes EXCEPT. INTERSECT运算符位于EXCEPT之前。In this case, the default precedence is also the precedence you want, so you don't need to intervene by using parentheses. 在这种情况下,默认优先级也是您想要的优先级,因此不需要使用括号进行干预。But you might prefer to add them for clarity, as shown here:但为了清晰起见,您可能更愿意添加它们,如下所示:
(SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160101' AND orderdate < '20160201'
INTERSECT
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20160201' AND orderdate < '20160301')
EXCEPT
SELECT custid, empid
FROM Sales.Orders
WHERE orderdate >= '20150101' AND orderdate < '20160101';
The problem here is that the individual queries are not allowed to have 这里的问题是,单个查询不允许有ORDER BY clauses, and for a good reason. ORDER BY子句,这是有充分理由的。You can solve the problem by adding a result column based on a constant to each of the queries involved in the operator (call it 您可以通过向运算符中涉及的每个查询(称为sortcol). sortcol)添加一个基于常量的结果列来解决此问题。In the query against 在针对Employees, specify a smaller constant than the one you specify in the query against Suppliers. Employees的查询中,指定一个小于您在针对供应商的查询中指定的常数。Define a table expression based on the query with the operator, and in the 使用运算符根据查询定义表表达式,并在外部查询的ORDER BY clause of the outer query, specify sortcol as the first sort column, followed by country, region, and city. ORDER BY子句中,将sortcol指定为第一个排序列,然后是country、region和city。Here's the complete solution query:以下是完整的解决方案查询:
SELECT country, region, city
FROM (SELECT 1 AS sortcol, country, region, city
FROM HR.Employees
UNION ALL
SELECT 2, country, region, city
FROM Production.Suppliers) AS D
ORDER BY sortcol, country, region, city;