Chapter 1第1章. Background to T-SQL querying and programmingT-SQL查询和编程背景
You're about to embark on a journey to a land that is like no other—a land that has its own set of laws. 你即将踏上一段旅程,来到一片与众不同的土地——一片拥有自己一套法律的土地。If reading this book is your first step in learning Transact-SQL (T-SQL), you should feel like Alice—just before she started her adventures in Wonderland. 如果阅读这本书是学习Transact-SQL(T-SQL)的第一步,那么你应该感觉自己就像爱丽丝刚刚开始她的仙境冒险。For me, the journey has not ended; instead, it's an ongoing path filled with new discoveries. 对我来说,旅程还没有结束;相反,这是一条充满新发现的持续道路。I envy you; some of the most exciting discoveries are still ahead of you!我羡慕你;一些最激动人心的发现仍然摆在你面前!
I've been involved with T-SQL for many years: teaching, speaking, writing, and consulting about it. 我从事T-SQL多年:教学、口语、写作和咨询。For me, T-SQL is more than just a language—it's a way of thinking. 对我来说,T-SQL不仅仅是一种语言,它还是一种思维方式。In my first few books about T-SQL, I've written extensively on advanced topics, and for years, I have postponed writing about fundamentals. 在我最初几本关于T-SQL的书中,我写了大量关于高级主题的文章,多年来,我一直推迟写关于基础知识的文章。This is not because T-SQL fundamentals are simple or easy—in fact, it's just the opposite. 这并不是因为T-SQL的基本原理简单,实际上恰恰相反。The apparent simplicity of the language is misleading. 这种语言表面上的简单是有误导性的。I could explain the language syntax elements in a superficial manner and have you writing queries within minutes. 我可以用一种肤浅的方式解释语言语法元素,让你在几分钟内编写查询。But that approach would only hold you back in the long run and make it harder for you to understand the essence of the language.但从长远来看,这种方法只会让你望而却步,让你更难理解语言的本质。
Acting as your guide while you take your first steps in this realm is a big responsibility. 当你在这个领域迈出第一步时,作为你的向导是一项重大责任。I wanted to make sure that I spent enough time and effort exploring and understanding the language before writing about fundamentals. 我想确保在写基础知识之前,我花了足够的时间和精力探索和理解这门语言。T-SQL is deep; learning the fundamentals the right way involves much more than just understanding the syntax elements and coding a query that returns the right output. T-SQL很深;以正确的方式学习基础知识远不止是理解语法元素和编写返回正确输出的查询。You pretty much need to forget what you know about other programming languages and start thinking in terms of T-SQL.你几乎需要忘记你对其他编程语言的了解,开始用T-SQL来思考。
Theoretical background理论背景
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. SQL代表结构化查询语言。SQL is a standard language that was designed to query and manage data in relational database management systems (RDBMSs). SQL是一种标准语言,旨在查询和管理关系数据库管理系统(RDBMS)中的数据。An RDBMS is a database management system based on the relational model (a semantic model for representing data), which in turn is based on two mathematical branches: set theory and predicate logic. RDBMS是基于关系模型(表示数据的语义模型)的数据库管理系统,而关系模型又基于两个数学分支:集合论和谓词逻辑。Many other programming languages and various aspects of computing evolved pretty much as a result of intuition. 许多其他编程语言和计算的各个方面都是直觉的结果。In contrast, to the degree that SQL is based on the relational model, it is based on a firm foundation—applied mathematics. 相比之下,SQL是基于关系模型的,它基于坚实的应用数学基础。T-SQL thus sits on wide and solid shoulders. 因此,T-SQL坐在宽阔坚实的肩膀上。Microsoft provides T-SQL as a dialect of, or extension to, SQL in Microsoft SQL Server data-management software, its RDBMS.微软提供T-SQL作为微软SQL Server数据管理软件RDBMS中SQL的方言或扩展。
This section provides a brief theoretical background about SQL, set theory and predicate logic, the relational model, and types of database systems. 本节简要介绍SQL、集合论和谓词逻辑、关系模型以及数据库系统类型的理论背景。Because this book is neither a mathematics book nor a design/data-modeling book, the theoretical information provided here is informal and by no means complete. 因为这本书既不是数学书,也不是设计/数据建模书,所以这里提供的理论信息是非正式的,绝对不完整。The goals are to give you a context for the T-SQL language and to deliver the key points that are integral to correctly understanding T-SQL later in the book.目标是为您提供T-SQL语言的上下文,并在本书后面的部分中提供正确理解T-SQL不可或缺的关键点。
See Also
For details about the deviations of SQL from the relational model, as well as how to use SQL in a relational way, see this book on the topic:有关SQL与关系模型的偏差,以及如何以关系方式使用SQL的详细信息,请参阅本书:SQL and Relational Theory: How to Write Accurate SQL Code, Third Edition SQL和关系理论:如何编写准确的SQL代码,第三版by C. J. Date (O'Reilly Media, 2015).
SQL
SQL is both an ANSI and ISO standard language based on the relational model, designed for querying and managing data in an RDBMS.SQL是基于关系模型的ANSI和ISO标准语言,旨在查询和管理RDBMS中的数据。
In the early 1970s, IBM developed a language called SEQUEL (short for Structured English QUEry Language) for its RDBMS product called System R. 20世纪70年代初,IBM为其RDBMS产品System R开发了一种名为SEQUEL(结构化英语查询语言的缩写)的语言。The name of the language was later changed from SEQUEL to SQL because of a trademark dispute. 由于商标纠纷,该语言的名称后来从SEQUEL改为SQL。SQL first became an ANSI standard in 1986, and then an ISO standard in 1987. SQL首先在1986年成为ANSI标准,然后在1987年成为ISO标准。Since 1986, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have been releasing revisions for the SQL standard every few years. 自1986年以来,美国国家标准协会(ANSI)和国际标准化组织(ISO)每隔几年就发布一次SQL标准的修订版。So far, the following standards have been released: SQL-86 (1986), SQL-89 (1989), SQL-92 (1992), SQL:1999 (1999), SQL:2003 (2003), SQL:2006 (2006), SQL:2008 (2008), and SQL:2011 (2011). 到目前为止,已经发布了以下标准:SQL-86(1986)、SQL-89(1989)、SQL-92(1992)、SQL:1999(1999)、SQL:2003(2003)、SQL:2006(2006)、SQL:2008(2008)和SQL:2011(2011)。The SQL standard is made of multiple parts. SQL标准由多个部分组成。Part 1 (Framework) and Part 2 (Foundation) pertain to the SQL language, whereas the other parts define standard extensions, such as SQL for XML and SQL-Java integration.第1部分(框架)和第2部分(基础)涉及SQL语言,而其他部分定义了标准扩展,例如SQL for XML和SQL Java集成。
Interestingly, SQL resembles English and is also very logical. Unlike many programming languages, which use an imperative programming paradigm, SQL uses a declarative one. 有趣的是,SQL类似于英语,也非常符合逻辑。与许多使用命令式编程范式的编程语言不同,SQL使用声明式编程范式。That is, SQL requires you to specify what you want to get and not how to get it, letting the RDBMS figure out the physical mechanics required to process your request.也就是说,SQL要求您指定想要获取的内容,而不是如何获取,让RDBMS了解处理请求所需的物理机制。
SQL has several categories of statements, including Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), and Data Control Language (DCL). SQL有几类语句,包括数据定义语言(DDL)、数据操作语言(DML)和数据控制语言(DCL)。DDL deals with object definitions and includes statements such as CREATE, ALTER, and DROP. DDL处理对象定义,包括CREATE、ALTER和DROP等语句。DML allows you to query and modify data and includes statements such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, TRUNCATE, and MERGE. DML允许您查询和修改数据,包括SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、TRUNCATE和MERGE等语句。It's a common misunderstanding that DML includes only data-modification statements, but as I mentioned, it also includes SELECT. DML只包括数据修改语句,这是一个常见的误解,但正如我提到的,它还包括SELECT。Another common misunderstanding is that TRUNCATE is a DDL statement, but in fact it is a DML statement. 另一个常见的误解是TRUNCATE是一个DDL语句,但实际上它是一个DML语句。DCL deals with permissions and includes statements such as GRANT and REVOKE. DCL处理权限,包括GRANT和REVOKE等语句。This book focuses on DML.这本书的重点是DML。
T-SQL is based on standard SQL, but it also provides some nonstandard/proprietary extensions. T-SQL基于标准SQL,但也提供了一些非标准/专有扩展。Moreover, T-SQL does not implement all of standard SQL. 此外,T-SQL并没有实现所有标准SQL。In other words, T-SQL is both a subset and a superset of SQL. 换句话说,T-SQL既是SQL的子集,也是SQL的超集。When describing a language element for the first time, I'll typically mention whether it is standard.在第一次描述语言元素时,我通常会提到它是否是标准的。
Set theory集合论
Set theory, which originated with the mathematician Georg Cantor, is one of the mathematical branches on which the relational model is based. 集合论起源于数学家乔治·坎托,是关系模型所基于的数学分支之一。Cantor's definition of a set follows:康托对集合的定义如下:
By a “set” we mean any collection M into a whole of definite, distinct objects m (which are called the “elements” of M) of our perception or of our thought.我们所说的“集合”指的是将知觉或思想集合成一个完整的、明确的、不同的对象(称为“元素”)。
—Joseph W. Dauben and Georg Cantor (Princeton University Press, 1990)Joseph W.Dauben和Georg Cantor(普林斯顿大学出版社,1990年)
Every word in the definition has a deep and crucial meaning. 定义中的每个词都有深刻而关键的意义。The definitions of a set and set membership are axioms that are not supported by proofs. 集合和集合成员的定义是证明所不支持的公理。Each element belongs to a universe, and either is or is not a member of the set.每个元素都属于一个宇宙,或者是集合的成员,或者不是集合的成员。
Let's start with the word whole in Cantor's definition. 让我们从康托定义中的“整体”一词开始。A set should be considered a single entity. 集合应被视为单个实体。Your focus should be on the collection of objects as opposed to the individual objects that make up the collection. 你的重点应该放在对象的集合上,而不是组成集合的单个对象上。Later on, when you write T-SQL queries against tables in a database (such as a table of employees), you should think of the set of employees as a whole rather than the individual employees. 稍后,当您针对数据库中的表(例如雇员表)编写T-SQL查询时,您应该将雇员集视为一个整体,而不是单个雇员。This might sound trivial and simple enough, but apparently many programmers have difficulty adopting this way of thinking.这听起来可能很琐碎和简单,但显然许多程序员很难采用这种思维方式。
The word distinct means that every element of a set must be unique. 单词distinct意味着集合中的每个元素都必须是唯一的。Jumping ahead to tables in a database, you can enforce the uniqueness of rows in a table by defining key constraints. 跳转到数据库中的表,可以通过定义键约束来强制表中行的唯一性。Without a key, you won't be able to uniquely identify rows, and therefore the table won't qualify as a set. 如果没有键,您将无法唯一标识行,因此该表不符合集合的条件。Rather, the table would be a multiset or a bag.相反,这张桌子应该是一个“多集”或一个“包”。
The phrase of our perception or of our thought implies that the definition of a set is subjective. “感知”或“思想”这一短语暗示着对集合的定义是主观的。Consider a classroom: one person might perceive a set of people, whereas another might perceive a set of students and a set of teachers. 考虑一个教室:一个人可以感知一组人,另一个人可以感知一组学生和一组教师。Therefore, you have a substantial amount of freedom in defining sets. 因此,在定义集合时有很大的自由度。When you design a data model for your database, the design process should carefully consider the subjective needs of the application to determine adequate definitions for the entities involved.当为数据库设计数据模型时,设计过程应仔细考虑应用程序的主观需求,以确定所涉及实体的适当定义。
As for the word object, the definition of a set is not restricted to physical objects, such as cars or employees, but rather is relevant to abstract objects as well, such as prime numbers or lines.至于“对象”这个词,集合的定义并不局限于物理对象,比如汽车或员工,而是与抽象对象相关,比如素数或直线。
What Cantor's definition of a set leaves out is probably as important as what it includes. 康托对集合的定义遗漏了什么,可能和它包含了什么一样重要。Notice that the definition doesn't mention any order among the set elements. 请注意,该定义没有提及集合元素之间的任何顺序。The order in which set elements are listed is not important. 集合元素的列出顺序并不重要。The formal notation for listing set elements uses curly brackets: {a, b, c}. 列出集合元素的形式表示法使用花括号:{a, b, c}。Because order has no relevance, you can express the same set as {b, a, c} or {b, c, a}. 因为顺序没有相关性,所以可以将相同的集合表示为{a, b, c}或{b, c, a}。Jumping ahead to the set of attributes (called columns in SQL) that make up the heading of a relation (called a table in SQL), an element is supposed to be identified by name—not by ordinal position.跳转到组成关系(SQL中称为表)标题的属性集(SQL中称为列),元素应该通过名称而不是顺序位置来标识。
Similarly, consider the set of tuples (called rows by SQL) that make up the body of the relation; an element is identified by its key values—not by position. 类似地,考虑组成关系体的元组(由SQL称为“行”);元素由其键值而不是位置来标识。Many programmers have a hard time adapting to the idea that, with respect to querying tables, there is no order among the rows. 许多程序员很难适应这样的想法,即在查询表时,行之间没有顺序。In other words, a query against a table can return table rows in any order unless you explicitly request that the data be sorted in a specific way, perhaps for presentation purposes.换句话说,对表的查询可以以任何顺序返回表行,除非您明确要求以特定的方式对数据进行排序,可能是出于表示的目的。
Predicate logic谓词逻辑
Predicate logic, whose roots reach back to ancient Greece, is another branch of mathematics on which the relational model is based. 谓词逻辑可以追溯到古希腊,是关系模型所基于的数学的另一个分支。Dr. Edgar F. Codd, in creating the relational model, had the insight to connect predicate logic to both the management and querying of data. Edgar F.Codd博士在创建关系模型时,洞察到将谓词逻辑与数据的管理和查询联系起来。Loosely speaking, a predicate is a property or an expression that either holds or doesn't hold—in other words, is either true or false. 粗略地说,“谓词”是一个属性或一个表达式,要么成立,要么不成立,换句话说,要么是真的,要么是假的。The relational model relies on predicates to maintain the logical integrity of the data and define its structure. 关系模型依赖谓词来维护数据的逻辑完整性并定义其结构。One example of a predicate used to enforce integrity is a constraint defined in a table called Employees that allows only employees with a salary greater than zero to be stored in the table. 用于强制执行完整性的谓词的一个示例是在名为Employees的表中定义的约束,该约束只允许工资大于零的员工存储在表中。The predicate is “salary greater than zero” (T-SQL expression: salary > 0).谓词是“salary大于零”(T-SQL表达式:salary>0)。
You can also use predicates when filtering data to define subsets, and more. 在筛选数据以定义子集时,还可以使用谓词,等等。For example, if you need to query the Employees table and return only rows for employees from the sales department, you use the predicate “department equals sales” in your query filter (T-SQL expression: department = 'sales').例如,如果需要查询Employees表并仅返回销售部门员工的行,则可以在查询筛选器中使用谓词“department equals sales”(T-SQL表达式:department='sales')。
In set theory, you can use predicates to define sets. 在集合论中,可以使用谓词定义集合。This is helpful because you can't always define a set by listing all its elements (for example, infinite sets), and sometimes for brevity it's more convenient to define a set based on a property. 这很有帮助,因为不能总是通过列出集合的所有元素(例如,无限集合)来定义集合,有时为了简洁起见,基于属性定义集合更方便。As an example of an infinite set defined with a predicate, the set of all prime numbers can be defined with the following predicate: “x is a positive integer greater than 1 that is divisible only by 1 and itself.” 作为一个用谓词定义的无限集的例子,所有素数的集合可以用以下谓词定义:“x是一个大于1的正整数,它只能被1和自身整除。”For any specified value, the predicate is either true or not true. 对于任何指定的值,谓词要么为true,要么为not true。The set of all prime numbers is the set of all elements for which the predicate is true. 所有素数的集合是谓词为真的所有元素的集合。As an example of a finite set defined with a predicate, the set {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} can be defined as the set of all elements for which the following predicate holds true: “x is an integer greater than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 9.”作为用谓词定义的有限集的一个例子,集合{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}可以定义为所有元素的集合,对于这些元素,以下谓词成立:“x是大于或等于0,小于或等于9的整数。”
The relational model关系模型
The relational model is a semantic model for data management and manipulation and is based on set theory and predicate logic. 关系模型是用于数据管理和操作的语义模型,基于集合论和谓词逻辑。As mentioned earlier, it was created by Dr. Edgar F. Codd, and later explained and developed by Chris Date, Hugh Darwen, and others. 如前所述,它由Edgar F.Codd博士创建,后来由Chris Date、Hugh Darwen和其他人解释和开发。The first version of the relational model was proposed by Codd in 1969 in an IBM research report called “Derivability, Redundancy, and Consistency of Relations Stored in Large Data Banks.” 第一个版本的关系模型是由Codd在1969年在IBM的一份名为“大型数据库中存储的关系的可派生性、冗余性和一致性”的研究报告中提出的。A revised version was proposed by Codd in 1970 in a paper called “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks,” published in the journal Communications of the ACM.Codd在1970年发表在《ACM通讯》杂志上的一篇题为“大型共享数据库的数据关系模型”的论文中提出了一个修订版本。
The goal of the relational model is to enable consistent representation of data with minimal or no redundancy and without sacrificing completeness, and to define data integrity (enforcement of data consistency) as part of the model. 关系模型的目标是在不牺牲完整性的情况下,以最小的冗余或无冗余实现数据的一致性表示,并将数据完整性(数据一致性的实施)定义为模型的一部分。An RDBMS is supposed to implement the relational model and provide the means to store, manage, enforce the integrity of, and query data. RDBMS应该实现关系模型,并提供存储、管理、加强数据完整性和查询数据的方法。The fact that the relational model is based on a strong mathematical foundation means that given a certain data-model instance (from which a physical database will later be generated), you can tell with certainty when a design is flawed, rather than relying solely on intuition.关系模型基于一个强大的数学基础的事实意味着给定一个特定的数据模型实例(从中产生一个物理数据库),你可以肯定地知道当一个设计有缺陷时,而不是仅仅依靠直觉。
The relational model involves concepts such as propositions, predicates, relations, tuples, attributes, and more. 关系模型涉及命题、谓词、关系、元组、属性等概念。For nonmathematicians, these concepts can be quite intimidating. 对于非数学学者来说,这些概念可能相当吓人。The sections that follow cover some key aspects of the model in an informal, nonmathematical manner and explain how they relate to databases.接下来的章节以非正式的、非数学的方式介绍了模型的一些关键方面,并解释了它们与数据库的关系。
Propositions, predicates, and relations命题、谓词和关系
The common belief that the term relational stems from relationships between tables is incorrect. 通常认为“关系”一词源于表之间的关系是不正确的。“Relational” actually pertains to the mathematical term relation. “关系”实际上属于数学术语“关系”。In set theory, a relation is a representation of a set. 在集合论中,关系是集合的表示。In the relational model, a relation is a set of related information, with the counterpart in SQL being a table—albeit not an exact counterpart. 在关系模型中,关系是一组相关信息,SQL中的对应项是一个表,尽管不是精确的对应项。A key point in the relational model is that a single relation should represent a single set (for example, Customers). 关系模型中的一个关键点是,单个关系应该表示单个集合(例如,Customers)。Note that operations on relations (based on relational algebra) result in a relation (for example, a join between two relations).请注意,对关系的操作(基于关系代数)会产生一个关系(例如,两个关系之间的连接)。
 Note
Note
The relational model distinguishes between a relation and a relation variable, but to keep things simple, I won't get into this distinction. 关系模型区分“关系”和“关系变量”,但为了简单起见,我不讨论这种区别。Instead, I'll use the term relation for both cases. 相反,我将对这两种情况使用术语“关系”。Also, a relation is made of a heading and a body. 此外,关系由标题和正文组成。The heading consists of a set of attributes (called columns in SQL), where each element is identified by an attribute name and a type name. 标题由一组属性(在SQL中称为列)组成,其中每个元素由属性名和类型名标识。The body consists of a set of tuples (called rows in SQL), where each element is identified by a key. 主体由一组元组(在SQL中称为行)组成,其中每个元素由一个键标识。To keep things simple, I'll refer to a table as a set of rows.为了简单起见,我将表称为一组行。
When you design a data model for a database, you represent all data with relations (tables). 为数据库设计数据模型时,使用关系(表)表示所有数据。You start by identifying propositions that you will need to represent in your database. 首先确定需要在数据库中表示的命题。A proposition is an assertion or a statement that must be true or false. 命题是必须是真或假的断言或陈述。For example, the statement, “Employee Itzik Ben-Gan was born on February 12, 1971, and works in the IT department” is a proposition. 例如,声明“员工伊兹克·本·甘出生于1971年2月12日,在IT部门工作”就是一个命题。If this proposition is true, it will manifest itself as a row in a table of Employees. 如果这个命题是真的,它将在员工表中显示为一行。A false proposition simply won't manifest itself. 一个错误的命题根本不会表现出来。This presumption is known as the closed-world assumption (CWA).这种假设被称为封闭世界假设(CWA)。
The next step is to formalize the propositions. 下一步是将命题形式化。You do this by taking out the actual data (the body of the relation) and defining the structure (the heading of the relation)—for example, by creating predicates out of propositions. 你可以通过提取实际数据(关系的主体)和定义结构(关系的标题)来实现这一点——例如,通过从命题中创建谓词。You can think of predicates as parameterized propositions. 可以将谓词视为参数化命题。The heading of a relation comprises a set of attributes. 关系的标题由一组属性组成。Note the use of the term “set”; in the relational model, attributes are unordered and distinct. 注意“集合”一词的用法;在关系模型中,属性是无序且不同的。An attribute is identified by an attribute name and a type name. 属性由属性名和类型名标识。For example, the heading of an Employees relation might consist of the following attributes (expressed as pairs of attribute names and type names): employeeid integer, firstname character string, lastname character string, birthdate date, and departmentid integer.例如,员工关系的标题可能包含以下属性(以属性名称和类型名称对表示):employeeid整型数、firstname字符串、lastname字符串、birthdate日期和departmentid整型数。
A type is one of the most fundamental building blocks for relations. 类型是关系最基本的组成部分之一。A type constrains an attribute to a certain set of possible or valid values. 类型将属性约束为一组可能的或有效的值。For example, the type INT is the set of all integers in the range –2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. 例如,INT类型是-2147483648到2147483647范围内所有整数的集合。A type is one of the simplest forms of a predicate in a database because it restricts the attribute values that are allowed. 类型是数据库中谓词的最简单形式之一,因为它限制了允许的属性值。For example, the database would not accept a proposition where an employee birth date is February 31, 1971 (not to mention a birth date stated as something like “abc!”). 例如,数据库不会接受员工出生日期为1971年2月31日的提议(更不用说像“abc!”这样的出生日期了)。Note that types are not restricted to base types such as integers or character strings; a type also can be an enumeration of possible values, such as an enumeration of possible job positions. 注意,类型不限于基类型,例如整数或字符串;类型也可以是可能值的枚举,例如可能职位的枚举。A type can be simple or complex. 类型可以是简单的,也可以是复杂的。Probably the best way to think of a type is as a class—encapsulated data and the behavior supporting it. 可能认为类型最好的方式是将数据和支持它的行为封装为类。An example of a complex type is a geometry type that supports polygons.复杂类型的一个示例是支持多边形的几何体类型。
Missing values缺失值
One aspect of the relational model is the source of many passionate debates—whether predicates should be restricted to two-valued logic. 关系模型的一个方面是关于谓词是否应该被限制为两值逻辑的许多激烈争论的根源。That is, in two-valued predicate logic, a predicate is either true or false. 也就是说,在二值谓词逻辑中,谓词不是真就是假。If a predicate is not true, it must be false. 如果一个谓词不是真的,它一定是假的。Use of two-valued predicate logic follows a mathematical law called “the law of excluded middle.” 二值谓词逻辑的使用遵循一个叫做“排除中间法则”的数学定律。However, some say that there's room for three-valued (or even four-valued) predicate logic, taking into account cases where values are missing. 然而,有人说,考虑到缺少值的情况,三值(甚至四值)谓词逻辑还有空间。A predicate involving a missing value yields neither true nor false—it yields unknown.涉及缺失值的谓词既不产生true,也不产生false,而是产生unknown。
Take, for example, a mobile phone attribute of an Employees relation. 以员工关系的手机属性为例。Suppose that a certain employee's mobile phone number is missing. 假设某个员工的手机号码丢失。How do you represent this fact in the database? 如何在数据库中表示这一事实?In a three-valued logic implementation, the mobile phone attribute should allow the use of a special marker for a missing value. 在三值逻辑实现中,mobile phone属性应该允许对缺失的值使用特殊标记。Then a predicate comparing the mobile phone attribute with some specific number will yield unknown for the case with the missing value. 然后,一个谓词将移动电话属性与某个特定的数字进行比较,将为缺少值的情况生成unknown。Three-valued predicate logic refers to the three possible logical values that can result from a predicate—true, false, and unknown.三值谓词逻辑是指谓词true、false和unknown可能产生的三个逻辑值。
Some people believe that three-valued predicate logic is nonrelational, whereas others believe that it is relational. 一些人认为三值谓词逻辑是非关系的,而另一些人则认为它是关系的。Codd actually advocated for four-valued predicate logic, saying that there were two different cases of missing values: missing but applicable (A-Values marker), and missing but inapplicable (I-Values marker). Codd实际上提倡四值谓词逻辑,说缺失值有两种不同的情况:缺失但适用(A值标记)和缺失但不适用(I值标记)。An example of “missing but applicable” is when an employee has a mobile phone, but you don't know what the mobile phone number is. “缺失但适用”的一个例子是,员工有手机,但你不知道手机号码。An example of “missing but inapplicable” is when an employee doesn't have a mobile phone at all. “缺失但不适用”的一个例子是员工根本没有手机。According to Codd, two special markers should be used to support these two cases of missing values. 根据Codd,应使用两种特殊标记来支持这两种缺失值的情况。SQL implements three-valued predicate logic by supporting the NULL marker to signify the generic concept of a missing value. SQL通过支持NULL标记来表示缺失值的一般概念,从而实现了三值谓词逻辑。Support for NULLs and three-valued predicate logic in SQL is the source of a great deal of confusion and complexity, though one can argue that missing values are part of reality. SQL中对NULL值和三值谓词逻辑的支持导致了大量的混乱和复杂性,尽管有人可能会认为缺少值是现实的一部分。In addition, the alternative—using only two-valued predicate logic—is no less problematic.此外,仅使用二值谓词逻辑的替代方案也同样存在问题。
 Note
Note
As mentioned, a NULL is not a value but rather a marker for a missing value. 如前所述,NULL不是一个值,而是一个缺失值的标记。Therefore, though unfortunately it's common, the use of the terminology “NULL value” is incorrect. 因此,尽管不幸的是这很常见,但术语“NULL值”的使用是不正确的。The correct terminology is “NULL marker” or just “NULL.” 正确的术语是“NULL标记”或只是“NULL”In the book, I chose to use the latter because it's more common in the SQL community.在本书中,我选择使用后者,因为它在SQL社区中更常见。
Constraints约束条件
One of the greatest benefits of the relational model is the ability to define data integrity as part of the model. 关系模型的最大好处之一是能够将数据完整性定义为模型的一部分。Data integrity is achieved through rules called constraints that are defined in the data model and enforced by the RDBMS. 数据完整性是通过在数据模型中定义并由RDBMS实施的称为“约束”的规则来实现的。The simplest methods of enforcing integrity are assigning an attribute type with its attendant “nullability” (whether it supports or doesn't support NULLs). 强制完整性的最简单方法是为属性类型分配相应的“nullability”(无论它是否支持Null)。Constraints are also enforced through the model itself; for example, the relation Orders(orderid, orderdate, duedate, shipdate) allows three distinct dates per order, whereas the relations Employees(empid) and EmployeeChildren(empid, childname) allow zero to countable infinity children per employee.约束也通过模型本身来实施;例如,关系Orders(orderid, orderdate, duedate, shipdate)允许每个订单有三个不同的日期,而关系Employees(empid)和EmployeeChildren(empid, childname)允许每个雇员有零到无限多个子女。
Other examples of constraints include candidate keys, which provide entity integrity, and foreign keys, which provide referential integrity. 约束的其他示例包括提供实体完整性的“候选键”和提供引用完整性的“外键”。A candidate key is a key defined on one or more attributes that prevents more than one occurrence of the same tuple (row in SQL) in a relation. 候选键是在一个或多个属性上定义的键,用于防止同一元组(SQL中的“行”)在关系中多次出现。A predicate based on a candidate key can uniquely identify a row (such as an employee). 基于候选键的谓词可以唯一标识行(例如雇员)。You can define multiple candidate keys in a relation. 可以在关系中定义多个候选键。For example, in an Employees relation, you can define candidate keys on employeeid, on SSN (Social Security number), and others. 例如,在员工关系中,可以在employeeid、SSN(社会安全号)和其他信息上定义候选键。Typically, you arbitrarily choose one of the candidate keys as the primary key (for example, employeeid in the Employees relation) and use that as the preferred way to identify a row. 通常,您可以任意选择一个候选键作为主键(例如,employeeid在员工关系中),并将其用作标识行的首选方式。All other candidate keys are known as alternate keys.所有其他候选密钥称为“备用键”。
Foreign keys are used to enforce referential integrity. 外键用于强制引用完整性。A foreign key is defined on one or more attributes of a relation (known as the referencing relation) and references a candidate key in another (or possibly the same) relation. 外键定义在关系(称为引用关系)的一个或多个属性上,并引用另一个(或可能相同)关系中的候选键。This constraint restricts the values in the referencing relation's foreign-key attributes to the values that appear in the referenced relation's candidate-key attributes. 此约束将引用关系的外键属性中的值限制为引用关系的候选键属性中出现的值。For example, suppose that the Employees relation has a foreign key defined on the attribute departmentid, which references the primary-key attribute departmentid in the Departments relation. 例如,假设Employees关系在属性departmentid上定义了一个外键,它引用Departments关系中的主键属性departmentid。This means that the values in Employees.departmentid are restricted to the values that appear in Departments.departmentid.这意味着Employees.departmentid中的值仅限于Departments.departmentid中显示的值。
Normalization规范化
The relational model also defines normalization rules (also known as normal forms). 关系模型还定义了“规范化规则”(也称为“范式”)。Normalization is a formal mathematical process to guarantee that each entity will be represented by a single relation. 规范化是一个正式的数学过程,可以保证每个实体都由一个关系表示。In a normalized database, you avoid anomalies during data modification and keep redundancy to a minimum without sacrificing completeness. 在规范化数据库中,可以避免数据修改期间出现异常,并在不牺牲完整性的情况下将冗余降至最低。If you follow Entity Relationship Modeling (ERM), and represent each entity and its attributes, you probably won't need normalization; instead, you will apply normalization only to reinforce and ensure that the model is correct. 如果遵循实体关系建模(Entity Relationship Modeling,ERM),并表示每个实体及其属性,则可能不需要规范化;相反,应用规范化只是为了加强并确保模型是正确的。You can find the definition of ERM in the following Wikipedia article: 你可以在以下维基百科文章中找到ERM的定义:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Entity%E2%80%93relationship_model.。
The following sections briefly cover the first three normal forms (1NF, 2NF, and 3NF) introduced by Codd.以下章节简要介绍了Codd引入的前三种范式(1NF、2NF和3NF)。
1NF
The first normal form says that the tuples (rows) in the relation (table) must be unique and attributes should be atomic. 第一种范式表示关系(表)中的元组(行)必须是唯一的,属性应该是原子的。This is a redundant definition of a relation; in other words, if a table truly represents a relation, it is already in first normal form.这是对关系的多余定义;换句话说,如果一个表真的代表了一个关系,那么它已经是第一范式了。
You achieve unique rows in SQL by defining a unique key for the table.通过为表定义唯一键,可以在SQL中实现唯一行。
You can operate on attributes only with operations that are defined as part of the attribute's type. 只能使用定义为属性类型一部分的操作对属性进行操作。Atomicity of attributes is subjective in the same way that the definition of a set is subjective. 属性的原子性是主观的,就像集合的定义是主观的一样。As an example, should an employee name in an Employees relation be expressed with one attribute (fullname), two (firstname and lastname), or three (firstname, middlename, and lastname)? 例如,Employees关系中的员工姓名应该用一个属性(fullname)、两个属性(firstname和lastname)或三个属性(firstname、middlename和lastname)表示吗?The answer depends on the application. 答案取决于应用程序。If the application needs to manipulate the parts of the employee's name separately (such as for search purposes), it makes sense to break them apart; otherwise, it doesn't.如果应用程序需要单独运算符工姓名的各个部分(例如用于搜索目的),则将其拆分是有意义的;否则就不会了。
In the same way that an attribute might not be atomic enough based on the needs of the applications that use it, an attribute might also be subatomic. 根据使用属性的应用程序的需要,属性可能不够原子化,同样,属性也可能是亚原子的。For example, if an address attribute is considered atomic for the applications that use it, not including the city as part of the address would violate the first normal form.例如,如果一个地址属性被认为是使用它的应用程序的原子属性,不将城市作为地址的一部分将违反第一个范式。
This normal form is often misunderstood. 这种常态经常被误解。Some people think that an attempt to mimic arrays violates the first normal form. 有些人认为,试图模仿数组违反了第一种范式。An example would be defining a YearlySales relation with the following attributes: salesperson, qty2014, qty2015, and qty2016. 例如,使用以下属性定义YearlySales关系:salesperson、qty2014、qty2015和qty2016。However, in this example, you don't really violate the first normal form; you simply impose a constraint—restricting the data to three specific years: 2014, 2015, and 2016.然而,在这个例子中,你并没有真正违反第一范式;您只需将数据限制在三个特定年份:2014年、2015年和2016年。
2NF
The second normal form involves two rules. One rule is that the data must meet the first normal form. 第二种范式涉及两条规则。一条规则是数据必须满足第一个标准形式。The other rule addresses the relationship between nonkey and candidate-key attributes. 另一条规则处理非关键属性和候选关键属性之间的关系。For every candidate key, every nonkey attribute has to be fully functionally dependent on the entire candidate key. 对于每个候选密钥,每个非密钥属性都必须在功能上完全依赖于整个候选密钥。In other words, a nonkey attribute cannot be fully functionally dependent on part of a candidate key. 换句话说,非键属性在功能上不能完全依赖于候选键的一部分。To put it more informally, if you need to obtain any nonkey attribute value, you need to provide the values of all attributes of a candidate key from the same tuple. 如果需要非正式地从某个键的所有属性中获取非元组值,则需要非正式地从该键的所有属性中获取非元组值。You can find any value of any attribute of any tuple if you know all the attribute values of a candidate key.如果知道候选键的所有属性值,则可以找到任何元组的任何属性的任何值。
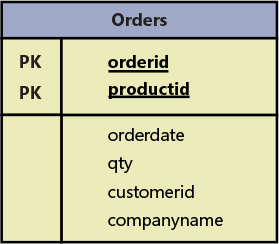
As an example of violating the second normal form, suppose that you define a relation called Orders that represents information about orders and order lines. 作为违反第二范式的示例,假设您定义了一个名为Orders的关系,该关系表示有关订单和订单行的信息。(See Figure 1-1.) (见Figure 1-1。)The Orders relation contains the following attributes: orderid, productid, orderdate, qty, customerid, and companyname. Orders关系包含以下属性:orderid、productid、orderdate、qty、customerid和companyname。The primary key is defined on orderid and productid.主键是在orderid和productid上定义的。
FIGURE 1-1 Data model before applying 2NF.应用2NF之前的数据模型。
The second normal form is violated in Figure 1-1 because there are nonkey attributes that depend on only part of a candidate key (the primary key, in this example). Figure 1-1中违反了第二个标准形式,因为存在仅依赖于候选密钥(本例中为主键)一部分的非密钥属性。For example, you can find the orderdate of an order, as well as customerid and companyname, based on the orderid alone.例如,您可以仅基于orderid来查找订单的orderdate,以及customerid和companyname。
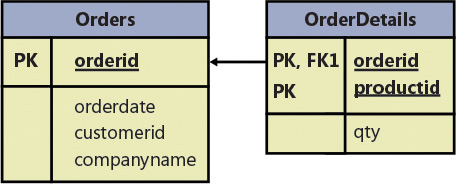
To conform to the second normal form, you would need to split your original relation into two relations: Orders and OrderDetails (as shown in Figure 1-2). 为了符合第二种范式,您需要将原始关系拆分为两种关系:Orders和OrderDetails(如Figure 1-2所示)。The Orders relation would include the attributes orderid, orderdate, customerid, and companyname, with the primary key defined on orderid. Orders关系将包括属性orderid、orderdate、customerid和companyname,主键定义在orderid上。The OrderDetails relation would include the attributes orderid, productid, and qty, with the primary key defined on orderid and productid.OrderDetails关系将包括属性orderid、productid和qty,主键定义在orderid和productid上。
FIGURE 1-2 Data model after applying 2NF and before 3NF.应用2NF后和3NF前的数据模型。
3NF
The third normal form also has two rules. 第三范式也有两条规则。The data must meet the second normal form. 数据必须满足第二个标准形式。Also, all nonkey attributes must be dependent on candidate keys nontransitively. 此外,所有非关键属性必须非传递地依赖于候选关键点。Informally, this rule means that all nonkey attributes must be mutually independent. 非正式地说,这条规则意味着所有非关键属性必须相互独立。In other words, one nonkey attribute cannot be dependent on another nonkey attribute.换句话说,一个非关键属性不能依赖于另一个非关键属性。
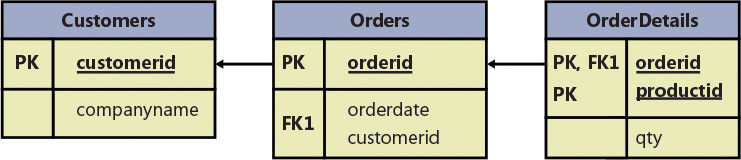
The Orders and OrderDetails relations described previously now conform to the second normal form. 前面描述的Orders和OrderDetails关系现在符合第二种范式。Remember that the Orders relation at this point contains the attributes orderid, orderdate, customerid, and companyname, with the primary key defined on orderid. 记住,此时的Orders关系包含orderid、orderdate、customerid和companyname属性,主键定义在orderid上。Both customerid and companyname depend on the whole primary key—orderid. customerid和companyname都依赖于整个主键orderid。For example, you need the entire primary key to find the customerid representing the customer who placed the order. 例如,您需要整个主键来查找代表下订单的客户的customerid。Similarly, you need the whole primary key to find the company name of the customer who placed the order. 同样,您需要整个主键来查找下订单的客户的公司名称。However, customerid and companyname are also dependent on each other. 然而,customerid和companyname也相互依赖。To meet the third normal form, you need to add a Customers relation (shown in Figure 1-3) with the attributes customerid (as the primary key) and companyname. 为了满足第三种标准形式,您需要添加一个Customers关系(如Figure 1-3所示),其属性为customerid(作为主键)和companyname。Then you can remove the companyname attribute from the Orders relation.然后可以从Orders关系中删除companyname属性。
FIGURE 1-3 Data model after applying 3NF.应用3NF后的数据模型。
Informally, 2NF and 3NF are commonly summarized with the sentence, “Every non-key attribute is dependent on the key, the whole key, and nothing but the key—so help me Codd.”非正式地说,2NF和3NF通常用这样一句话来概括:“每个非键属性都依赖于键,整个键,除了键什么都不依赖,所以帮帮我Codd。”
There are higher normal forms beyond Codd's original first three normal forms that involve compound primary keys and temporal databases, but they are outside the scope of this book.除了Codd最初的前三个范式之外,还有更高的范式,涉及复合主键和时态数据库,但它们不在本书的范围之内。
 Note
Note
SQL, as well as T-SQL, permit violating all the normal forms in real tables. SQL和T-SQL都允许违反实表中的所有规范形式。It's the data modeler's prerogative and responsibility to design a normalized model.设计规范化模型是数据建模者的特权和责任。
Types of database systems数据库系统的类型
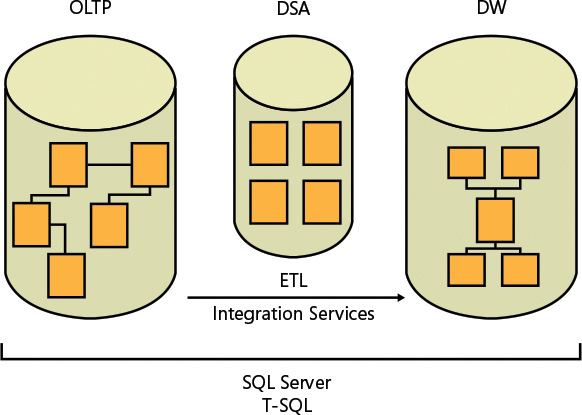
Two main types of systems, or workloads, use SQL Server as their database and T-SQL to manage and manipulate the data: online transactional processing (OLTP) and data warehouses (DWs). 两种主要类型的系统或工作负载使用SQL Server作为其数据库,使用T-SQL管理和操作数据:在线事务处理(OLTP)和数据仓库(DWs)。Figure 1-4 illustrates those systems and the transformation process that usually takes place between them.Figure 1-4说明了这些系统以及它们之间通常发生的转换过程。
FIGURE 1-4 Classes of database systems.数据库系统的类别。
Here's a quick description of what each acronym represents:下面是对每个首字母缩写词所代表的内容的快速描述:

OLTP: online transactional processing联机事务处理

DSA: data-staging areaDSA:数据暂存区

DW: data warehouse数据仓库

ETL: extract, transform, and loadETL:提取、转换和加载
Online transactional processing在线事务处理
Data is entered initially into an online transactional processing system. 数据最初输入在线事务处理系统。The primary focus of an OLTP system is data entry and not reporting—transactions mainly insert, update, and delete data. OLTP系统的主要重点是数据输入,而不是报告事务,主要是插入、更新和删除数据。The relational model is targeted primarily at OLTP systems, where a normalized model provides both good performance for data entry and data consistency. 关系模型主要针对OLTP系统,其中规范化模型提供了良好的数据输入性能和数据一致性。In a normalized environment, each table represents a single entity and keeps redundancy to a minimum. 在规范化环境中,每个表代表一个实体,并将冗余保持在最低限度。When you need to modify a fact, you need to modify it in only one place. 当你需要修改一个事实时,你只需要在一个地方修改它。This results in optimized performance for data modifications and little chance for error.这使得数据修改的性能得到优化,出错的可能性很小。
However, an OLTP environment is not suitable for reporting purposes because a normalized model usually involves many tables (one for each entity) with complex relationships. 然而,OLTP环境不适合用于报告目的,因为规范化模型通常涉及多个具有复杂关系的表(每个实体一个)。Even simple reports require joining many tables, resulting in complex and poorly performing queries.即使是简单的报表也需要连接多个表,从而导致查询复杂且性能不佳。
You can implement an OLTP database in SQL Server and both manage it and query it with T-SQL.您可以在SQL Server中实现OLTP数据库,并使用T-SQL对其进行管理和查询。
Data warehouses数据仓库
A data warehouse (DW) is an environment designed for data-retrieval and reporting purposes. 数据仓库(DW)是为数据检索和报告目的而设计的环境。When it serves an entire organization, such an environment is called a data warehouse; when it serves only part of the organization (such as a specific department) or a subject matter area in the organization, it is called a data mart. 当它服务于整个组织时,这种环境称为数据仓库;当它只服务于组织的一部分(如特定部门)或组织中的一个主题领域时,它被称为数据集市。The data model of a data warehouse is designed and optimized mainly to support data-retrieval needs. 数据仓库的数据模型主要是为了支持数据检索需求而设计和优化的。The model has intentional redundancy, fewer tables, and simpler relationships, ultimately resulting in simpler and more efficient queries than an OLTP environment.该模型具有有意的冗余、更少的表和更简单的关系,最终导致比OLTP环境更简单、更高效的查询。
The simplest data-warehouse design is called a star schema. 最简单的数据仓库设计称为星型模式。The star schema includes several dimension tables and a fact table. 星型模式包括几个维度表和一个事实表。Each dimension table represents a subject by which you want to analyze the data. 每个维度表都代表一个主题,您希望通过它来分析数据。For example, in a system that deals with orders and sales, you will probably want to analyze data by dimensions such as customers, products, employees, and time.例如,在一个处理订单和销售的系统中,您可能希望按客户、产品、员工和时间等维度分析数据。
In a star schema, each dimension is implemented as a single table with redundant data. 在星型模式中,每个维度都实现为一个带有冗余数据的表。For example, a product dimension could be implemented as a single ProductDim table instead of three normalized tables: Products, ProductSubCategories, and ProductCategories. 例如,产品维度可以实现为单个ProductDim表,而不是三个规范化的表:Products、ProductSubCategories和ProductCategories。If you normalize a dimension table, which results in multiple tables representing that dimension, you get what's known as a snowflake dimension. 如果对一个维度表进行规范化,这会导致多个表表示该维度,那么就得到了所谓的雪花维度。A schema that contains snowflake dimensions is known as a snowflake schema. 包含雪花维度的架构称为雪花架构。A star schema is considered a special case of a snowflake schema.星型架构被认为是雪花架构的特例。
The fact table holds the facts and measures, such as quantity and value, for each relevant combination of dimension keys. 事实表为每个维度键的相关组合保存事实和度量,例如数量和值。For example, for each relevant combination of customer, product, employee, and day, the fact table would have a row containing the quantity and value. 例如,对于customer、product、employee和day的每个相关组合,事实表都会有一行包含数量和值。Note that data in a data warehouse is typically preaggregated to a certain level of granularity (such as a day), unlike data in an OLTP environment, which is usually recorded at the transaction level.请注意,与OLTP环境中的数据不同,数据仓库中的数据通常预先聚合到一定的粒度级别(例如一天),OLTP环境中的数据通常在事务级别记录。
Historically, early versions of SQL Server mainly targeted OLTP environments, but eventually SQL Server also started targeting data-warehouse systems and data-analysis needs. 从历史上看,早期版本的SQL Server主要针对OLTP环境,但最终SQL Server也开始针对数据仓库系统和数据分析需求。You can implement a data warehouse as a SQL Server database and manage and query it with T-SQL.您可以将数据仓库实现为SQL Server数据库,并使用T-SQL对其进行管理和查询。
The process that pulls data from source systems (OLTP and others), manipulates it, and loads it into the data warehouse is called extract, transform, and load, or ETL. 从源系统(OLTP和其他)提取数据、对其进行操作并将其加载到数据仓库的过程称为提取、转换和加载,或ETL。SQL Server provides a tool called Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) to handle ETL needs.SQL Server提供了一个名为Microsoft SQL Server集成服务(SSIS)的工具来处理ETL需求。
Often the ETL process will involve the use of a data-staging area (DSA) between the OLTP and the DW. ETL过程通常涉及在OLTP和DW之间使用数据暂存区(DSA)。The DSA usually resides in a relational database, such as a SQL Server database, and is used as the data-cleansing area. DSA通常位于关系数据库(如SQL Server数据库)中,并用作数据清理区域。The DSA is not open to end users.DSA不对最终用户开放。
SQL Server architectureSQL Server体系结构
This section will introduce you to the SQL Server architecture, the different RDBMS flavors that Microsoft offers, the entities involved—SQL Server instances, databases, schemas, and database objects—and the purpose of each entity.本节将向您介绍SQL Server体系结构、Microsoft提供的不同RDBMS风格、涉及SQL Server实例、数据库、模式和数据库对象的实体以及每个实体的用途。
The ABCs of Microsoft RDBMS flavors微软RDBMS的基础架构
Initially, Microsoft offered mainly one enterprise-level RDBMS—an on-premises flavor called Microsoft SQL Server. 最初,微软主要提供一种企业级RDBMS,即微软SQL Server。These days, Microsoft offers an overwhelming plethora of options as part of its data platform, which constantly keeps evolving. 如今,微软在其不断发展的数据平台中提供了大量选项。Within its data platform, Microsoft offers three main RDBMS flavors, which you can think of as the ABC flavors: A for Appliance, B for Box (on-premises), and C for Cloud.在其数据平台中,微软提供了三种主要的RDBMS风格,您可以将其视为ABC风格:A代表设备,B代表盒子(内部部署),C代表云。
Box
The box, or on-premises RDBMS flavor, that Microsoft offers is called Microsoft SQL Server, or just SQL Server. 微软提供的盒子或内部RDBMS风格被称为微软SQL Server,或仅仅是SQL Server。This is the traditional flavor, usually installed on the customer's premises. 这是传统风味,通常安装在客户的场所。The customer is responsible for everything—getting the hardware, installing the software, patching, high availability and disaster recovery, security, and everything else.客户负责获取硬件、安装软件、修补、高可用性和灾难恢复、安全以及其他一切。
The customer can install multiple instances of the product on the same server (more on this in the next section) and can write queries that interact with multiple databases. 客户可以在同一台服务器上安装多个产品实例(下一节将对此进行详细介绍),并可以编写与多个数据库交互的查询。It is also possible to switch the connection between databases, unless one of them is a contained database (defined later).也可以在数据库之间切换连接,除非其中一个是包含的数据库(稍后定义)。
The querying language used is T-SQL. 使用的查询语言是T-SQL。You can run all the code samples and exercises in this book on an on-premises SQL Server implementation, if you want. 如果需要,可以在本地SQL Server实现上运行本书中的所有代码示例和练习。See the Appendix for details about obtaining and installing an evaluation edition of SQL Server, as well as creating the sample database.有关获取和安装SQL Server评估版以及创建示例数据库的详细信息,请参阅附录。
Appliance器具
The idea behind the appliance flavor is to provide the customer a complete turnkey solution with preconfigured hardware and software. 设备风格背后的理念是为客户提供一个完整的交钥匙解决方案,包括预配置的硬件和软件。Speed is achieved by things being co-located, with the storage being close to the processing. 速度是通过将东西放在同一个位置来实现的,存储距离处理很近。The appliance is hosted locally at the customer site. 该设备在客户站点本地托管。Microsoft partners with hardware vendors such as Dell and HP to provide the appliance offering. 微软与戴尔和惠普等硬件供应商合作提供该设备。Experts from Microsoft and the hardware vendor handle the performance, security, and availability aspects for the customer.来自微软和硬件供应商的专家为客户处理性能、安全性和可用性方面的问题。
There are several appliances available today, one of which is the Microsoft Analytics Platform System (APS), which focuses on data warehousing and big data technologies. 目前有几种设备可用,其中之一是微软分析平台系统(APS),该系统专注于数据仓库和大数据技术。This appliance includes a data-warehouse engine called Parallel Data Warehouse (PDW), which implements massively parallel processing (MPP) technology. 该设备包括一个名为并行数据仓库(PDW)的数据仓库引擎,它实现了大规模并行处理(MPP)技术。It also includes HDInsight, which is Microsoft's Hadoop distribution (big data solution). 它还包括HDInsight,这是微软的Hadoop发行版(大数据解决方案)。APS also includes a querying technology called PolyBase, which allows using T-SQL queries across relational data from PDW and nonrelational data from HDInsight.APS还包括一种名为PolyBase的查询技术,它允许跨PDW的关系数据和HDInsight的非关系数据使用T-SQL查询。
Cloud云
Cloud computing provides computing resources on demand from a shared pool of resources. 云计算通过共享资源池按需提供计算资源。Microsoft's RDBMS technologies can be provided both as private-cloud and public-cloud services. 微软的RDBMS技术可以作为私有云和公共云服务提供。A private cloud is cloud infrastructure that services a single organization and usually uses virtualization technology. 私有云是为单个组织提供服务的云基础设施,通常使用虚拟化技术。It's typically hosted locally at the customer site, and maintained by the IT group in the organization. 它通常在客户站点本地托管,并由组织中的It团队维护。It's about self-service agility, allowing the users to deploy resources on demand. 这是关于自助服务的灵活性,允许用户根据需要部署资源。It provides standardization and usage metering. 它提供标准化和使用计量。The database engine is usually a box engine (hence the same T-SQL is used to manage and manipulate the data).数据库引擎通常是一个box引擎(因此使用相同的T-SQL来管理和操作数据)。
As for the public cloud, the services are provided over the network and available to the public. 至于公共云,这些服务是通过网络提供的,公众可以使用。Microsoft provides two forms of public RDBMS cloud services: infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS). 微软提供两种形式的公共RDBMS云服务:基础设施即服务(IaaS)和平台即服务(PaaS)。With IaaS, you provision a virtual machine (VM) that resides in Microsoft's cloud infrastructure. 使用IaaS,您可以提供驻留在Microsoft云基础设施中的虚拟机(VM)。As a starting point, you can choose between several preconfigured VMs that already have a certain version and edition of SQL Server (box engine) installed on them. 首先,您可以在几个预配置的虚拟机之间进行选择,这些虚拟机上已经安装了特定版本的SQL Server(box engine)。The hardware is maintained by Microsoft, but you're responsible for maintaining and patching the software. 硬件由微软维护,但你负责维护和修补软件。It's essentially like maintaining your own SQL Server installation—one that happens to reside on Microsoft's hardware.这本质上就像维护自己的SQL Server安装,而SQL Server安装恰好位于Microsoft的硬件上。
With PaaS, Microsoft provides the database cloud platform as a service. 通过PaaS,微软将数据库云平台作为一项服务提供。It's hosted in Microsoft's data centers. 它托管在微软的数据中心。Hardware, software installation and maintenance, high availability and disaster recovery, and patching are all responsibilities of Microsoft. 硬件、软件安装和维护、高可用性和灾难恢复以及修补都是微软的责任。The customer is still responsible for index and query tuning, however.然而,客户仍然负责索引和查询调优。
Microsoft provides a number of PaaS database offerings. 微软提供了许多PaaS数据库产品。For OLTP systems, it offers the Azure SQL Database service. 对于OLTP系统,它提供Azure SQL数据库服务。It's also referred to more shortly as just SQL Database. 简称为SQL,简称为SQL数据库。The customer can have multiple databases on the cloud server (a conceptual server, of course) but cannot switch between databases.客户可以在云服务器(当然是概念服务器)上拥有多个数据库,但不能在数据库之间切换。
Interestingly, Microsoft uses the same code base for SQL Database and SQL Server. 有趣的是,微软对SQL数据库和SQL Server使用相同的代码库。So most of the T-SQL language surface is exposed (eventually) in both environments in the same manner. 因此,T-SQL语言的大部分表面(最终)以相同的方式暴露在两种环境中。Therefore, most of the T-SQL you'll learn about in this book is applicable to both environments. 因此,您将在本书中了解的大部分T-SQL都适用于这两种环境。You can read about the differences that do exist here: 你可以在这里了解存在的差异:https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/sql-database-transact-sql-information。You should also note that the update and deployment rate of new versions of SQL Database are faster than that of the on-premises SQL Server. 您还应该注意,新版本SQL数据库的更新和部署速度比本地SQL Server快。Therefore, some T-SQL features might be exposed in SQL Database before they show up in the on-premises SQL Server version.因此,一些T-SQL功能可能会在SQL数据库中公开,然后才显示在本地SQL Server版本中。
Microsoft also provides a PaaS offering for data-warehouse systems called Microsoft Azure SQL Data Warehouse (also called Azure SQL Data Warehouse or just SQL Data Warehouse). Microsoft还为数据仓库系统提供PaaS产品,称为Microsoft Azure SQL数据仓库(也称为Azure SQL数据仓库或SQL数据仓库)。This service is basically PDW/APS in the cloud. 该服务基本上是云中的PDW/APS。Microsoft uses the same code base for both the appliance and the cloud service. 微软对设备和云服务使用相同的代码库。You manage and manipulate data in APS and SQL Data Warehouse with T-SQL, although it's not the same T-SQL surface as in SQL Server and SQL Database, yet.您可以使用T-SQL管理和操作APS和SQL数据仓库中的数据,尽管它与SQL Server和SQL数据库中的T-SQL表面不同。
Microsoft also offers other cloud data services, such as Data Lake for big data–related services, Azure DocumentDB for NoSQL document database services, and others.微软还提供其他云数据服务,如用于大数据相关服务的data Lake、用于NoSQL文档数据库服务的Azure DocumentDB等。
Confused? If it's any consolation, you're not alone. Like I said, Microsoft provides an overwhelming plethora of database-related technologies. 困惑的如果有什么安慰的话,你并不孤单。正如我所说,微软提供了大量与数据库相关的技术。Curiously, the one thread that is common to many of them is T-SQL.
SQL Server instancesSQL Server实例
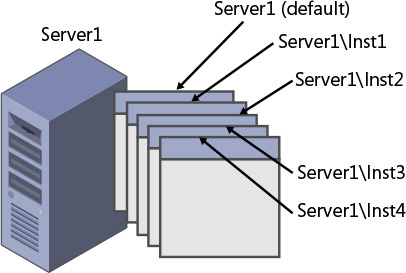
In the box product, an instance of SQL Server, as illustrated in Figure 1-5, is an installation of a SQL Server database engine or service. 在box产品中,SQL Server实例(如Figure 1-5所示)是SQL Server数据库引擎或服务的安装。You can install multiple instances of on-premises SQL Server on the same computer. 您可以在同一台计算机上安装多个本地SQL Server实例。Each instance is completely independent of the others in terms of security and the data that it manages, and in all other respects. 每个实例在安全性、它管理的数据以及所有其他方面都完全独立于其他实例。At the logical level, two different instances residing on the same computer have no more in common than two instances residing on two separate computers. 在逻辑级别上,驻留在同一台计算机上的两个不同实例与驻留在两台独立计算机上的两个实例没有更多的共同点。Of course, same-computer instances do share the server's physical resources, such as CPU, memory, and disk.当然,相同的计算机实例确实共享服务器的物理资源,例如CPU、内存和磁盘。
FIGURE 1-5 Multiple instances of SQL Server on the same computer.同一台计算机上有多个SQL Server实例。
You can set up one of the multiple instances on a computer as the default instance, whereas all others must be named instances. 可以将计算机上的多个实例中的一个设置为默认实例,而所有其他实例都必须是命名实例。You determine whether an instance is the default or a named one upon installation; you cannot change that decision later. 在安装时确定实例是默认实例还是命名实例;你以后不能改变这个决定。To connect to a default instance, a client application needs to specify the computer's name or IP address. 要连接到默认实例,客户端应用程序需要指定计算机的名称或IP地址。To connect to a named instance, the client needs to specify the computer's name or IP address, followed by a backslash (\), followed by the instance name (as provided upon installation). 要连接到命名实例,客户端需要指定计算机的名称或IP地址,后跟反斜杠(\),后跟实例名称(安装时提供)。For example, suppose you have two instances of SQL Server installed on a computer called Server1. 例如,假设在名为Server1的计算机上安装了两个SQL Server实例。One of these instances was installed as the default instance, and the other was installed as a named instance called Inst1. 其中一个实例作为默认实例安装,另一个作为名为Inst1的命名实例安装。To connect to the default instance, you need to specify only Server1 as the server name. 要连接到默认实例,只需将Server1指定为服务器名。However, to connect to the named instance, you need to specify both the server and the instance name: Server1\Inst1.但是,要连接到命名实例,需要同时指定服务器和实例名称:Server1\Inst1。
There are various reasons why you might want to install multiple instances of SQL Server on the same computer, but I'll mention only a couple here. 您可能希望在同一台计算机上安装多个SQL Server实例的原因有很多,但这里我只提几个。One reason is to save on support costs. 一个原因是节省支持成本。For example, to test the functionality of features in response to support calls or reproduce errors that users encounter in the production environment, the support department needs local installations of SQL Server that mimic the user's production environment in terms of version, edition, and service pack of SQL Server. 例如,为了测试响应支持调用的功能或再现用户在生产环境中遇到的错误,支持部门需要在本地安装SQL Server,以模拟用户的生产环境,包括SQL Server的版本、版本和service pack。If an organization has multiple user environments, the support department needs multiple installations of SQL Server. 如果一个组织有多个用户环境,则支持部门需要多次安装SQL Server。Rather than having multiple computers, each hosting a different installation of SQL Server that must be supported separately, the support department can have one computer with multiple installed instances. 支持部门可以有一台计算机和多个已安装实例,而不是有多台计算机,每台计算机上都有不同的SQL Server安装,必须分别支持这些安装。Of course, you can achieve a similar result by using multiple virtual machines.当然,您可以通过使用多个虚拟机来实现类似的结果。
As another example, consider people like me who teach and lecture about SQL Server. 作为另一个例子,考虑像我这样教和讲授SQL Server的人。For us, it is convenient to be able to install multiple instances of SQL Server on the same laptop. 对我们来说,能够在同一台笔记本电脑上安装多个SQL Server实例非常方便。This way, we can perform demonstrations against different versions of the product, showing differences in behavior between versions, and so on.通过这种方式,我们可以对不同版本的产品进行演示,显示不同版本之间的行为差异,等等。
As a final example, providers of database services sometimes need to guarantee their customers complete security separation of their data from other customers' data. 最后一个例子是,数据库服务提供商有时需要保证其客户的数据与其他客户的数据完全安全隔离。At least in the past, the database provider could have a very powerful data center hosting multiple instances of SQL Server, rather than needing to maintain multiple less-powerful computers, each hosting a different instance. 至少在过去,数据库提供商可以拥有一个功能强大的数据中心,托管多个SQL Server实例,而不需要维护多台功能较弱的计算机,每台计算机托管一个不同的实例。More recently, cloud solutions and advanced virtualization technologies make it possible to achieve similar goals.最近,云解决方案和先进的虚拟化技术使实现类似目标成为可能。
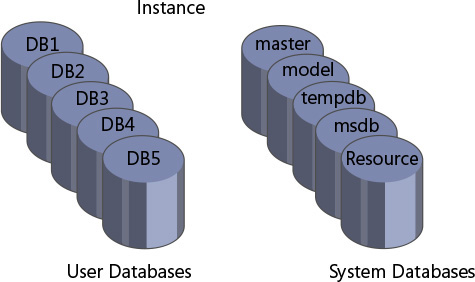
Databases数据库
You can think of a database as a container of objects such as tables, views, stored procedures, and other objects. 可以将数据库视为对象(如表、视图、存储过程和其他对象)的容器。Each instance of SQL Server can contain multiple databases, as illustrated in Figure 1-6. SQL Server的每个实例都可以包含多个数据库,如Figure 1-6所示。When you install an on-premises flavor of SQL Server, the setup program creates several system databases that hold system data and serve internal purposes. 安装本地版本的SQL Server时,安装程序会创建多个系统数据库,这些数据库保存系统数据并用于内部用途。After the installation of SQL Server, you can create your own user databases that will hold application data.安装SQL Server后,您可以创建自己的用户数据库来保存应用程序数据。
FIGURE 1-6 An example of multiple databases on a SQL Server instance.SQL Server实例上多个数据库的示例。
The system databases that the setup program creates include master, Resource, model, tempdb, and msdb. 安装程序创建的系统数据库包括master、Resource、model、tempdb和msdb。A description of each follows:以下是对每种方法的描述:

master The master database holds instance-wide metadata information, the server configuration, information about all databases in the instance, and initialization information.master数据库保存实例范围的元数据信息、服务器配置、有关实例中所有数据库的信息以及初始化信息。

Resource The Resource database is a hidden, read-only database that holds the definitions of all system objects. Resource数据库是一个隐藏的只读数据库,包含所有系统对象的定义。When you query system objects in a database, they appear to reside in the sys schema of the local database, but in actuality their definitions reside in the Resource database.在数据库中查询系统对象时,它们似乎位于本地数据库的sys架构中,但实际上它们的定义位于Resource数据库中。

model The model database is used as a template for new databases. model数据库用作新数据库的模板。Every new database you create is initially created as a copy of model. 您创建的每个新数据库最初都是作为model的副本创建的。So if you want certain objects (such as data types) to appear in all new databases you create, or certain database properties to be configured in a certain way in all new databases, you need to create those objects and configure those properties in the model database. 因此,如果希望某些对象(例如数据类型)出现在您创建的所有新数据库中,或者希望某些数据库属性在所有新数据库中以某种方式配置,则需要创建这些对象并在model数据库中配置这些属性。Note that changes you apply to the model database will not affect existing databases—only new databases you create in the future.请注意,应用于model数据库的更改不会影响现有数据库,只会影响将来创建的新数据库。

tempdb The tempdb database is where SQL Server stores temporary data such as work tables, sort and hash table data, row versioning information, and so on. tempdb数据库是SQL Server存储临时数据的地方,例如工作表、排序和哈希表数据、行版本控制信息等。With SQL Server, you can create temporary tables for your own use, and the physical location of those temporary tables is tempdb. 使用SQL Server,您可以创建供自己使用的临时表,这些临时表的物理位置是tempdb。Note that this database is destroyed and re-created as a copy of the model database every time you restart the instance of SQL Server.请注意,每次重新启动SQL Server实例时,此数据库都会被销毁并重新创建为model数据库的副本。

msdb The msdb database is used mainly by a service called SQL Server Agent to store its data. msdb数据库主要由一个名为SQL Server Agent的服务用来存储其数据。SQL Server Agent is in charge of automation, which includes entities such as jobs, schedules, and alerts. SQLServer代理负责自动化,包括作业、计划和警报等实体。SQL Server Agent is also the service in charge of replication. SQL Server代理也是负责复制的服务。The msdb database also holds information related to other SQL Server features, such as Database Mail, Service Broker, backups, and more.msdb数据库还保存与其他SQL Server功能相关的信息,如数据库邮件、Service Broker、备份等。
In an on-premises installation of SQL Server, you can connect directly to the system databases master, model, tempdb, and msdb. 在SQL Server的内部部署安装中,可以直接连接到系统数据库master、model、tempdb和msdb。In SQL Database, you can connect directly only to the system database master. 在SQL数据库中,只能直接连接到系统数据库master。If you create temporary tables or declare table variables (more on this topic in Chapter 11, “Programmable objects”), they are created in tempdb, but you cannot connect directly to tempdb and explicitly create user objects there.如果创建临时表或声明表变量(第11章“可编程对象”中有更多关于此主题的内容),它们将在tempdb中创建,但不能直接连接到tempdb并在那里显式创建用户对象。
You can create multiple user databases (up to 32,767) within an instance. 您可以在一个实例中创建多个用户数据库(最多32767个)。A user database holds objects and data for an application.用户数据库保存应用程序的对象和数据。
You can define a property called collation at the database level that will determine default language support, case sensitivity, and sort order for character data in that database. 可以在数据库级别定义名为collation的属性,该属性将确定该数据库中字符数据的默认语言支持、大小写敏感度和排序顺序。If you do not specify a collation for the database when you create it, the new database will use the default collation of the instance (chosen upon installation).如果在创建数据库时未为其指定排序规则,则新数据库将使用实例的默认排序规则(在安装时选择)。
To run T-SQL code against a database, a client application needs to connect to a SQL Server instance and be in the context of, or use, the relevant database. 要对数据库运行T-SQL代码,客户机应用程序需要连接到SQL Server实例,并处于相关数据库的上下文中或使用相关数据库。The application can still access objects from other databases by adding the database name as a prefix.应用程序仍然可以通过添加数据库名称作为前缀来访问其他数据库中的对象。
In terms of security, to be able to connect to a SQL Server instance, the database administrator (DBA) must create a login for you. 就安全性而言,为了能够连接到SQL Server实例,数据库管理员(DBA)必须为您创建一个登录名。The login can be tied to your Microsoft Windows credentials, in which case it is called a Windows authenticated login. 登录可以绑定到您的Microsoft Windows凭据,在这种情况下,它被称为“Windows身份验证登录”。With a Windows authenticated login, you can't provide login and password information when connecting to SQL Server because you already provided those when you logged on to Windows. 使用Windows身份验证登录,您在连接到SQL Server时无法提供登录信息和密码信息,因为您在登录到Windows时已经提供了这些信息。The login can be independent of your Windows credentials, in which case it's called a SQL Server authenticated login. 登录可以独立于Windows凭据,在这种情况下,它被称为“SQL Server身份验证登录”。When connecting to SQL Server using a SQL Server authenticated login, you will need to provide both a login name and a password.使用SQL Server身份验证登录连接到SQL Server时,需要同时提供登录名和密码。
The DBA needs to map your login to a database user in each database you are supposed to have access to. DBA需要将您的登录映射到您应该有权访问的每个数据库中的数据库用户。The database user is the entity that is granted permissions to objects in the database.数据库用户是向数据库中的对象授予权限的实体。
SQL Server supports a feature called contained databases that breaks the connection between a database user and an instance-level login. SQL Server支持名为“包含的数据库”的功能,该功能可断开数据库用户和实例级登录之间的连接。The user (Windows or SQL authenticated) is fully contained within the specific database and is not tied to a login at the instance level. 用户(Windows或SQL认证)完全包含在特定数据库中,并且不与实例级别的登录绑定。When connecting to SQL Server, the user needs to specify the database he or she is connecting to, and the user cannot subsequently switch to other user databases.当连接到SQL Server时,用户需要指定他或她正在连接的数据库,并且用户随后无法切换到其他用户数据库。
So far, I've mainly mentioned the logical aspects of databases. 到目前为止,我主要提到了数据库的逻辑方面。If you're using SQL Database, your only concern is that logical layer. 如果您使用的是SQL数据库,那么您唯一关心的就是该逻辑层。You do not deal with the physical layout of the database data and log files, tempdb, and so on. 您不需要处理数据库数据和日志文件、tempdb等的物理布局。But if you're using a box version of SQL Server, you are responsible for the physical layer as well. 但是,如果您使用的是盒式版本的SQL Server,那么您也要负责物理层。Figure 1-7 shows a diagram of the physical database layout.Figure 1-7显示了物理数据库布局图。
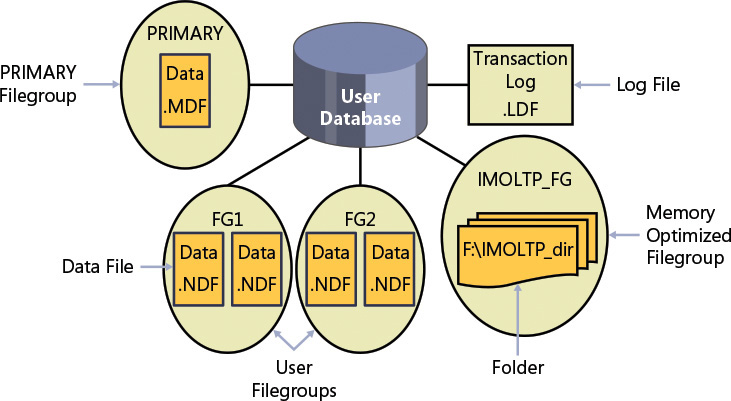
FIGURE 1-7 Database layout.数据库布局。
The database is made up of data files, transaction log files, and optionally checkpoint files holding memory-optimized data (part of a feature called In-Memory OLTP, which I describe shortly). 数据库由数据文件、事务日志文件和可选的检查点文件组成,这些文件包含内存优化的数据(这是名为内存OLTP的功能的一部分,我将简要介绍)。When you create a database, you can define various properties for data and log files, including the file name, location, initial size, maximum size, and an autogrowth increment. 创建数据库时,可以为数据和日志文件定义各种属性,包括文件名、位置、初始大小、最大大小和自动增长增量。Each database must have at least one data file and at least one log file (the default in SQL Server). 每个数据库必须至少有一个数据文件和一个日志文件(SQL Server中的默认值)。The data files hold object data, and the log files hold information that SQL Server needs to maintain transactions.数据文件保存对象数据,日志文件保存SQL Server维护事务所需的信息。
Although SQL Server can write to multiple data files in parallel, it can write to only one log file at a time, in a sequential manner. 尽管SQL Server可以并行写入多个数据文件,但它一次只能以顺序方式写入一个日志文件。Therefore, unlike with data files, having multiple log files does not result in a performance benefit. 因此,与数据文件不同,拥有多个日志文件不会带来性能优势。You might need to add log files if the disk drive where the log resides runs out of space.如果日志所在的磁盘驱动器空间不足,则可能需要添加日志文件。
Data files are organized in logical groups called filegroups. 数据文件被组织在称为文件组的逻辑组中。A filegroup is the target for creating an object, such as a table or an index. 文件组是创建对象(如表或索引)的目标。The object data will be spread across the files that belong to the target filegroup. 对象数据将分布在属于目标文件组的文件中。Filegroups are your way of controlling the physical locations of your objects. 文件组是控制对象物理位置的方式。A database must have at least one filegroup called PRIMARY, and it can optionally have other user filegroups as well. 一个数据库必须至少有一个名为PRIMARY的文件组,并且还可以选择有其他用户文件组。The PRIMARY filegroup contains the primary data file (which has an .mdf extension) for the database, and the database's system catalog. PRIMARY文件组包含数据库的主数据文件(具有mdf扩展名)和数据库的系统目录。You can optionally add secondary data files (which have an .ndf extension) to PRIMARY. 您可以选择将辅助数据文件(具有.ndf扩展名)添加到PRIMARY数据文件。User filegroups contain only secondary data files. 用户文件组仅包含辅助数据文件。You can decide which filegroup is marked as the default filegroup. 您可以决定将哪个文件组标记为默认文件组。Objects are created in the default filegroup when the object creation statement does not explicitly specify a different target filegroup.当object creation语句没有明确指定其他目标文件组时,将在默认文件组中创建对象。
The SQL Server database engine includes a memory-optimized engine called In-Memory OLTP. SQL Server数据库引擎包括一个名为内存OLTP的内存优化引擎。You can use this feature to integrate memory-optimized objects, such as memory-optimized tables and natively compiled procedures, into your database. 可以使用此功能将内存优化对象(如内存优化表和本机编译的过程)集成到数据库中。To do so, you need to create a filegroup in the database marked as containing memory-optimized data and, within it, at least one path to a folder. 为此,需要在数据库中创建一个标记为包含内存优化数据的文件组,并在其中至少创建一个文件夹路径。SQL Server stores checkpoint files with memory-optimized data in that folder, and it uses those to recover the data every time SQL Server is restarted.SQL Server将带有内存优化数据的检查点文件存储在该文件夹中,并在每次重新启动SQL Server时使用这些文件恢复数据。
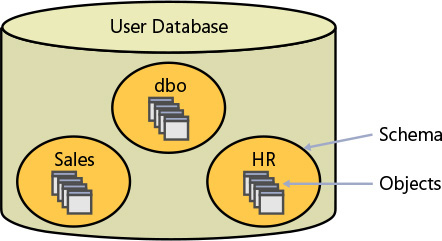
Schemas and objects模式和对象
When I said earlier that a database is a container of objects, I simplified things a bit. 当我之前说数据库是对象的容器时,我简化了一些事情。As illustrated in Figure 1-8, a database contains schemas, and schemas contain objects. 如Figure 1-8所示,数据库包含模式,模式包含对象。You can think of a schema as a container of objects, such as tables, views, stored procedures, and others.可以将模式视为对象的容器,例如表、视图、存储过程等。
FIGURE 1-8 A database, schemas, and database objects.数据库、模式和数据库对象。
You can control permissions at the schema level. 您可以在架构级别控制权限。For example, you can grant a user SELECT permissions on a schema, allowing the user to query data from all objects in that schema. 例如,您可以授予用户对模式的SELECT权限,允许用户从该模式中的所有对象查询数据。So security is one of the considerations for determining how to arrange objects in schemas.因此,安全性是决定如何在模式中排列对象的考虑因素之一。
The schema is also a namespace—it is used as a prefix to the object name. 模式也是一个名称空间,用作对象名称的前缀。For example, suppose you have a table named Orders in a schema named Sales. 例如,假设在名为Sales的架构中有一个名为Orders的表。The schema-qualified object name (also known as the two-part object name) is Sales.Orders. 模式限定对象名(也称为“两部分对象名”)是Sales.Orders。You can refer to objects in other databases by adding the database name as a prefix (three-part object name), and to objects in other instances by adding the instance name as a prefix (four-part object name). 通过将数据库名称添加为前缀(“三部分对象名”),可以引用其他数据库中的对象;通过将实例名称添加为前缀(由四部分组成的对象名称),可以引用其他实例中的对象。If you omit the schema name when referring to an object, SQL Server will apply a process to resolve the schema name, such as checking whether the object exists in the user's default schema and, if the object doesn't exist, checking whether it exists in the dbo schema. 如果在引用对象时省略了架构名称,SQL Server将应用一个过程来解析架构名称,例如检查该对象是否存在于用户的默认架构中,如果该对象不存在,则检查它是否存在于dbo架构中。Microsoft recommends that when you refer to objects in your code you always use the two-part object names. Microsoft建议在代码中引用对象时,始终使用由两部分组成的对象名。There are some relatively insignificant extra costs involved in resolving the schema name when you don't specify it explicitly. 当您没有明确指定模式名称时,解析模式名称所涉及的额外成本相对较小。But as insignificant as this extra cost might be, why pay it? 但是,尽管这笔额外的费用可能微不足道,为什么还要支付呢?Also, if multiple objects with the same name exist in different schemas, you might end up getting a different object than the one you wanted.此外,如果在不同的模式中存在多个同名的对象,那么最终可能会得到一个与所需对象不同的对象。
Creating tables and defining data integrity创建表和定义数据完整性
This section describes the fundamentals of creating tables and defining data integrity using T-SQL. 本节介绍使用T-SQL创建表和定义数据完整性的基础知识。Feel free to run the included code samples in your environment.可以在您的环境中运行附带的代码示例。
 More Info
More Info
If you don't know yet how to run code against SQL Server, the Appendix will help you get started.如果您还不知道如何在SQL Server上运行代码,附录将帮助您开始。
As mentioned earlier, DML rather than DDL is the focus of this book. 如前所述,DML而非DDL是本书的重点。Still, you need to understand how to create tables and define data integrity. 不过,您需要了解如何创建表和定义数据完整性。I won't go into the explicit details here, but I'll provide a brief description of the essentials.这里我不会详细介绍,但我会简要介绍一下要点。
Before you look at the code for creating a table, remember that tables reside within schemas, and schemas reside within databases. 在查看创建表的代码之前,请记住表驻留在模式中,模式驻留在数据库中。The examples use the book's sample database, TSQLV4, and a schema called dbo.这些示例使用了本书的示例数据库TSQLV4和一个名为dbo的架构。
 More Info
More Info
See the Appendix for details on creating the sample database.有关创建示例数据库的详细信息,请参阅附录。
The examples here use a schema named dbo that is created automatically in every database and is also used as the default schema for users who are not explicitly associated with a different schema.这里的示例使用一个名为dbo的架构,该模式在每个数据库中自动创建,并且还用作未明确与不同模式关联的用户的默认模式。
Creating tables创建表
The following code creates a table named Employees in the dbo schema in the TSQLV4 database:以下代码在TSQLV4数据库的dbo架构中创建一个名为Employees的表:
Click here to view code image
USE TSQLV4;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dbo.Employees;
CREATE TABLE dbo.Employees
(
empid INT NOT NULL,
firstname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
lastname VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
hiredate DATE NOT NULL,
mgrid INT NULL,
ssn VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
salary MONEY NOT NULL
);
The USE statement sets the current database context to that of TSQLV4. USE语句将当前数据库上下文设置为TSQLV4的上下文。It is important to incorporate the USE statement in scripts that create objects to ensure that SQL Server creates the objects in the specified database. 在创建对象的脚本中合并USE语句非常重要,以确保SQL Server在指定的数据库中创建对象。In an on-premises SQL Server implementation, the USE statement can actually change the database context from one to another. 在本地SQL Server实现中,USE语句实际上可以将数据库上下文从一个更改为另一个。In SQL Database, you cannot switch between different databases, but the USE statement will not fail as long as you are already connected to the target database. 在SQL数据库中,不能在不同的数据库之间切换,但只要已连接到目标数据库,USE语句就不会失败。So even in SQL Database, I recommend having the USE statement to ensure that you are connected to the right database when creating your objects.因此,即使在SQL数据库中,我也建议使用USE语句,以确保在创建对象时连接到正确的数据库。
The DROP IF EXISTS command drops the table if it already exists. 如果表已经存在,则DROP IF EXISTS命令会删除该表。Note that this command was introduced in SQL Server 2016. 请注意,此命令是在SQL Server 2016中引入的。If you're using earlier versions of SQL Server, use the following statement instead:如果使用的是早期版本的SQL Server,请使用以下语句:
Click here to view code image
IF OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.Employees', N'U') IS NOT NULL DROP TABLE dbo.Employees;
The IF statement invokes the OBJECT_ID function to check whether the Employees table already exists in the current database. IF语句调用OBJECT_ID函数来检查Employees表是否已经存在于当前数据库中。The OBJECT_ID function accepts an object name and type as inputs. OBJECT_ID函数接受对象名称和类型作为输入。The type U represents a user table. 类型U代表一个用户表。This function returns the internal object ID if an object with the specified input name and type exists, and NULL otherwise. 如果存在具有指定输入名称和类型的对象,则此函数返回内部对象ID,否则返回NULL。If the function returns a NULL, you know that the object doesn't exist. 如果函数返回NULL值,就知道对象不存在。In our case, the code drops the table if it already exists and then creates a new one. 在例子中,如果表已经存在,代码会删除它,然后创建一个新表。Of course, you can choose a different treatment, such as simply not creating the object if it already exists.当然,您可以选择不同的处理方式,例如,如果对象已经存在,则不创建该对象。
The CREATE TABLE statement is in charge of defining what I referred to earlier as the heading of the relation. CREATE TABLE语句负责定义我前面提到的关系的标题。Here you specify the name of the table and, in parentheses, the definition of its attributes (columns).这里指定表的名称,并在括号中指定其属性(列)的定义。
Notice the use of the two-part name dbo.Employees for the table name, as recommended earlier. 请注意,如前所述,表名使用了由两部分组成的名称dbo.Employees。If you omit the schema name, for ad-hoc queries SQL Server will assume the default schema associated with the database user running the code. 如果省略模式名称,对于特殊查询,SQL Server将采用与运行代码的数据库用户关联的默认模式。For queries in stored procedures, SQL Server will assume the schema associated with the procedure's owner.对于存储过程中的查询,SQL Server将采用与过程所有者关联的模式。
For each attribute, you specify the attribute name, data type, and whether the value can be NULL (which is called nullability).对于每个属性,指定属性名称、数据类型以及值是否可以为NULL(称为“可空性”)。
In the Employees table, the attributes empid (employee ID) and mgrid (manager ID) are each defined with the INT (four-byte integer) data type; the firstname, lastname, and ssn (US Social Security number) are defined as VARCHAR (variable-length character string with the specified maximum supported number of characters); and hiredate is defined as DATE and salary is defined as MONEY.在Employees表中,属性empid(雇员ID)和mgrid(管理者ID)都是用INT(四字节整数)数据类型定义的;firstname、lastname和ssn(美国社会保险号)定义为VARCHAR(具有指定最大支持字符数的可变长度字符串);hiredate被定义为DATETIME,salary被定义为MONEY。
If you don't explicitly specify whether a column allows or disallows NULLs, SQL Server will have to rely on defaults. 如果没有明确指定列是否允许NULL值,SQL Server将不得不依赖默认值。Standard SQL dictates that when a column's nullability is not specified, the assumption should be NULL (allowing NULLs), but SQL Server has settings that can change that behavior. 标准SQL规定,如果未指定列的可空性,则假定为NULL(允许为NULL),但SQL Server具有可以更改该行为的设置。I recommend that you be explicit and not rely on defaults. 我建议你要明确,不要依赖默认值。Also, I recommend defining a column as NOT NULL unless you have a compelling reason to support NULLs. 此外,我建议将列定义为NOT NULL,除非您有充分的理由支持NULL。If a column is not supposed to allow NULLs and you don't enforce this with a NOT NULL constraint, you can rest assured that NULLs will occur. 如果一个列不应该允许NULL值,并且您没有使用NOT NULL约束来强制执行这一点,那么您可以放心,将出现NULL值。In the Employees table, all columns are defined as NOT NULL except for the mgrid column. 在Employees表中,除mgrid列外,所有列都定义为NOT NULL。A NULL in the mgrid column would represent the fact that the employee has no manager, as in the case of the CEO of the organization.mgrid列中的NULL表示该员工没有经理,譬如该组织的首席执行官。
 Note
Note
The SQL Server documentation indicates that not terminating T-SQL statements with a semicolon is a deprecated feature. SQL Server文档表明,不使用分号终止T-SQL语句是不推荐使用的功能。This means that the long-term goal is to enforce use of the semicolon in a future version of the product. 这意味着长期目标是在未来版本的产品中强制使用分号。That's one more reason to get into the habit of terminating all your statements, even where it's currently not required.这是养成终止所有陈述的习惯的另一个原因,即使在目前不需要的地方。
Defining data integrity定义数据完整性
As mentioned earlier, one of the great benefits of the relational model is that data integrity is an integral part of it. 如前所述,关系模型的一大好处是数据完整性是其中不可或缺的一部分。Data integrity enforced as part of the model—namely, as part of the table definitions—is considered declarative data integrity. 作为模型的一部分强制执行的数据完整性,即作为表定义的一部分,被视为“声明性数据完整性”。Data integrity enforced with code—such as with stored procedures or triggers—is considered procedural data integrity.使用存储过程或触发器等代码强制实现的数据完整性被视为“过程数据完整性”。
Data type and nullability choices for attributes and even the data model itself are examples of declarative data integrity constraints. 属性的数据类型和可空性选择,甚至数据模型本身都是声明性数据完整性约束的示例。In this section, I will describe other examples of declarative constraints: primary key, unique, foreign key, check, and default constraints. 在本节中,我将描述声明性约束的其他示例:主键、唯一、外键、检查和默认约束。You can define such constraints when creating a table as part of the CREATE TABLE statement, or you can define them for already-created tables by using an ALTER TABLE statement. 在CREATE TABLE语句中创建表时,可以定义此类约束,也可以使用ALTER TABLE语句为已创建的表定义这些约束。All types of constraints except for default constraints can be defined as composite constraints—that is, based on more than one attribute.除了默认约束之外,所有类型的约束都可以定义为“复合约束”,即基于多个属性。
Primary-key constraints主键约束
A primary-key constraint enforces the uniqueness of rows and also disallows NULLs in the constraint attributes. 主键约束强制行的唯一性,并且禁止约束属性中的NULL值。Each unique set of values in the constraint attributes can appear only once in the table—in other words, only in one row. 约束属性中的每个唯一值集只能在表中出现一次,换句话说,只能出现在一行中。An attempt to define a primary-key constraint on a column that allows NULLs will be rejected by the RDBMS. RDBMS将拒绝尝试在允许NULL值的列上定义主键约束。Each table can have only one primary key.每个表只能有一个主键。
Here's an example of defining a primary-key constraint on the empid attribute in the Employees table that you created earlier:下面是一个在您之前创建的Employees表中的empid属性上定义主键约束的示例:
Click here to view code image
ALTER TABLE dbo.Employees
ADD CONSTRAINT PK_Employees
PRIMARY KEY(empid);
With this primary key in place, you can be assured that all empid values will be unique and known. 有了这个主键,就可以确保所有empid值都是唯一的和已知的。An attempt to insert or update a row such that the constraint would be violated will be rejected by the RDBMS and result in an error.如果试图插入或更新行,从而违反约束,RDBMS将拒绝并导致错误。
To enforce the uniqueness of the logical primary-key constraint, SQL Server will create a unique index behind the scenes. 为了加强逻辑主键约束的唯一性,SQL Server将在后台创建一个唯一的索引。A unique index is a physical mechanism used by SQL Server to enforce uniqueness. 唯一索引是SQL Server用来强制唯一性的物理机制。Indexes (not necessarily unique ones) are also used to speed up queries by avoiding unnecessary full table scans (similar to indexes in books).索引(不一定是唯一的)还可以通过避免不必要的全表扫描(类似于书籍中的索引)来加速查询。
Unique constraints唯一约束
A unique constraint enforces the uniqueness of rows, allowing you to implement the concept of alternate keys from the relational model in your database. 唯一约束强制行的唯一性,允许您在数据库的关系模型中实现备用键的概念。Unlike with primary keys, you can define multiple unique constraints within the same table. 与主键不同,您可以在同一个表中定义多个唯一约束。Also, a unique constraint is not restricted to columns defined as NOT NULL.此外,唯一约束不限于定义为NOT NULL的列。
The following code defines a unique constraint on the ssn column in the Employees table:以下代码定义了Employees表中ssn列的唯一约束:
Click here to view code image
ALTER TABLE dbo.Employees
ADD CONSTRAINT UNQ_Employees_ssn
UNIQUE(ssn);
As with a primary-key constraint, SQL Server will create a unique index behind the scenes as the physical mechanism to enforce the logical unique constraint.与主键约束一样,SQL Server将在后台创建唯一索引,作为强制执行逻辑唯一约束的物理机制。
According to standard SQL, a column with a unique constraint is supposed to allow multiple NULLs (as if two NULLs were different from each other). 根据标准SQL,具有唯一约束的列应该允许多个NULL值(就好像两个NULL值彼此不同)。However, SQL Server's implementation rejects duplicate NULLs (as if two NULLs were equal to each other). 然而,SQL Server的实现拒绝重复的NULL值(就像两个空值彼此相等一样)。To emulate the standard unique constraint in SQL Server you can use a unique filtered index that filters only non-NULL values. 要模拟SQL Server中的标准唯一约束,可以使用只筛选非NULL值的唯一筛选索引。For example, suppose that the column ssn allowed NULLs, and you wanted to create such an index instead of a unique constraint. 例如,假设列ssn允许NULL值,您希望创建这样的索引,而不是唯一约束。You would have used the following code:您应该使用以下代码:
Click here to view code image
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX idx_ssn_notnull ON dbo.Employees(ssn) WHERE ssn IS NOT NULL;
The index is defined as a unique one, and the filter excludes NULLs from the index, so duplicate NULLs will be allowed, whereas duplicate non-NULL values won't be allowed.索引被定义为唯一索引,并且筛选器从索引中排除NULL值,因此允许重复NULL值,而不允许重复非NULL值。
Foreign-key constraints外键约束
A foreign-key enforces referential integrity. 外键强制引用完整性。This constraint is defined on one or more attributes in what's called the referencing table and points to candidate-key (primary-key or unique-constraint) attributes in what's called the referenced table. 该约束在被称为引用表的一个或多个属性上定义,并指向被称为引用表的候选键(主键或唯一约束)属性。Note that the referencing and referenced tables can be one and the same. 请注意,引用表和被引用表可以是同一个表。The foreign key's purpose is to restrict the values allowed in the foreign-key columns to those that exist in the referenced columns.外键的目的是将外键列中允许的值限制为引用列中存在的值。
The following code creates a table called Orders with a primary key defined on the orderid column:下面的代码创建了一个名为Orders的表,其主键在orderid列上定义:
Click here to view code image
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dbo.Orders;
CREATE TABLE dbo.Orders
(
orderid INT NOT NULL,
empid INT NOT NULL,
custid VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
orderts DATETIME2 NOT NULL,
qty INT NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Orders
PRIMARY KEY(orderid)
);
Suppose you want to enforce an integrity rule that restricts the values supported by the empid column in the Orders table to the values that exist in the empid column in the Employees table. 假设您想要实施一个完整性规则,将Orders表中empid列支持的值限制为Employees表中empid列中存在的值。You can achieve this by defining a foreign-key constraint on the empid column in the Orders table pointing to the empid column in the Employees table, like the following:可以通过在Orders表中指向Employees表中empid列的empid列上定义外键约束来实现这一点,如下所示:
Click here to view code image
ALTER TABLE dbo.Orders
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_Orders_Employees
FOREIGN KEY(empid)
REFERENCES dbo.Employees(empid);
Similarly, if you want to restrict the values supported by the mgrid column in the Employees table to the values that exist in the empid column of the same table, you can do so by adding the following foreign key:类似地,如果要将Employees表中的mgrid列支持的值限制为同一表的empid列中存在的值,可以通过添加以下外键来实现:
Click here to view code image
ALTER TABLE dbo.Employees
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_Employees_Employees
FOREIGN KEY(mgrid)
REFERENCES dbo.Employees(empid);
Note that NULLs are allowed in the foreign-key columns (mgrid in the last example) even if there are no NULLs in the referenced candidate-key columns.请注意,即使引用的候选键列中没有NULL值,外键列(上一个示例中为mgrid)中也允许NULL值。
The preceding two examples are basic definitions of foreign keys that enforce a referential action called no action. 前两个例子是外键的基本定义,外键执行一个称为“无操作”的引用操作。No action means that attempts to delete rows from the referenced table or update the referenced candidate-key attributes will be rejected if related rows exist in the referencing table. 如果引用表中存在相关行,则无操作意味着从引用表中删除行或更新引用的候选键属性的尝试将被拒绝。For example, if you try to delete an employee row from the Employees table when there are related orders in the Orders table, the RDBMS will reject such an attempt and produce an error.例如,当订单表中存在相关订单时,如果尝试从Employees表中删除员工行,RDBMS将拒绝这种尝试并产生错误。
You can define the foreign key with actions that will compensate for such attempts (to delete rows from the referenced table or update the referenced candidate-key attributes when related rows exist in the referencing table). 您可以使用补偿此类尝试的操作定义外键(从引用表中删除行,或在引用表中存在相关行时更新引用的候选键属性)。You can define the options ON DELETE and ON UPDATE with actions such as CASCADE, SET DEFAULT, and SET NULL as part of the foreign-key definition. 在外键定义中,可以使用诸如CASCADE、SET DEFAULT和SET NULL等操作来定义ON DELETE选项和ON UPDATE选项。CASCADE means that the operation (delete or update) will be cascaded to related rows. CASCADE意味着操作(删除或更新)将级联到相关行。For example, ON DELETE CASCADE means that when you delete a row from the referenced table, the RDBMS will delete the related rows from the referencing table. 例如,ON DELETE CASCADE意味着当您从引用表中删除一行时,RDBMS将从引用表中删除相关行。SET DEFAULT and SET NULL mean that the compensating action will set the foreign-key attributes of the related rows to the column's default value or NULL, respectively. SET DEFAULT和SET NULL表示补偿操作将分别将相关行的外键属性设置为列的默认值或NULL。Note that regardless of which action you choose, the referencing table will have only orphaned rows in the case of the exception with NULLs that I mentioned earlier. 请注意,无论选择哪种操作,在我前面提到的带有NULL值的异常情况下,引用表都将只有孤立行。Parents with no children are always allowed.没有孩子的父母总是被允许的。
Check constraints检查约束
You can use a check constraint to define a predicate that a row must meet to be entered into the table or to be modified. 您可以使用“检查约束”定义一个谓词,一行必须满足该谓词才能输入到表中或进行修改。For example, the following check constraint ensures that the salary column in the Employees table will support only positive values:例如,以下检查约束确保Employees表中的salary列只支持正值:
Click here to view code image
ALTER TABLE dbo.Employees
ADD CONSTRAINT CHK_Employees_salary
CHECK(salary > 0.00);
An attempt to insert or update a row with a nonpositive salary value will be rejected by the RDBMS. RDBMS将拒绝尝试插入或更新具有非正薪资值的行。Note that a check constraint rejects an attempt to insert or update a row when the predicate evaluates to FALSE. 注意,当谓词的计算结果为FALSE时,检查约束拒绝插入或更新行的尝试。The modification will be accepted when the predicate evaluates to either TRUE or UNKNOWN. 当谓词的计算结果为TRUE或UNKNOWN时,将接受修改。For example, salary –1000 will be rejected, whereas salaries 50000 and NULL will both be accepted (if the column allowed NULLs). 例如,salary -1000将被拒绝,而salary 50000和NULL都将被接受(如果该列允许NULL)。As mentioned earlier, SQL is based on three-valued logic, which results in two actual actions. 如前所述,SQL基于三值逻辑,这会导致两个实际操作。With a check constraint, the row is either accepted or rejected.通过检查约束,该行要么被接受,要么被拒绝。
When adding check and foreign-key constraints, you can specify an option called WITH NOCHECK that tells the RDBMS you want it to bypass constraint checking for existing data. 添加检查约束和外键约束时,可以指定一个名为WITH NOCHECK的选项,告诉RDBMS您希望它绕过现有数据的约束检查。This is considered a bad practice because you cannot be sure your data is consistent. 这被认为是一种不好的做法,因为你不能确定你的数据是一致的。You can also disable or enable existing check and foreign-key constraints.还可以禁用或启用现有的检查和外键约束。
Default constraints默认约束
A default constraint is associated with a particular attribute. 默认约束与特定属性相关联。It's an expression that is used as the default value when an explicit value is not specified for the attribute when you insert a row. 当插入行时未为属性指定显式值时,它是一个用作默认值的表达式。For example, the following code defines a default constraint for the orderts attribute (representing the order's time stamp):例如,以下代码为orderts属性(表示订单的时间戳)定义了一个默认约束:
Click here to view code image
ALTER TABLE dbo.Orders
ADD CONSTRAINT DFT_Orders_orderts
DEFAULT(SYSDATETIME()) FOR orderts;
The default expression invokes the SYSDATETIME function, which returns the current date and time value. 默认表达式调用SYSDATETIME函数,该函数返回当前日期和时间值。After this default expression is defined, whenever you insert a row in the Orders table and do not explicitly specify a value in the orderts attribute, SQL Server will set the attribute value to SYSDATETIME.定义此默认表达式后,每当您在Orders表中插入一行,并且没有在orderts属性中显式指定值时,SQL Server都会将属性值设置为SYSDATETIME。
When you're done, run the following code for cleanup:完成后,运行以下代码进行清理:
Click here to view code image
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS dbo.Orders, dbo.Employees;
Conclusion结论
This chapter provided a brief background to T-SQL querying and programming. 本章简要介绍了T-SQL查询和编程的背景知识。It presented a theoretical background, explaining the strong foundations that T-SQL is based on. 它提供了一个理论背景,解释了T-SQL所基于的强大基础。It gave an overview of the SQL Server architecture and concluded with sections that demonstrated how to use T-SQL to create tables and define data integrity. 它概述了SQLServer体系结构,并以演示如何使用T-SQL创建表和定义数据完整性的部分结束。I hope that by now you see that there's something special about SQL, and that it's not just a language that can be learned as an afterthought. 我希望到现在为止,您能看到SQL有一些特殊之处,它不仅仅是一种可以事后学习的语言。This chapter equipped you with fundamental concepts—the actual journey is just about to begin.这一章为你提供了基本概念,真正的旅程即将开始。
 Note
Note