Lesson: Interfaces and Inheritance
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
Inheritance遗产
In the preceding lessons, you have seen inheritance mentioned several times. 在前面的课程中,您已经多次提到了继承。In the Java language, classes can be derived from other classes, thereby inheriting fields and methods from those classes.在Java语言中,类可以从其他类派生,从而从这些类继承字段和方法。
Object, which has no superclass, every class has one and only one direct superclass (single inheritance). Object之外,每个类都有一个且只有一个直接超类(单继承)。Object.Object的子类。Object. Object派生。Object. Object。The idea of inheritance is simple but powerful: When you want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that you want, you can derive your new class from the existing class. 继承的思想很简单,但功能强大:当您想要创建一个新类,并且已经有一个类包含您想要的一些代码时,您可以从现有类派生新类。In doing this, you can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class without having to write (and debug!) them yourself.通过这样做,您可以重用现有类的字段和方法,而无需编写(和调试!)你自己动手吧。
A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass. 子类从其超类继承所有成员(字段、方法和嵌套类)。Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass.构造函数不是成员,因此它们不会被子类继承,但是可以从子类调用超类的构造函数。
The Java Platform Class HierarchyJava平台类层次结构
The Object class, defined in the java.lang package, defines and implements behavior common to all classes—including the ones that you write. java.lang包中定义的Object类定义并实现了所有类共有的行为—包括你写的那些。In the Java platform, many classes derive directly from 在Java平台中,许多类直接Object, other classes derive from some of those classes, and so on, forming a hierarchy of classes.从Object派生,其他类从其中的一些类派生,依此类推,形成了类的层次结构。
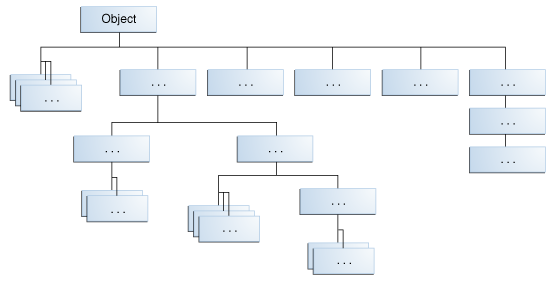
All Classes in the Java Platform are Descendants of ObjectJava平台中的所有类都是对象的后代
At the top of the hierarchy, 在层次结构的顶部,Object is the most general of all classes. Object是所有类中最通用的。Classes near the bottom of the hierarchy provide more specialized behavior.靠近层次结构底部的类提供了更专门的行为。
An Example of Inheritance继承的例子
Here is the sample code for a possible implementation of a 以下是在“类和对象”课程中介绍的Bicycle class that was presented in the Classes and Objects lesson:Bicycle类的可能实现的示例代码:
public class Bicycle {
// the Bicycle class has three fields
public int cadence;
public int gear;
public int speed;
// the Bicycle class has one constructor
public Bicycle(int startCadence, int startSpeed, int startGear) {
gear = startGear;
cadence = startCadence;
speed = startSpeed;
}
// the Bicycle class has four methods
public void setCadence(int newValue) {
cadence = newValue;
}
public void setGear(int newValue) {
gear = newValue;
}
public void applyBrake(int decrement) {
speed -= decrement;
}
public void speedUp(int increment) {
speed += increment;
}
}A class declaration for a 作为MountainBike class that is a subclass of Bicycle might look like this:Bicycle类的子类的MountainBike类的类声明可能如下所示:
public class MountainBike extends Bicycle {
// the MountainBike subclass adds one field
public int seatHeight;
// the MountainBike subclass has one constructor
public MountainBike(int startHeight,
int startCadence,
int startSpeed,
int startGear) {
super(startCadence, startSpeed, startGear);
seatHeight = startHeight;
}
// the MountainBike subclass adds one method
public void setHeight(int newValue) {
seatHeight = newValue;
}
}MountainBike inherits all the fields and methods of Bicycle and adds the field seatHeight and a method to set it. MountainBike继承了Bicycle的所有字段和方法,并添加了字段seatHeight和设置它的方法。Except for the constructor, it is as if you had written a new 除了构造函数之外,就好像您完全从头开始编写了一个新的MountainBike class entirely from scratch, with four fields and five methods. MountainBike类,包含四个字段和五个方法。However, you didn't have to do all the work. 然而,你不必做所有的工作。This would be especially valuable if the methods in the 如果Bicycle class were complex and had taken substantial time to debug.Bicycle类中的方法很复杂,并且需要花费大量时间进行调试,那么这将特别有价值。
What You Can Do in a Subclass在子类中可以做什么
A subclass inherits all of the public and protected members of its parent, no matter what package the subclass is in. 子类继承其父类的所有公开成员和受保护成员,而不管该子类在哪个包中。If the subclass is in the same package as its parent, it also inherits the package-private members of the parent. 如果子类与其父类位于同一个包中,则它还继承父类的包私有成员。You can use the inherited members as is, replace them, hide them, or supplement them with new members:您可以按原样使用继承的成员、替换它们、隐藏它们或用新成员补充它们:
The inherited fields can be used directly, just like any other fields.继承的字段可以像其他字段一样直接使用。You can declare a field in the subclass with the same name as the one in the superclass, thus hiding it (not recommended).您可以在子类中声明一个与超类中的字段同名的字段,从而将其隐藏(不推荐)。You can declare new fields in the subclass that are not in the superclass.可以在子类中声明不在超类中的新字段。The inherited methods can be used directly as they are.继承的方法可以直接使用。You can write a new instance method in the subclass that has the same signature as the one in the superclass, thus overriding it.您可以在子类中编写一个新的实例方法,该子类具有与超类中相同的签名,从而覆盖它。You can write a new static method in the subclass that has the same signature as the one in the superclass, thus hiding it.您可以在子类中编写一个新的静态方法,该方法与超类中的方法具有相同的签名,从而隐藏它。You can declare new methods in the subclass that are not in the superclass.可以在子类中声明不在超类中的新方法。You can write a subclass constructor that invokes the constructor of the superclass, either implicitly or by using the keyword您可以编写一个子类构造函数来调用超类的构造函数,可以隐式调用,也可以使用关键字super.super来调用。
The following sections in this lesson will expand on these topics.本课程中的以下部分将对这些主题进行扩展。
Private Members in a Superclass超类中的私有成员
A subclass does not inherit the 子类不继承其父类的private members of its parent class. private成员。However, if the superclass has public or protected methods for accessing its private fields, these can also be used by the subclass.但是,如果超类具有访问其私有字段的公共或受保护方法,则子类也可以使用这些方法。
A nested class has access to all the private members of its enclosing class—both fields and methods. 嵌套类可以访问其封闭类的所有私有成员—字段和方法。Therefore, a public or protected nested class inherited by a subclass has indirect access to all of the private members of the superclass.因此,子类继承的公共或受保护的嵌套类可以间接访问超类的所有私有成员。
Casting Objects强制转换对象的类型
We have seen that an object is of the data type of the class from which it was instantiated. 我们已经看到,对象的数据类型与从中实例化它的类的数据类型相同。For example, if we write例如,如果我们编写
public MountainBike myBike = new MountainBike();
then 那么myBike is of type MountainBike.myBike就属于MountainBike类型。
MountainBike is descended from Bicycle and Object. MountainBike是Bicycle和Object的后代。Therefore, a 因此,MountainBike is a Bicycle and is also an Object, and it can be used wherever Bicycle or Object objects are called for.MountainBike既是Bicycle也是Object,它可以在任何需要Bicycle或Object的地方使用。
The reverse is not necessarily true: a 反过来不一定正确:Bicycle may be a MountainBike, but it isn't necessarily. Bicycle可能是MountainBike,但不一定是。Similarly, an 类似地,Object may be a Bicycle or a MountainBike, but it isn't necessarily.Object可能是Bicycle或MountainBike,但不一定是。
Casting shows the use of an object of one type in place of another type, among the objects permitted by inheritance and implementations. 强制转换显示在继承和实现所允许的对象中,使用一种类型的对象代替另一种类型的对象。For example, if we write例如,如果我们编写
Object obj = new MountainBike();
then 则obj is both an Object and a MountainBike (until such time as obj is assigned another object that is not a MountainBike). obj既是一个Object又是一个MountainBike(直到obj被指定为另一个非MountainBike的对象)。This is called implicit casting.这称为隐式强制转换。
If, on the other hand, we write另一方面,如果我们编写
MountainBike myBike = obj;
we would get a compile-time error because 我们会得到一个编译时错误,因为编译器不知道obj is not known to the compiler to be a MountainBike. obj是MountainBike。However, we can tell the compiler that we promise to assign a 但是,我们可以告诉编译器,我们承诺通过显式强制转换将MountainBike to obj by explicit casting:MountainBike分配给obj:
MountainBike myBike = (MountainBike)obj;
This cast inserts a runtime check that 此强制转换插入一个运行时检查,确保obj is assigned a MountainBike so that the compiler can safely assume that obj is a MountainBike. obj被分配了一个MountainBike,以便编译器可以安全地假定obj是一个MountainBike。If 如果obj is not a MountainBike at runtime, an exception will be thrown.obj在运行时不是MountainBike,则会抛出异常。
Note:
instanceof operator. instanceof操作符对特定对象的类型进行逻辑测试。if (obj instanceof MountainBike) {
MountainBike myBike = (MountainBike)obj;
}Here the 在这里,instanceof operator verifies that obj refers to a MountainBike so that we can make the cast with knowledge that there will be no runtime exception thrown.instanceof操作符验证obj引用了一个MountainBike,这样我们就可以在知道不会抛出运行时异常的情况下进行转换。