The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8.Java教程是为JDK 8编写的。Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.本页中描述的示例和实践没有利用后续版本中引入的改进,并且可能使用不再可用的技术。See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.有关Java SE 9及其后续版本中更新的语言特性的摘要,请参阅Java语言更改。
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.有关所有JDK版本的新功能、增强功能以及已删除或不推荐的选项的信息,请参阅JDK发行说明。
Java 2D RenderingJava 2D渲染
The Java 2D API provides a uniform rendering model across different types of devices.Java2D API提供了跨不同类型设备的一致性渲染模型。At the application level, the rendering process is the same whether the target rendering device is a screen or a printer.在应用程序级别,无论目标渲染设备是屏幕还是打印机,渲染过程都是相同的。When a component needs to be displayed, its 当需要显示组件时,将使用适当的图形上下文自动调用其paint or update method is automatically invoked with the appropriate Graphics context.paint方法或update方法。
The Java 2D API includes the Java 2D API包括java.awt.Graphics2D class, which extends the Graphics class to provide access to the enhanced graphics and rendering features of the Java 2D API.java.awt.Graphics2D类,该类扩展了Graphics类,以提供对Java 2D API的增强图形和渲染功能的访问。These features include:
Rendering the outline of any geometric primitive, using the stroke and paint attributes (使用笔划和绘制属性(drawmethod).draw方法)渲染任何几何图元的轮廓。Rendering any geometric primitive by filling its interior with the color or pattern specified by the paint attributes (通过使用“绘制属性”(fillmethod).fill方法)指定的颜色或图案填充几何图元的内部来渲染任何几何图元。Rendering any text string (the呈现任何文本字符串(drawStringmethod).drawString方法)。The font attribute is used to convert the string to glyphs, which are then filled with the color or pattern specified by the paint attributes.font属性用于将字符串转换为glyph,然后用paint属性指定的颜色或图案填充glyph。Rendering the specified image (the呈现指定的图像(drawImagemethod).drawImage方法)。
In addition, the 此外,Graphics2D class supports the Graphics rendering methods for particular shapes, such as drawOval and fillRect.Graphics2D类支持特定形状的图形渲染方法,如drawOval和fillRect。All methods that are represented above can be divided into two groups:上述所有方法可分为两组:
Methods to draw a shape绘制形状的方法Methods that affect rendering影响渲染的方法
The second group of the methods uses the state attributes that form the 第二组方法使用构成Graphics2D context for following purposes:Graphics2D上下文的状态属性,用于以下目的:
To vary the stroke width更改笔划宽度的步骤To change how strokes are joined together更改笔划连接方式的步骤To set a clipping path to limit the area that is rendered设置剪裁路径以限制渲染区域的步骤To translate, rotate, scale, or shear objects when they are rendered渲染对象时平移、旋转、缩放或剪切对象的步骤To define colors and patterns to fill shapes with定义用于填充形状的颜色和图案的步骤To specify how to compose multiple graphics objects指定如何组合多个图形对象的步骤
To employ Java 2D API features in the application, cast the 要在应用程序中使用Java 2D API功能,请将传递到组件渲染方法中的Graphics object passed into a component's rendering method to a Graphics2D object.Graphics对象强制转换为Graphics2D对象。For example:例如:
public void paint (Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
...
}As the following figure shows, the 如下图所示,Graphics2D class rendering context contains several attributes.Graphics2D类呈现上下文包含几个属性。
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
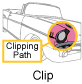 |
Shape object used to define the clipping path.Shape object that is used to define the clip.Shape对象。 |
 |
|
 |
To learn more about transforming and compositing see the Advanced Topics in Java2D lesson.要了解有关转换和合成的更多信息,请参阅Java2D课程中的高级主题。
When an attribute is set, the appropriate attribute object is passed.设置属性时,将传递相应的属性对象。As the following example shows, to change the paint attribute to a blue-green gradient fill, you construct a 如以下示例所示,要将GradientPaint object and then call the setPaint method.paint属性更改为蓝绿色渐变填充,请构造GradientPaint对象,然后调用setPaint方法。
gp = new GradientPaint(0f,0f,blue,0f,30f,green); g2.setPaint(gp);